
A 1.00-mol sample of an ideal monatomic gas is taken through the cycle shown in Figure P18.63. The process A→B is a reversible isothermal expansion. Calculate (a) the net work done by the gas, (b) the energy added to the gas by heat, (c) the energy exhausted from the gas by heat, and (d) the efficiency of the cycle. (e) Explain how the efficiency compares with that of a Carnot engine operating between the same temperature extremes.
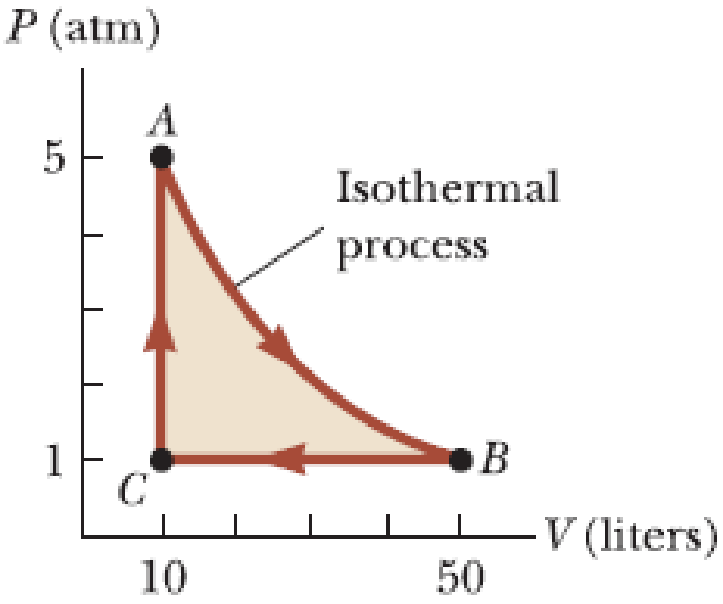
Figure P18.63
(a)
Net work done by the gas.
Answer to Problem 63P
Net work done by the gas is
Explanation of Solution
For an isothermal process AB, the work on the gas is
Here
Write the equation for work done in the process BC,
Here
Work done in the process CA is zero because the volume is constant.
Write the equation for met work done
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Net work done by the gas is
(b)
Energy added to the gas by heat.
Answer to Problem 63P
Total energy absorbed by heat is
Explanation of Solution
The change in internal energy for the process AB is zero as it is isothermal.
Then,
Write the equation for specific heat capacity at constant volume
Here
Write the ideal gas equation in terms of temperature
Similarly,
Here
Write the equation for heat transfer for the process CA,
Substitute (V) in (VIII)
Write the equation for total energy absorbed by heat
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Total energy absorbed by heat is
(c)
Energy exhausted from the gas by heat.
Answer to Problem 63P
The energy exhausted is
Explanation of Solution
Write the equation for heat energy transferred
Here
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Substitute
The energy exhausted is
(d)
Efficiency of the cycle.
Answer to Problem 63P
The efficiency is
Explanation of Solution
Write the equation for efficiency an engine in terms of work done
Here
Conclusion:
Substitute
The efficiency is
(e)
Compare with the efficiency of a Carnot engine.
Answer to Problem 63P
The efficiency of this system is lower than the Carnot engine
Explanation of Solution
Write the equation for efficiency of a Carnot engine
Here
Conclusion:
Substitute
The efficiency of this system is much lower than the Carnot engine
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
- please solve and answer the question correctly. thank you!!arrow_forwardplease solve and answer the question correctly. thank you!! (hint in 2nd photo)arrow_forwardNewton's Laws of Motion - Please help with the first angle calculations of standard deviation and margin of error. I just need a model and I can figure out the other two angles. Thanks!arrow_forward
- 2. A battleship simultaneously fires two shells at enemy ships. If the shells follow the parabolic trajectories shown, which ship gets hit first? a. A b. both at the same time C. B d. need more information battleship Barrow_forwardA m₁ = 1.70-kg aluminum block and a m₂ = 8.00-kg copper block are connected by a light string over a frictionless pulley. The two blocks are allowed to move on a fixed steel block wedge (of angle 0 = 31.5°) as shown in the figure. (For aluminum on steel, μk k = 0.36.) Мк Aluminum m Copper = 0.47. For copper on steel, Steel m2 Ꮎ (a) the acceleration of the two blocks m/s² (b) the tension in the string Narrow_forwardWhile the 83.3 kg Dora Milaje is in equilibrium, the rope makes a 70.0˚ angle with the horizontal. Assuming the coefficient of friction between her shoes and the ship is 0.772 and her static friction is at its maximum value, what is the tension in the cable?arrow_forward
- Can someone help me asnwer this thank youarrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the problem correctly please. Be sure to give explanations on each step and write neatlyplease. Thank you!! ( preferably type the explantion, steps and solution please )arrow_forwardA square coil that has 17.5 cm on each side containing 17 loops lies flat on your desk as shown on this page. A uniform magnetic field of magnitude 4.60 × 10-ST points into this page. If a 8.50-A clockwise Current flows through the coil. ca) determine the torque on the coil. N.m (b) which edge of the coil rises up? choose one 。 Bottom отор and explain. O Right • None of these О Left.arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





