
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation : To classify the given saccharide as mono, di, tri or polysaccharide.
Concept Introduction : Carbohydrates are composed of certain monomer units called as monosaccharides. Monosaccharides are polyhydroxy
(a)
Answer to Problem 75UTC
Melezitose is a tri-saccharide as it is composed of three monosaccharide units.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
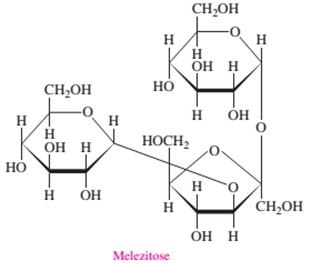
In the given structure of molecule there are three sugar molecules bonded with each other. Hence there are three monosaccharide units bonded to each other by two glycosidic linkages that make it a tri-saccharide molecule.
(b)
Interpretation : To identify the keto and aldohexose present in melezitose.
Concept Introduction : Carbohydrates are composed of certain monomer units called as monosaccharides. Monosaccharides are polyhydroxy aldehyde and ketones which are bonded with each other to form polysaccharides.
(b)
Answer to Problem 75UTC
Melezitose is composed of two aldohexose (glucose) and one ketohexose (fructose) units.
Explanation of Solution
In the given structure of molecule there are three sugar molecules; out of which two are pyranose rings with total 6 C atoms hence they should be aldohexose monosaccharides whereas one is furanose ring bonded with two −CH2OH groups at both terminals that proves it as a ketohexose. Hence Melezitose is composed of two aldohexose and one ketohexose units.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Basic Chemistry Plus Mastering Chemistry With Pearson Etext -- Access Card Package (6th Edition)
- Г C-RSA CHROMATOPAC CH=1 DATA 1: @CHRM1.C00 ATTEN=10 SPEED= 10.0 0.0 b.092 0.797 1.088 1.813 C-RSA CHROMATOPAC CH=1 Report No. =13 ** CALCULATION REPORT ** DATA=1: @CHRM1.000 11/03/05 08:09:52 CH PKNO TIME 1 2 0.797 3 1.088 4 1.813 AREA 1508566 4625442 2180060 HEIGHT 207739 701206 V 287554 V MK IDNO CONC NAME 18.1447 55.6339 26.2213 TOTAL 8314067 1196500 100 C-R8A CHROMATOPAC CH=1 DATA 1: @CHRM1.C00 ATTEN=10 SPEED= 10.0 0. 0 087 337. 0.841 1.150 C-R8A CHROMATOPAC CH=1 Report No. =14 DATA=1: @CHRM1.000 11/03/05 08:12:40 ** CALCULATION REPORT ** CH PKNO TIME AREA 1 3 0.841 1099933 41.15 4039778 HEIGHT MK IDNO 170372 649997¯¯¯ CONC NAME 21.4007 78.5993 TOTAL 5139711 820369 100 3 C-R8A CHROMATOPAC CH=1 DATA 1: @CHRM1.C00 ATTEN=10 SPEED= 10.0 0.100 0:652 5.856 3 1.165 C-RSA CHROMATOPAC CH-1 Report No. =15 DATA=1: @CHRM1.000 11/03/05 08:15:26 ** CALCULATION REPORT ** CH PKNO TIME AREA HEIGHT MK IDNO CONC NAME 1 3 3 0.856 4 1.165 TOTAL 1253386 4838738 175481 708024 V 20.5739 79.4261 6092124…arrow_forwardIndicate the product that is obtained if the benzotriazole reacts with the use of a medium basic product.arrow_forwardIndicate the product that is obtained if the benzotriazol reacts with dimethyl sulfate.arrow_forward
- Indicate how to obtain 2-metilbencimidazol from 1,2-diaminobenzene.arrow_forwardbreak down both reactions shown and explain it correctly using the bromonium ion mechanism, instead of the (disproven) carbocation-based mechanism.arrow_forwardIndicate how from 1,2-diaminobenzene to obtain 1-metilbenzotriazol.arrow_forward
- -C = C - C - + Br₂ + I" -> -C-C-c -C = C -C- + Br² + I₂ -C=C Br I + Brū + Iz -7- C - C-C- I Br Mechanism; - C = c - c - + Br - Br > - C-c-c- Br -C-C-C- + 1 - - -Ċ-Ċ'-c' - Br Br Iarrow_forwardWrite the mechanism of the esterification reaction (please show the mechanism included line pairs and arrows)arrow_forwardHow do I break down the reaction shown on the chalkboard and explain it correctly using the bromonium ion mechanism, instead of the (disproven) carbocation-based mechanismarrow_forward
- ¿Qué the product is obtained from tetraethoxypropano and hidrazina?. Indicate the reason why the corresponding dial is used.arrow_forwardIf CH3COCH2CH(OCH3)2 is reacted with hydrazine, two isomeric products are formed. Indicate their structures and the major product.arrow_forwardIs it possible to obtain addition derivatives to nitrogen in position 2 of pyrazoles by reaction with electrophilic agents? Reason for this.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning



