
(a)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism of the given reaction in the acidic medium is to be drawn, and major organic product is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
When an
Answer to Problem 18.56P
The complete, detailed mechanism of the given reaction in the acidic medium is shown below; an acetal is the major product.
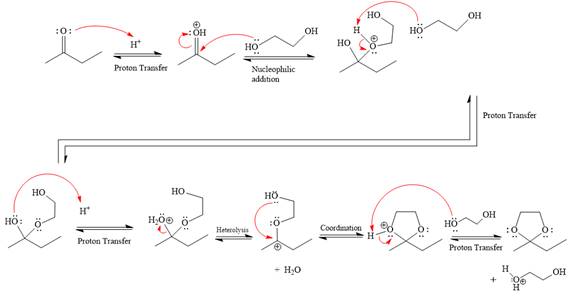
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
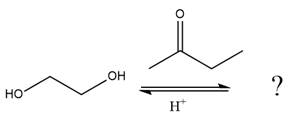
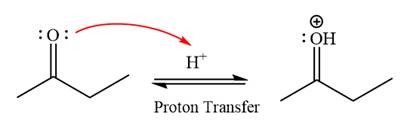
This is an acetal formation reaction in which the reaction is catalyzed by an acid, and the excess
First three steps are that of the acid catalyzed nucleophilic addition reactions on ketone. In the first step, the
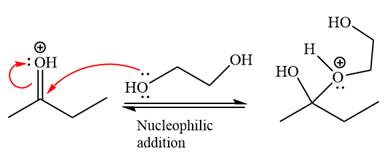
Next, the weak nucleophile, diol, attacks the activated electrophilic carbon by nucleophilic addition reaction.
In the next step, deprotonation produces the uncharged hemiacetal.
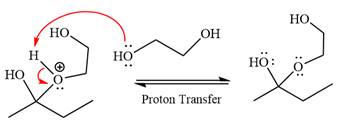
The remaining steps essentially make up the
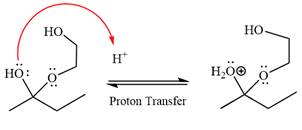
The
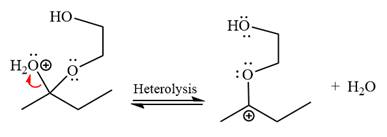
The resonance stabilized carbocation is further attacked by the diol nucleophile, which produces positively charged acetal. The carbonation step is intramolecular because it forms a five-membered ring, and it is stable.
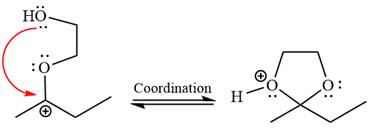
In the last step, the deprotonation of the charged acetal by alcohol results in the uncharged acetal formation. Acetal is the major product of the given aldehyde.
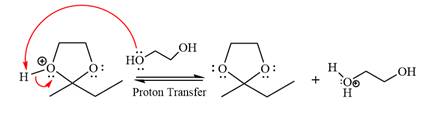
The complete, detailed mechanism of the given reaction in the acidic medium is shown below; an acetal is the major product.
The complete, detailed mechanism of the given reaction under acidic medium and excess alcohol is drawn.
(b)
The complete, detailed mechanism of the given reaction in the acidic medium is to be drawn, and major organic product is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
When an aldehyde or ketone is treated with an alcohol under acidic conditions, a hemiacetal product is formed. Use of an excess amount of alcohol under acidic conditions and after that the nucleophilic addition produces hemiacetals, which further form an acetal. The acetal has two alkoxy groups bonded to the same carbon. The formation of the acetal product is favored by using excess alcohol. This type of reactions is carried forward by proton transfer and nucleophilic addition on the carbonyl carbon. An acetal is produced under acidic conditions by a ketone or aldehyde but not under basic conditions because the nucleophilic substitution requires the leaving group to be
Answer to Problem 18.56P
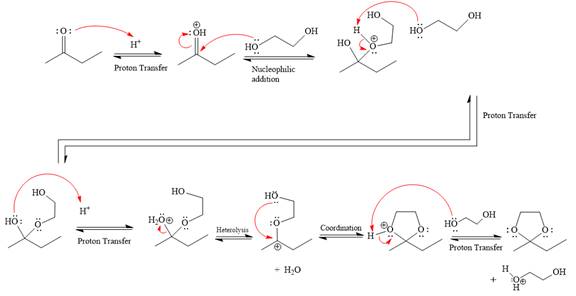
The complete, detailed mechanism of the given reaction in the acidic medium is shown below; an acetal is the major product.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
This is an acetal formation reaction in which the reaction is catalyzed by sulfuric acid, and the excess diols act as the nucleophile.
