
Concept explainers
Find the consolidation settlement of the group.
Answer to Problem 18.25P
The consolidation settlement of the group is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The total load
The length
The length
The length
The unit weight
The saturated unit weight
The initial void ratio
The coefficient of consolidation
The saturated unit weight
The initial void ratio
The coefficient of consolidation
The saturated unit weight
The initial void ratio
The coefficient of consolidation
The saturated unit weight
The initial void ratio
The coefficient of consolidation
Calculation:
Show the pressure diagram as in Figure 1.
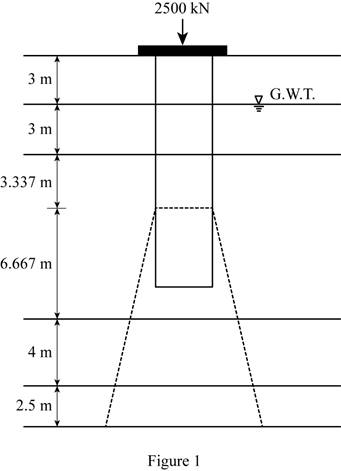
Determine the total length L of pile using the formula.
Substitute 3 m for
The load starts transmitting to the soil at the pile depth of
Determine the depth at which the load on the group pile
Here, L is the depth of normally consolidated clay layer 1.
Substitute 10 m for L.
Thus, the settlement starts in NCC layer 1.
Determine the stress
Here,
Take the unit weight of water as
Substitute
Determine the stress
Here,
Substitute
Determine the stress
Here,
Substitute
Calculate the stress
Here,
Substitute 2,500 kN for
Calculate the stress
Substitute 2,500 kN for
Calculate the stress
Substitute 2,500 kN for
Determine the value of
Substitute
Determine the value of
Substitute
Determine the value of
Substitute
Determine the consolidated settlement
Here,
Substitute 0.30 for
Determine the consolidated settlement
Here,
Substitute 0.35 for
Determine the consolidated settlement
Here,
Substitute 0.26 for
Determine the total
Substitute 0.186 m for
Therefore, the consolidated settlement of the group pile is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF GEOTECHNICAL ENGINE
- Consider the geometric and traffic characteristics shown below. Approach (Width) North South East West (56 ft) (56 ft) (68 ft) (68 ft) Peak hour Approach Volumes: Left Turn 165 105 200 166 Through Movement 447 400 590 543 Right Turn 162 157 191 200 Conflicting Pedestrian Volumes 900 1,200 1,200 900 PHF 0.95 0.95 0.95 0.95 For the following saturation flows: Through lanes: 1,600 veh/h/In Through-right lanes: 1,400 veh/h/In Left lanes: 1,000 veh/h/In Left-through lanes: 1,200 veh/h/In Left-through-right lanes: 1,100 veh/h/In The total cycle length was 283 s. Now assume the saturation flow rates are 10% higher, that is, assume the following saturation flow rates: Through lanes: 1,760 veh/h/In Through-right lanes: 1,540 veh/h/In Left lanes: 1,100 veh/h/In Left-through lanes: 1,320 veh/h/In 1,210 veh/h/In Left-through-right lanes: Determine a suitable signal phasing system and phase lengths (in s) for the intersection using the Webster method. (Enter the sum of green and yellow times for…arrow_forwardThe given beam has continuous lateral support. If the live load is twice the dead load, what is the maximum total service load, in kips / ft, that can be supported? A992 steel is used: Fy = 50 ksi, Fu=65 ksi. Take L = 30 ft. bf For W40 x 149: 2tf = 7.11, = = 54.3, Z 598 in.³ tw W W40 X 149 L (Express your answers to three significant figures.) a. Use LRFD. Wtotal = kips/ft b. Use ASD. Wtotal kips/ftarrow_forwardThe beam shown in the figure below is a W16 × 31 of A992 steel and has continuous lateral support. The two concentrated loads are service live loads. Neglect the weight of the beam and determine whether the beam is adequate. Suppose that P = 52 k. For W16 × 31: d = 15.9 in., tw = 0.275 in., h/tw = 51.6, and M = M₁ = 203 ft-kip, Mn/₁ = Mp/α = 135 ft-kip. P Р W16 x 31 a. Use LRFD. Calculate the required moment strength, the allowable shear strength, and the maximum shear. (Express your answers to three significant figures.) Mu = OvVn = ft-kip kips kips Vu = Beam is -Select- b. Use ASD. Calculate the required moment strength, the allowable shear strength, and the maximum shear. (Express your answers to three significant figures.) Ma = Vn/b - Va = Beam is -Select- ft-kip kips kipsarrow_forward
- Determine the smallest value of yield stress Fy, for which a W-, M-, or S-shape from the list below will become slender. bf/2tfh/tw Shape W12 × 72 8.99 22.6 W12 × 26 8.54 47.2 M4 × 6 11.9 22.0 M12 x 11.8 6.81 62.5 M6 × 4.4 5.39 47.0 S24 × 80 4.02 41.4 S10 × 35 5.03 13.4 (Express your answer to three significant figures.) Fy = ksi To which shape does this value apply? -Select- ✓arrow_forwardCompute the nominal shear strength of an M12 × 11.8 of A572 Grade 60 steel (Fy = 60 ksi). For M12 x 11.8: d = 12 in., tw = 0.177 in., h/tw = 62.5. Vn = kipsarrow_forwardA flexural member is fabricated from two flange plates 1/2 × 71/2 and a web plate 3/8 × 19. The yield stress of the steel is 50 ksi. a. Compute the plastic section modulus Z and the plastic moment Mp with respect to the major principal axis. (Express your answers to three significant figures.) Z = Mp = in. 3 ft-kips b. Compute the elastic section modulus S and the yield moment My with respect to the major principal axis. (Express your answers to three significant figures.) S = My = in.3 ft-kipsarrow_forward
- = 65 ksi. A W16×36 of A992 steel has two holes in each flange for 7/8-inch-diameter bolts. For A992 steel: Fy = 50 ksi, Fu For a W16×36: bƒ = 6.99 in., tƒ = 0.430 in., Z = 64.0 in.³ and Sx = 56.5 in.³ a. Assuming continuous lateral support, verify that the holes must be accounted for and determine the nominal flexural strength. (Express your answer to three significant figures.) Mn = ft-kips b. What is the percent reduction in strength? (Express your answer to three significant figures.) Reduction = %arrow_forwardFind the reinforcements for the mid span and supports for an interior 9 in. thick slab (S-2) in thefloor from Problem 1. Ignore the beams and assume that the slab is supported by columns only (i.e.a flat plate). Sketch the slab and show the reinforcements including the shrinkage andtemperature reinforcement steel. Use f c’ = 4,000 psi and f y = 60,000 psi.NOTE: Problem 3 requires additional column placements at locations such as C and D. The stripof slab between these two columns will behave as a beam support to the one-way slab (with 10 ft.span). Problem 1. The figures below shows the framing plan and section of a reinforced concrete floor system.Floor beams are shown as dotted lines. The weight of the ceiling and floor finishing is 6 psf,that of the mechanical and electrical systems is 7 psf, and the weight of the partitions is 180psf. The floor live load is 105 psf. The 7 in. thick slab exterior bay (S-1) is reinforced with #5rebars @ 10 in. o.c. as the main positive…arrow_forward1- A study of freeway flow at a particular site has resulted in a calibrated speed-density relationship, as follows u = 57.5(10.008k) a) Find the free-flow speed and jam density b) Derive the equations describing flow versus speed and flow versus density c) Determine the capacity of the road 2- A rural freeway has a demand volume of 6750 v/hr. It has four 3.4 m lanes in each direction. The traffic stream is comprised of 8% heavy vehicles and a PHF of 0.94. The terrain is rolling throughout the segment. What is the level of service for the facility? What is the capacity? 3- For an urban freeway, how many 3.6 m lanes in each direction are needed to achieve LOS C on a freeway with a peak hour traffic volume of 5725 v/hr and with a PHF = 0.967 The traffic stream is comprised of 11% heavy vehicles and the location is level terrain.arrow_forward
- Note: Provide a clear, step-by-step simplified handwritten solution (with no extra explanations) that is entirely produced by hand without any AI help. I require an expert-level answer, and I will assess it based on the quality and accuracy of the work, referring to the attached image for additional guidance. Make sure every detail is carefully verified for correctness before you submit. Thanks!.arrow_forwardExample 3 Design a rectangular reinforced concrete beam having a 6 m simple span. A service dead load of 25 kN/m (not including the beam weight) and a service live load 10kn/m are to be supported. use f'c = 25 MPa and fy = 420MPaarrow_forwardNote:arrow_forward
 Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning



