
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction of propanal with the given reagents has to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Lithium aluminum hydride and sodium borohydride are strong reducing agents. They are inorganic compounds which are used as the reducing agents in
In the reaction of
By catalytic hydrogenation, aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols. Grignard reagents react with ketones and aldehydes to form alcohols. These reactions are nucleophilic addition reactions. The Grignard reagent adds to the carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones due to electronegativity difference between carbon and oxygen.
An organolithium reagent acts like a good nucleophiles and strong bases. They used for the conversion of aldehydes and ketones into primary and secondary alcohols. Acetal is an organic compound with general formula
Answer to Problem 27P
Solution:
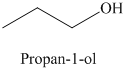
a) The product of the reaction of propanal with lithium aluminum hydride, followed by water is shown below.
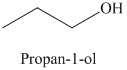
b) The product of the reaction of propanal with sodium borohydride, methanol is shown below.
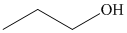
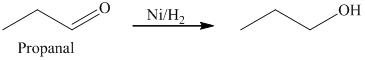
c) The product of the reaction of propanal with hydrogen (nickel catalyst) is shown below.
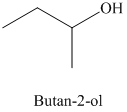
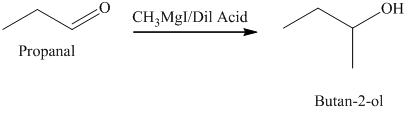
d) The product of the reaction of propanal with methylmagnesium iodide, followed by dilute acid is shown below.
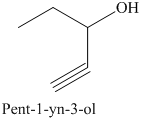
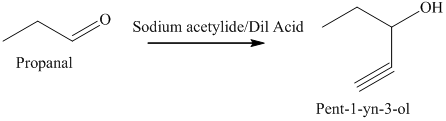
e) The product of the reaction of propanal with sodium acetylide, followed by dilute acid is shown below.
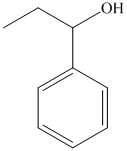
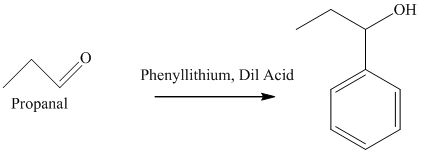
f) The product of the reaction of propanal with phenyllithium, followed by dilute acid is shown below.
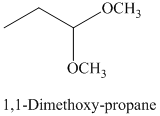
g) The product of the reaction of propanal with methanol containing dissolved hydrogen chloride is shown below.
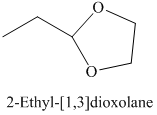
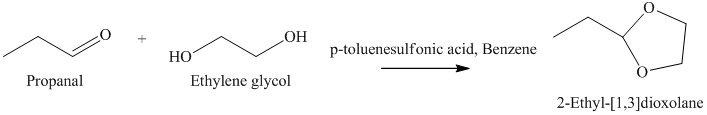
h) The product of the reaction of propanal with ethylene glycol, p-toluenesulfonic acid, benzene is shown below.
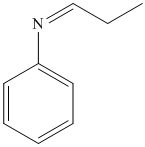
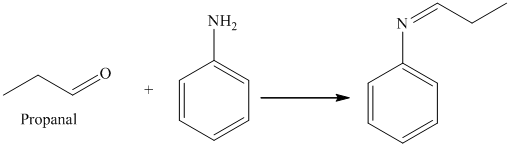
i) The product of the reaction of propanal with aniline
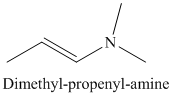
j) The product of the reaction of propanal with dimethylamine, p-toluenesulfonic acid, benzene is shown below.
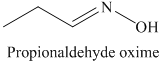
k) The product of the reaction of propanal with hydroxylamine is shown below.
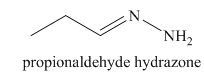
l) The product of the reaction of propanal with hydrazine is shown below.
m) The product of the reaction of propanal with product of part (l) heated in triethylene glycol with sodium hydroxide is shown below.
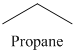
n) The product of the reaction of propanal with p-Nitrophenylhydrazine is shown below.