First three steps are that of the acid catalyzed nucleophilic addition reactions on ketone. In the first step, the
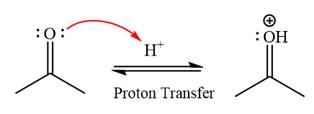
Next, the weak nucleophile, alcohol, attacks the activated electrophilic carbon by nucleophilic addition reaction.
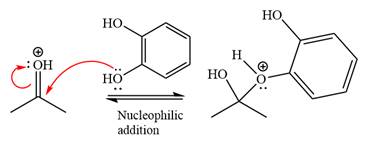
In the next step, deprotonation produces the uncharged hemiacetal.
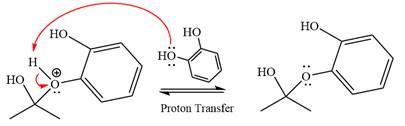
The remaining steps essentially make up an
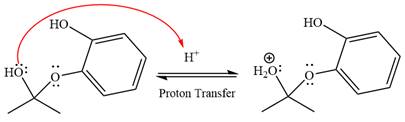
The
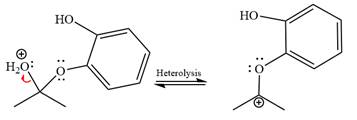
The resonance stabilized carbocation is further attacked by the diol nucleophile, which produces positively charged acetal. The carbonation step is intramolecular because it forms a five-membered ring, and it is stable.
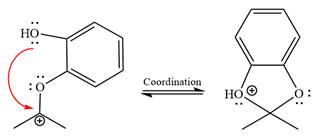
In the last step, the deprotonation of charged acetal by alcohol results in the uncharged acetal formation. Acetal is the major product of the given aldehyde.
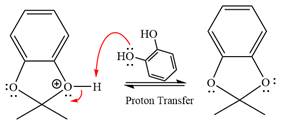
The complete, detailed mechanism of the given reaction in the acidic medium is shown below; an acetal is the major product.
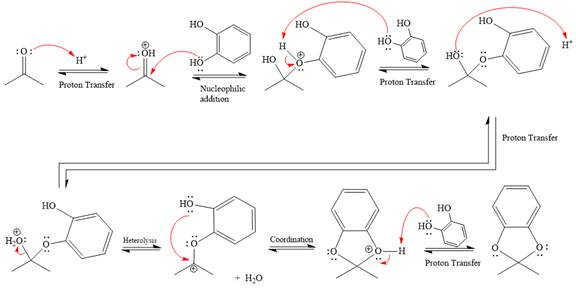
The complete, detailed mechanism of the given reaction under acidic medium and excess alcohol is drawn.
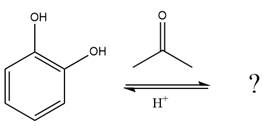
(c)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism of the given reaction in the acidic medium is to be drawn, and major organic product is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
When an aldehyde or ketone is treated with an alcohol under acidic conditions, a hemiacetal product is formed. Use of an excess amount of alcohol under acidic conditions and after that the nucleophilic addition produces hemiacetals, which further form an acetal. The acetal has two alkoxy groups bonded to the same carbon. The formation of the acetal product is favored by using excess alcohol. This type of reactions is carried forward by proton transfer and nucleophilic addition on the carbonyl carbon. An acetal is produced under acidic conditions by a ketone or aldehyde but not under basic conditions because the nucleophilic substitution requires the leaving group to be
Answer to Problem 18.56P
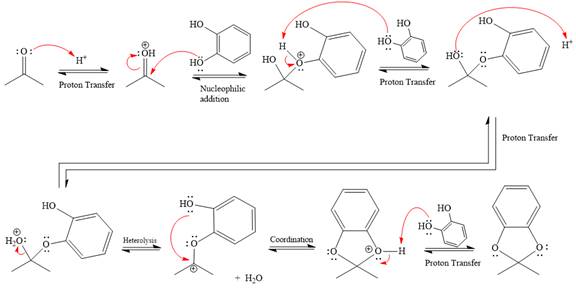
The complete, detailed mechanism of the given reaction in the acidic medium is shown below; an acetal is the major product.
