
Concept explainers
a. 1
Prepare a schedule showing units started and completed in the Molding Department during April.
a. 1
Explanation of Solution
It is a method of cost accounting used by an enterprise with processes categorised by continuous production. The cost for manufacturing those products are assigned to the manufacturing department before the averaged over units are being produced.
Prepare a schedule showing units started and completed in the Molding Department during April.
| Particulars | Units |
| Flow of physical units: Molding Department | |
| Units in beginning inventory, April 1 | 2,800 |
| Units started in April | 48,200 |
| Units in process during April | 51,000 |
| Units in ending inventory, April 30 | (3,400) |
| Units transferred to Finishing Department in April | 47,600 |
| Units in beginning inventory, April 1 | (2,800) |
| Units started and completed in April | 44,800 |
(Table 1)
Therefore, the units started and completed in the Molding Department during April is 44,800.
a. 2
Compute the equivalent units of direct materials and conversion for the Molding Department in April.
a. 2
Explanation of Solution
Compute the equivalent units of direct materials and conversion for the Molding Department in April.
| Particulars | Input Resources | |
| Direct Materials | Conversion | |
| To finish units in process on April 1: | ||
| Direct materials (2,800 units require 10% to complete) | 280 | |
| Conversion (2,800 units require 70% to complete) | 1,960 | |
| To start and complete 44,800 units in April | 44,800 | 44,800 |
| To start units in process on April 30: | ||
| Direct materials (3,400 units 80% complete) | 2,720 | |
| Conversion (3,400 units 20% complete) | 680 | |
| Equivalent units of resources in April | 47,800 | 47,440 |
(Table 2)
Therefore, the equivalent units of direct materials and conversion for the Molding Department in April are 47,800 and 47,440.
a. 3
Calculate the cost per equivalent unit of input resource for the Molding Department during April.
a. 3
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the cost per equivalent unit of input resource for the Molding Department during April.
| Particulars | Direct Materials in $ | Conversion Cost in $ |
| Cost per equivalent unit in April : | ||
| Costs incurred by Molding Department in April (A) | 669,200 | 521,840 |
| Equivalent units in April (B) | 47,800 | 47,440 |
| Cost per equivalent unit in April (A÷B) | 14 | 11 |
(Table 3)
Therefore, the cost per equivalent unit of input resource for the Molding Department during April is $14 per unit and $11 per unit respectively.
a. 4
Prepare journal entry to record the units transferred from the Molding Department to the Finishing Department during April.
a. 4
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry to record the transfer units from the Molding Department to the Finishing Department during April.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
|
Work in process: Finishing Department (4) | 1,190,000 | ||
| Work in process: Molding Department | 1,190,000 | ||
| (To record the transfer of 47,600 units to the Finishing department in April) |
(Table 4)
- Work in process: Finishing department is an asset and there is an increase in the value of an asset. Hence, debit the work in process: finishing department by $1,190,000.
- Work in process: Molding department is an asset and there is a decrease in the value of an asset. Hence, credit the work in process: molding department by $1,190,000.
Working Notes:
Calculate the cost of beginning inventory:
(1)
Calculate the cost of direct materials during the month April:
(2)
Calculate the cost of conversion during the month April:
(3)
Calculate the total cost of units transferred:
| Particulars | Amount in $ |
| Cost of beginning inventory, April 1 (1) | 44,520 |
| April direct materials cost (2) | 631,120 |
| April conversion cost (3) | 514,360 |
| Total cost of units transferred | 1,190,000 |
(Table 5)
(4)
a.5
Compute the costs assigned to ending inventory in the Molding Department on April 30.
a.5
Explanation of Solution
Compute the costs assigned to ending inventory in the Molding Department on April 30.
| Particulars | Amount in $ |
| Work in Process: Molding Department, April 30: | |
| Direct materials cost (5) | 38,080 |
| Conversion cost (6) | 7,480 |
| Ending inventory in process, April 30 | 45,560 |
(Table 6)
Working Notes:
Calculate the cost of direct materials during the month end of April 30:
(5)
Calculate the cost of conversion during the month end of April 30:
(6)
b. 1
Prepare a schedule showing units started and completed in the Finishing Department during April.
