
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
To draw the structural formula of given organic compounds.
Concept Introduction:
Ester, amide and anhydride are derivatives of
Answer to Problem 1P
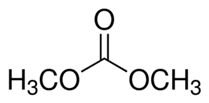
Explanation of Solution
We know that
(b)
Interpretation:
To draw the structural formula of given organic compounds.
Concept Introduction:
Ester, amide and anhydride are derivatives of carboxylic acid.
Answer to Problem 1P
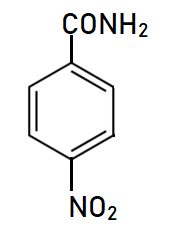
Explanation of Solution
This is a nitro derivative of benzamide in which nitro group is bonded at para position with respect to amide group. Benzamide is
(c)
Interpretation:
To draw the structural formula of given organic compounds.
Concept Introduction:
Ester, amide and anhydride are derivatives of carboxylic acid.
Answer to Problem 1P
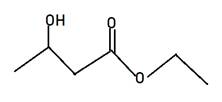
Explanation of Solution
Alkyl alkanoate is the general name for ester. Here Alkyl indicates the small alkyl group in RCOOR and alkanoate is RCOO- part. The name given is ethyl 3-hydroxybutanate, hence 3-hydroxybutanate will be RCOO-part and ethyl will be another r of ester. Therefore, the structure of ethyl 3-hydroxybutanate will be
(d)
Interpretation:
To draw the structural formula of given organic compounds.
Concept Introduction:
Ester, amide and anhydride are derivatives of carboxylic acid.
Answer to Problem 1P
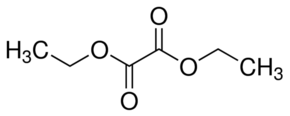
Explanation of Solution
Diethyl oxalate is the diester of oxalic acid (HOOC-COOH). As name suggested, diethyl stands for two ethyl group bonded at both carbon atoms of oxalic acid hence the formula will be
(e)
Interpretation:
To draw the structural formula of given organic compounds.
Concept Introduction:
Ester, amide and anhydride are derivatives of carboxylic acid.
Answer to Problem 1P
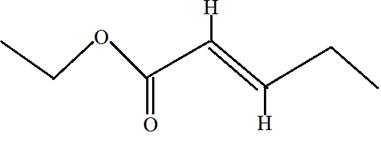
Ethyl trans-2-pentenoate.
Explanation of Solution
Ethyl trans-2-pentenoate is the ester of 2-pentenoic acid with ethanol. Here trans indicates the position of H on both double bonded carbon atoms. Hence in the formula of ester R1 -COO-R2 ; R2 will be ethyl group from alcohol and R1 will be alkyl group from acid.
(f)
Interpretation:
To draw the structural formula of given organic compounds.
Concept Introduction:
Ester, amide and anhydride are derivatives of carboxylic acid.
Answer to Problem 1P
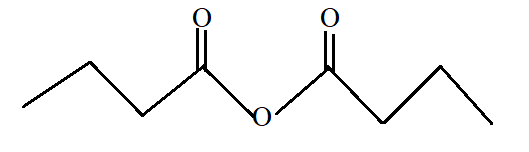
Butanoic anhydride.
Explanation of Solution
Butanoic anhydride is the anhydride of butanoic acid with −COOCO- as
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
INTRO.TO GENERAL,ORGAN...-OWLV2 ACCESS
- What is the name of the following compound? SiMe3arrow_forwardK Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
