
Analysis Case 19–13
Analyzing financial statements; price-earnings ratio; dividend payout ratio
• LO19–13
IGF Foods Company is a large, primarily domestic, consumer foods company involved in the manufacture, distribution, and sale of a variety of food products. Industry averages are derived from Troy’s The Almanac of Business and Industrial Financial Ratios and Dun and Bradstreet’s Industry Norms and Key Business Ratios. Following are the 2018 and 2017 comparative income statements and
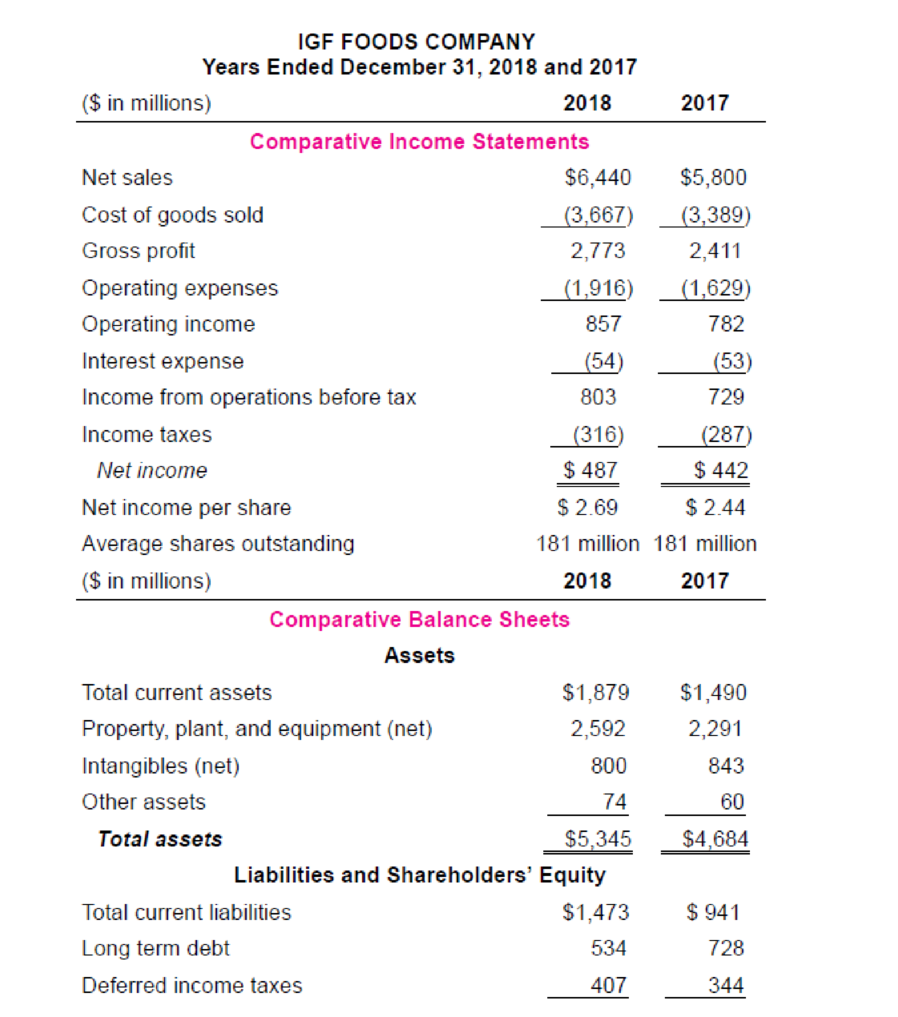
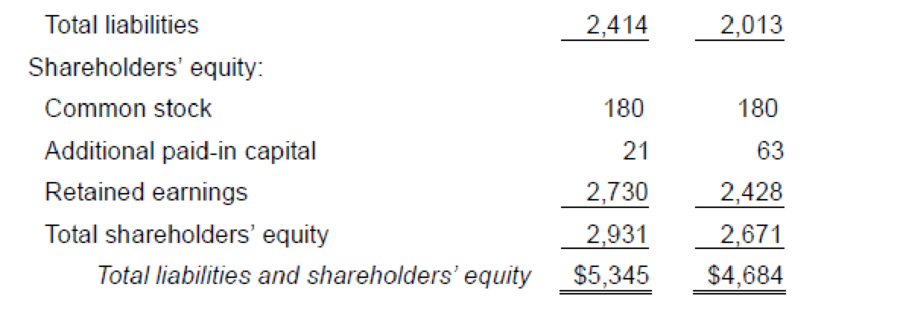
Some ratios express income, dividends, and market prices on a per share basis. As such, these ratios appeal primarily to common shareholders, particularly when weighing investment possibilities. These ratios focus less on the fundamental soundness of a company and more on its investment characteristics.
Required:
1. Earnings per share expresses a firm’s profitability on a per share basis. Calculate 2018 earnings per share for IGF.
2. Calculate IGF’s 2018 price-earnings ratio. The average price-earnings ratio for the stocks listed on the New York Stock Exchange in a comparable time period was 18.5. What does your calculation indicate about IGF’s earnings?
3. Calculate IGF’s 2018 dividend payout ratio. What information does the calculation provide an investor?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 19 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting
- I am looking for help with this general accounting question using proper accounting standards.arrow_forwardI need assistance with this financial accounting problem using valid financial procedures.arrow_forwardPlease provide the correct answer to this general accounting problem using accurate calculations.arrow_forward
- Please provide the correct answer to this general accounting problem using accurate calculations.arrow_forwardI am looking for a step-by-step explanation of this financial accounting problem with correct standards.arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting problem with appropriate steps and explanations?arrow_forward
- I need help with this financial accounting question using standard accounting techniques.arrow_forwardCould you help me solve this financial accounting question using appropriate calculation techniques?arrow_forwardI am searching for the correct answer to this financial accounting problem with proper accounting rules.arrow_forward
 Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781285065137Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781285065137Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781305635937Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781305635937Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning





