
(a)
Interpretation:
The structures of the
Concept introduction:
The Wilkinson’s Catalyst is a common name of coordination compound
Answer to Problem 18.15P
The structures of the transition-metal complexes involved in each of the given mechanistic step are shown below.
1. The oxidative addition reaction is shown below.
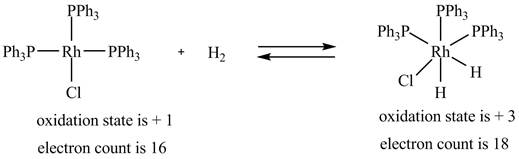
2. The ligand substitution of one
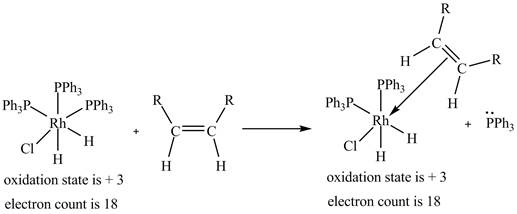
3. 1, 2-insertion of alkene into a
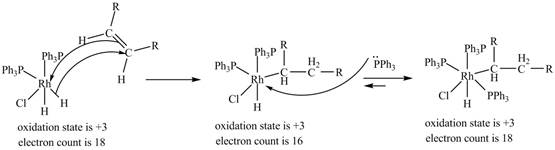
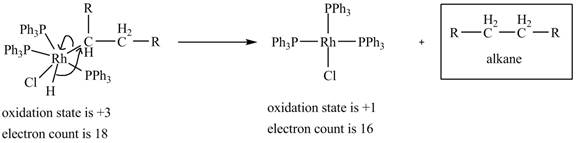
4. Reductive elimination of the
Explanation of Solution
The general formula for the calculation of electron count in a given formula is shown below.
The number of valence electrons present in rhodium is
1. In oxidative addition reaction, the central metal atom gets oxidized with the addition of two ligands and there is an increase in electron count at the central metal atom.
The oxidative addition reaction is shown below.
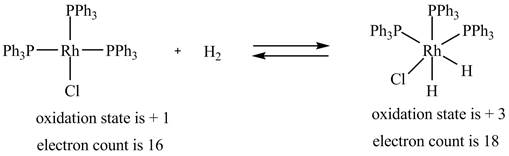
Figure 1
The electron count in
The electron count in
2. The ligand substitution reaction of one
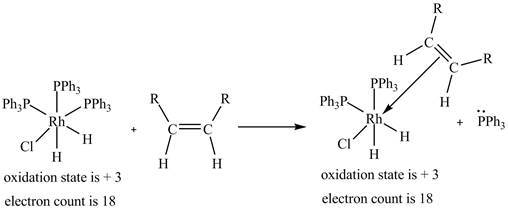
Figure 2
The electron count in
The electron count in
3. 1, 2-insertion of alkene into a
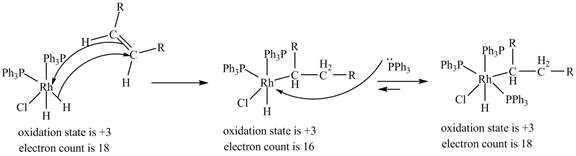
Figure 3
The electron count in
The electron count in
The electron count in
4. Reductive elimination of the alkane product to generate the catalyst is shown below.
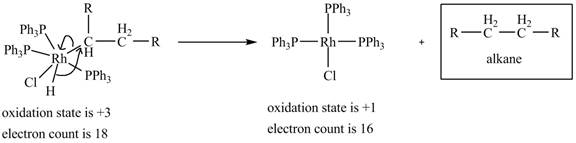
Figure 4
The electron count in
The electron count in
The catalytic hydrogenation of alkene by wilkinson’s catalyst and electron count is shown in Figure 1, 2, 3 and 4.
(b)
Interpretation:
The stereochemistry of the product if
Concept introduction:
The complex that follows
Answer to Problem 18.15P
The reaction between cis-alkene with the deuterium substituted wilkinson’s catalyst is shown below.
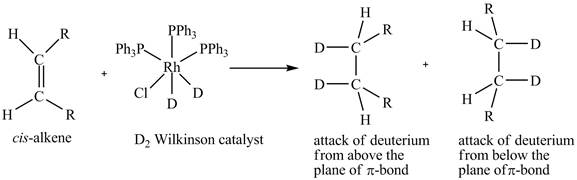
This shows syn-addition of deuterium on alkene.
Explanation of Solution
Reduction of cis-alkene with the deuterium substituted Wilkinson’s catalyst.
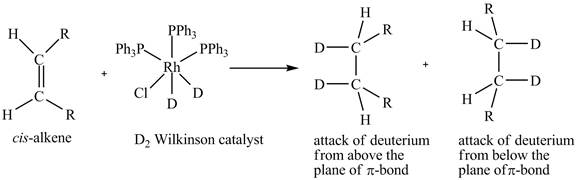
Figure 5
In the reduction of cis-alkene with the deuterium substituted Wilkinson’s catalyst. Hydrogen added on Wilkinson’s catalyst for hydrogenation of alkene is replaced by deuterium. The alkene is present in the plane of the paper, the deuterium can attack the alkene either from below the plane or above the plane.
Therefore, this shows that syn-addition of deuterium also takes place.
The reaction in Figure 5 shows that syn addition of hydrogen takes place even when it is substituted by deuterium.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Hi, I need your help with the drawing, please. I have attached the question along with my lab instructions. Please use the reaction from the lab only, as we are not allowed to use outside sources. Thank you!arrow_forwardHi, I need your help i dont know which one to draw please. I’ve attached the question along with my lab instructions. Please use the reaction from the lab only, as we are not allowed to use outside sources. Thank you!arrow_forward5. Write the formation reaction of the following complex compounds from the following reactants: 6. AgNO₃ + K₂CrO₂ + NH₄OH → 7. HgNO₃ + excess KI → 8. Al(NO₃)₃ + excess NaOH →arrow_forward
- Indicate whether the product formed in the reaction exhibits tautomerism. If so, draw the structure of the tautomers. CO₂C2H5 + CH3-NH-NH,arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction N-(cyclohex-1-en-1-yl)-1-(pyrrolidino) reacts with CH2=CHCHO, heat, H3O+arrow_forwardDraw the starting material that would be needed to make this product through an intramolecular Dieckmann reactionarrow_forward
- Draw the major product of this reaction. Nitropropane reacts + pent-3-en-2-one reacts with NaOCH2CH3, CH3CHOHarrow_forwardIndicate whether the product formed in the reaction exhibits tautomerism. If so, draw the structure of the tautomers. OC2H5 + CoHs-NH-NH,arrow_forwardExplain how substitutions at the 5-position of barbituric acid increase the compound's lipophilicity.arrow_forward
- Explain how substitutions at the 5-position of phenobarbital increase the compound's lipophilicity.arrow_forwardName an interesting derivative of barbituric acid, describing its structure.arrow_forwardBriefly describe the synthesis mechanism of barbituric acid from the condensation of urea with a β-diketone.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