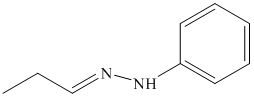
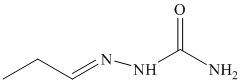
o) The product of the reaction of propanal with semicarbazide is shown below.
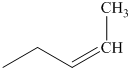
p) The product of the reaction of propanal with ethylidenetriphenylphosphorane is shown below.
q) The product of the reaction of propanal with sodium cyanide with addition of sulfuric acid is shown below.
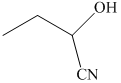
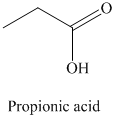
r) The product of the reaction of propanal with chromic acid is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
a) The product obtained by the reaction between, propanal and the reagent, lithium aluminum hydride, followed by water.
The reaction of propanal with lithium aluminum hydride, followed by water gives primary alcohol as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
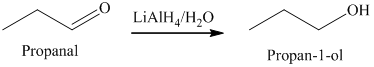
b) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and the reagent, sodium borohydride, methanol.
The reaction of propanal with sodium borohydride, followed by methanol gives primary alcohol as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
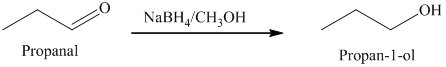
c) The product obtained by the reaction between the given compound, propanal and the reagent, hydrogen (nickel catalyst).
The reaction of propanal with hydrogen in the presence of nickel catalyst gives
d) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and the reagent, methylmagnesium iodide, followed by dilute acid.
The reaction of propanal with methylmagnesium iodide that is Grignard reagent, followed by dilute acid gives alcohol as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
e) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and the reagent, sodium acetylide, followed by dilute acid.
The reaction of aldehyde with sodium acetylide is fundamentally similar to the Grignard reaction. The reaction of propanal with sodium acetylide, followed by dilute acid gives alcohol. The product of this reaction is shown below.
f) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and the reagent, phenyllithium, followed by dilute acid.
The reaction of propanal with phenyllithium, followed by dilute acid gives alcohol as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
g) The product obtained by the reaction between the given compound, propanal and the reagent, methanol containing dissolved hydrogen chloride.
The reaction of aldehydes with two equivalents of an alcohol results in the formation of acetals. The product of this reaction is shown below.
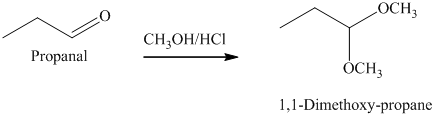
h) The product obtained by the reaction between the given compound, propanal and the reagent, Ethylene glycol, p-toluenesulfonic acid, benzene.
In the reaction of aldehyde with ethylene glycol, p-toluenesulfonic acid and benzene, the protection of the carbonyl group of aldehyde takes place. For carbonyl protection, ethylene glycol is the commonly used group. The final product resembles like ether and known as ketal during the protection of carbonyl group using ethylene glycol. The product of this reaction is shown below.
i) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and the reagent, aniline
The reaction of aldehyde with primary
j) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and the reagent, dimethylamine, p-toluenesulfonic acid, benzene.
The reaction of aldehyde with secondary amine forms enamine as the final product. The reaction of propanal with dimethylamine in the presence of p-toluenesulfonic acid and benzene gives

k) The product obtained by the reaction between the given compound, propanal and the reagent, hydroxylamine.
The reaction of aldehyde with hydroxylamine gives oxime as the final product. The reaction of propanal with hydroxylamine results in the formation of propionaldehyde oxime. The product of this reaction is shown below.
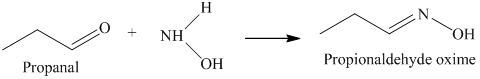
l) The product obtained by the reaction between the given compound, propanal and the reagent, hydrazine.
The reaction of aldehyde with hydrazine gives hydrazone. The reaction of propanal with hydrazine gives propionaldehyde hydrazone as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
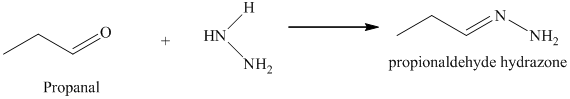
m) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and the product of part (l) heated in triethylene glycol with sodium hydroxide.
The reaction of aldehyde with hydrazine gives hydrazone. The reaction of propanal with hydrazine gives propionaldehyde hydrazone as the final product. The heating of propionaldehyde hydrazone in triethylene glycol with sodium hydroxide forms

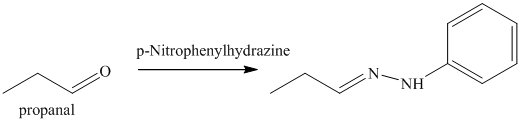
n) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and p-nitrophenylhydrazine.
The reaction of aldehyde with hydrazine gives hydrazone. The reaction of propanal with p-Nitrophenylhydrazine gives propionaldehyde phenylhydrazone as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.
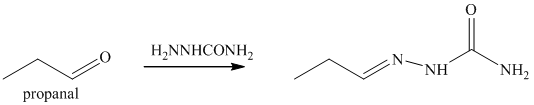
o) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and semicarbazide.
The reaction of aldehyde with semicarbazide results in the formation of semicarbazone. The reaction of propanal with
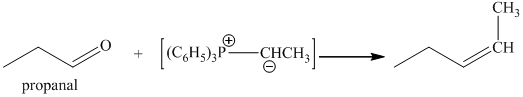
p) The product obtained by the reaction between the given compound, propanal and ethylidenetriphenylphosphorane.
The reaction of propanal with ethylidenetriphenylphosphorane gives
q) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and sodium cyanide with addition of sulfuric acid.
The reaction of aldehyde with sodium cyanide results in the formation of cyanohydrin. The product of this reaction is shown below.
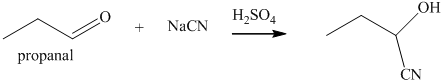
r) The product obtained by the reaction between propanal and chromic acid.
The reaction of propanal with chromic acid gives propionic acid as the final product. The product of this reaction is shown below.

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - Standalone book
- What is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? R+ HO-C-CH2-CH3 0= CH3 CH3 —CH, C−NH—CH CH3 + H₂O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them. If there is no reasonable answer, check the No answer box under the drawing area. Note for advanced students: you may assume no products other than those shown above are formed. No Answer Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. €arrow_forward个 CHEM&131 9267 - $25 - Intro to Mail - Hutchison, Allison (Student x Aktiv Learnin https://app.aktiv.com Draw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. + Na2Cr2O7 Acetone, H2SO4 Type here to search Dryng OH W Prarrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: OH + NaOH A? Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No reaction Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ✓ Sarrow_forward
- Predict the products of this organic reaction: CH3-C-O-CH2-CH2-C-CH3 + H₂O ? A Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. :☐ darrow_forwardDE d. Draw an arrow pushing mechanism for the following IN O CI N fo 人 P Polle DELL prt sc home end ins F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 F11 F12arrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: + H₂O H* ? A Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No Reaction Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
- Predict the major organic products of the reaction below and draw them on right side of the arrow. If there will be no significant reaction, check the box below the drawing area instead. C Cl CH, OH There will be no significant reaction. + pyridine G Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? H R+ H2O Δ OH 0= CH3-CH-O-CH3 + CH3-C-OH Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them. If there is no reasonable answer, check the No answer box under the drawing area. No Answer Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. dyarrow_forwardYou are trying to determine whether the following organic reaction can be done in a single synthesis step. If so, add any missing reagents or conditions in the drawing area below. If it isn't possible to do this reaction in a single synthesis step, check the box below the drawing area instead. Note for advanced students: if you have a choice of reagents to add, you should choose the least reactive and most economical reagents possible. Cl It isn't possible to do this reaction in a single synthesis step. + T OHarrow_forward
- Predict the products of this organic reaction: CH3 O CH3-CH-C-O-CH2-CH2-CH3 + H₂OH+ Η ? A Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No Reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure.arrow_forward€ CH3-CH-C-O-CH2-CH2-CH3 + NaOH A? Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. Predict the products of this organic reaction: CH3 O Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. No reaction ✓ Garrow_forwardA molecule can have a temporary or permanent depending on the structure and the way the electrons can move. True Falsearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





