
Concept explainers
a.1
Prepare a schedule showing units started and completed in the Assembly department during March.
a.1
Explanation of Solution
Prepare a schedule showing units started and completed in the assembly department during March as follows:
| Flow of Physical units: Assembly Department | |
| Particulars | Units |
| Beginning work in process inventory | 5,000 |
| Add: units started | 80,000 |
| Units in process | 85,000 |
| Less: Ending work in process inventory | 9,000 |
| Units transferred to assembly department | 76,000 |
| Less: beginning work in process inventory | 5,000 |
| Units started and completed | 71,000 |
Table (1)
2.
Compute the equivalent units of direct materials and conversion for the Assembly department during March.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare a schedule showing units started and completed in the forging department during March as follows:
| Particulars | Direct materials | Conversion |
| Beginning work in process inventory | 0 | 3,500 |
| Units start and complete | 71,000 | 71,000 |
| Ending work in process inventory | 9,000 | 7,200 |
| Equivalent units of production | 80,000 | 81,700 |
Table (2)
Working note:
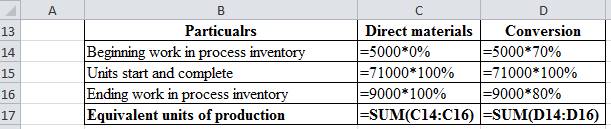
Figure (1)
3.
Identify the cost per equivalent unit of input resource for the assembly department during March.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Identify the cost per equivalent unit of input resource for the assembly department during March as follows:
| Particulars | Direct materials | Conversion |
| Cost incurred by Forging department (A) | $720,000 | $490,200 |
| Equivalent units (B) | 80,000 | 81,700 |
| Cost per equivalent unit (A ÷ B) | $9 | $6 |
Table (3)
4.
Prepare the
4.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entry to transfer units from Assembly department to the assembly department during March as follows:
| Account titles and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| Work in process inventory - Packaging department | $1,140,000 | |
| Work in process inventory - assembly department | $1,140,000 | |
| (To record transfer of 76,000 units to the packaging department) |
Table (4)
Working note:
Calculate total unit cost transferred.
| Particulars | Amount |
| Beginning work in process inventory ($45,000 +$9,000) | $54,000 |
| Add: Start and complete cost: | |
| Materials (71,000 units × $9) | $639,000 |
| Conversion (74,500 units × $6) | $447,000 |
| Total cost of units transferred | $1,140,000 |
Table (5)
- Work in process inventory – packaging department is a current asset, and it is increased. Therefore, debit work in process inventory account – packaging department for $1,140,000.
- Work in process inventory – assembly department is a current asset, and it is decreased. Therefore, credit work in process inventory –assembly department account for $1,140,000.
5.
Compute cost assigned to ending inventory in the forging department on March 31.
5.
Explanation of Solution
Compute cost assigned to ending inventory in the forging department on March 31 as follows:
b.1
Prepare a schedule showing units started and completed in the packaging department during March.
b.1
Explanation of Solution
| Flow of Physical units: Packaging Department | |
| Particulars | Units |
| Beginning work in process inventory | 4,000 |
| Add: units started | 76,000 |
| Units in process | 80,000 |
| Less: Ending work in process inventory | 20,000 |
| Units transferred to assembly department | 60,000 |
| Less: beginning work in process inventory | 4,000 |
| Units started and completed | 56,000 |
Table (6)
2.
Compute equivalent units of direct materials and conversion for the packaging department in March.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Compute equivalent units of direct materials and conversion for the packaging department in March as follows:
| Particulars | Direct materials | Conversion |
| Beginning work in process inventory | 4,000 | 3,200 |
| Units start and complete | 56,000 | 56,000 |
| Ending work in process inventory | - | 6,000 |
| Equivalent units of production | 60,000 | 65,200 |
Table (7)
Working note:
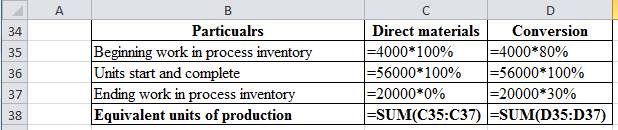
Figure (2)
3.
Compute equivalent cost per unit of input resource for the packaging department during March.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Compute equivalent cost per unit of input resource for the packaging department during March as follows:
| Particulars | Direct materials | Conversion |
| Cost incurred by department (A) | $840,000 | $260,800 |
| Equivalent units (B) | 60,000 | 65,200 |
| Cost per equivalent unit (A ÷ B) | $14 | $4 |
Table (8)
4.
Prepare journal entry to record transfer units from the assembly department to finished goods inventory during March.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry to record transfer units from the assembly department to finished goods inventory during March as follows:
| Account titles and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| Finished goods inventory | $1,980,000 | |
| Work in process inventory - packaging department | $1,980,000 | |
| (To record transfer of 60,000 units to the assembly department) |
Table (9)
Working note:
Calculate total unit cost transferred.
| Particulars | Amount |
| Beginning work in process inventory ($60,000 +$3,200) | $63,200 |
| Add: Start and complete cost: | |
| Materials (60,000 units × $14) | $840,000 |
| March forging materials (56,000 units × $15) | $840,000 |
| Conversion (59,200 units × $4) | $236,800 |
| Total cost of units transferred | $1,980,000 |
Table (10)
- Finished goods inventory is a current asset, and it is increased. Therefore, debit finished goods inventory account for $1,980,000.
- Work in process inventory – packaging department is a current asset, and it is decreased. Therefore, credit work in process inventory – packaging department account for $1,920,000.
5.
Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory in the packaging department.
5.
Explanation of Solution
Compute cost assigned to ending inventory in the packaging department on March 31 as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Financial & Managerial Accounting
- Need help with this question solution general accounting questionarrow_forwardDifferential Chemical produced 18,000 gallons of Preon and 39,000 gallons of Paron. Joint costs incurred in producing the two products totaled $8,500. At the split-off point, Preon has a market value of $11 per gallon and Paron $3.5 per gallon. Compute the portion of the joint costs to be allocated to Preon if the value basis is used.arrow_forwardAvalon Corporation has set a target return on investmentarrow_forward
- i need correct ans no chatgpt ,arrow_forwardApex manufacturing repoted a debt to equity ratio accounting questions fast answer and correct solutionarrow_forwardMID Company had originally expected to earn operating income of $130,000 in the coming year. MID's degree of operating leverage is 3.5. Recently, MID revised its plans and now expects to increase sales by 23% next year. What is the percent change in operating income expected by MID in the coming year?arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