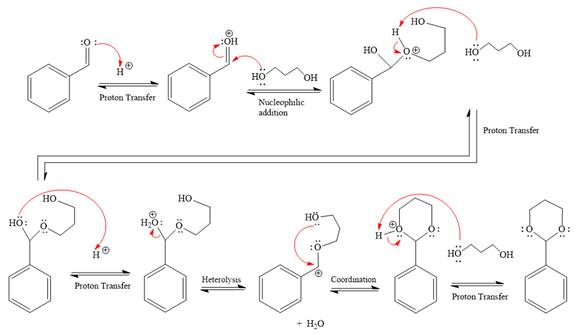
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
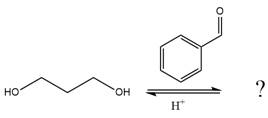
This is an acetal formation reaction in which the reaction is catalyzed by sulfuric acid, and the excess diol acts as the nucleophile.
First three steps are that of the acid catalyzed nucleophilic addition reactions on the aldehyde. In the first step, the
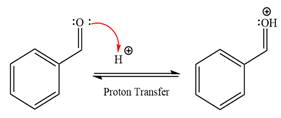
Next, the weak nucleophile, alcohol, attacks the activated electrophilic carbon by nucleophilic addition reaction.
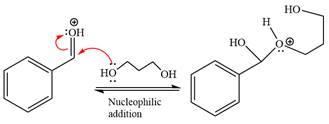
In the next step, deprotonation produces the uncharged hemiacetal.
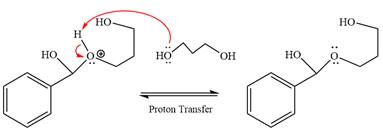
The remaining steps essentially make up an
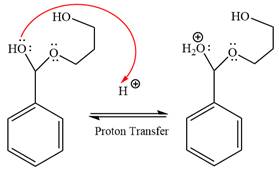
The
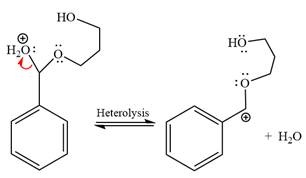
The resonance stabilized carbocation is further attacked by the diol nucleophile, which produced positively charged acetal. The carbonation step is intramolecular because it forms a six-membered ring, and it is stable.
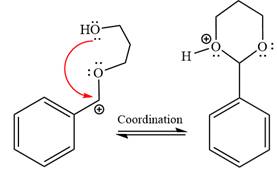
In the last step, the deprotonation of the charged acetal by alcohol results in the uncharged acetal formation. Acetal is the major product of the given aldehyde.
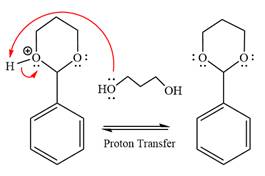
The complete, detailed mechanism of the given reaction in the acidic medium is shown below; an acetal is the major product.
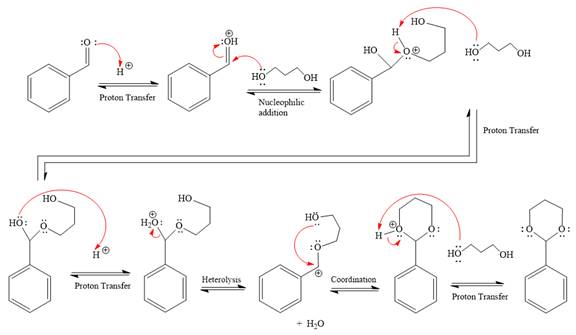
The complete, detailed mechanism of the given reaction under acidic medium and excess alcohol is drawn.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Get Ready for Organic Chemistry
- Write all of Me Possible Products For each Of the Following reactions. In each case identity all pains of enantiomers, all digsterzoners and all Meso compounds 9. 11-60 11-0-11 V-G Η Η H ~ C-11 +HB+ - 1 H b. पन्ना 171-0-11 H-C-H Н C-C=c-call +HBr Perendez ==arrow_forwardHow can i draw the mechanisms for this molecule?arrow_forwarda. Discuss and explain he difference IN Stability between the Chai and Boat Гольцу от судомехане b. For the Following Molecule draw both possible Clain conformations and explain which one is more stable and for what Reason. H. CH₂ CH₂ H "Harrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