b. 1
Explanation of Solution
Prepare a schedule showing units started and completed in the finishing Department during April.
| Particulars | Units |
| Flow of physical units: Finishing Department | |
| Units in beginning inventory, April 1 | 5,000 |
| Units started in April | 47,600 |
| Units in process during April | 52,600 |
| Units in ending inventory, April 30 | (2,000) |
| Units transferred to Finishing Department in April | 50,600 |
| Units in beginning inventory, April 1 | (5,000) |
| Units started and completed in April | 45,600 |
(Table 7)
Therefore, the units started and completed in the Finishing Department during April is 45,600
b. 2
Compute the equivalent units of direct materials and conversion for the Finishing Department in April.
b. 2
Explanation of Solution
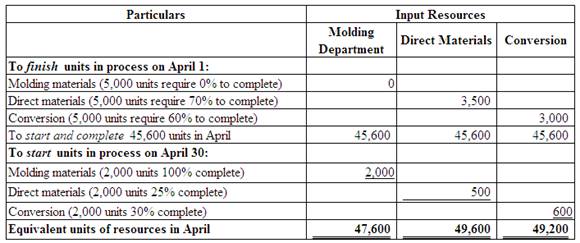
(Figure 4)
b. 3
Calculate the cost per equivalent unit of input resource for the Finishing Department during April.
b. 3
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the cost per equivalent unit of input resource for the Finishing Department during April.
| Particulars | Input Resources | ||
| Molding materials in $ | Direct Materials in $ | Conversion in $ | |
| Cost per equivalent unit in April | |||
| Costs charged to Finishing Department in April (A) | 1,190,000 | 496,000 | 147,600 |
| Equivalent units in April (B) | 47,600 | 49,600 | 49,200 |
| Cost per equivalent unit in April (A÷B) | 25 | 10 | 3 |
(Table 8)
Note:
Total cost of Molding Department $1,190,000 is transferred to the Finishing Department in April.
b.4
Prepare journal entry to record the units transferred from the Finishing Department to Finished goods inventory during April.
b.4
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry to record the transfer of units from the Finishing Department to Finished goods inventory during April.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Finished goods inventory | 1,922,800 | ||
|
Work in process: Finishing Department (9) | 1,922,800 | ||
| (To record the transfer of 50,600 units to the Finishing goods in April) |
(Table 9)
- Finished goods inventory is an asset and there is an increase in the value of an asset. Hence, debit the finished goods inventory by $1,922,800
- Work in process: Molding department is an asset and there is a decrease in the value of an asset. Hence, credit the work in process: molding department by $1,922,800.
Working Notes:
Calculate the cost of beginning inventory:
(5)
Calculate the cost of molding department during the month April:
(6)
Calculate the cost of direct materials during the month April for finishing department:
(7)
Calculate the cost of conversion during the month April for finishing department:
(8)
Calculate the total cost of units transferred:
| Particulars | Amount in $ |
| Cost of beginning inventory, April 1 (5) | 146,000 |
| April molding materials (6) | 1,140,000 |
| April direct materials cost (7) | 491,000 |
| April conversion cost (8) | 145,800 |
| Total cost of units transferred | 1,922,800 |
(Table 10)
(9)
a.5
Compute the costs assigned to ending inventory in the Finishing Department on April 30.
a.5
Explanation of Solution
Compute the costs assigned to ending inventory in the Finishing Department on April 30.
| Particulars | Amount in $ |
| Work in Process: Finishing department, April 30: | |
| Molding materials (10) | 50,000 |
| Direct materials cost (11) | 5,000 |
| Conversion cost (12) | 1,800 |
| Ending inventory in process, April 30 | 56,800 |
(Table 11)
Working Notes:
Calculate the cost of molding materials during the month end of April 30 for finishing department:
(10)
Calculate the cost of direct materials during the month end of April 30 for finishing department:
(11)
Calculate the cost of conversion during the month end of April 30 for finishing department:
(12)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Financial & Managerial Accounting

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





