
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product on reaction of
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one
Answer to Problem 18.46AP
No product is formed on reaction of
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
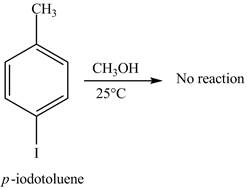
Figure 1
Aryl iodides cannot undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction. Aryl iodides neither undergo
There is no product formed on reaction of
(b)
Interpretation:
The product on reaction of
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron rich chemical species that contains negative charge or lone pair of electrons are known as nucleophile. In nucleophilc acyl substitution reaction, nucleophile takes the position of leaving group.
Answer to Problem 18.46AP
No product is formed on reaction of
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
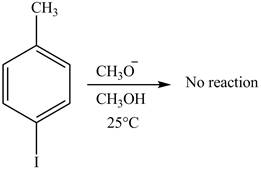
Figure 2
Aryl iodides cannot undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction. Aryl iodides neither undergo
There is no product formed on reaction of
(c)
Interpretation:
The product on reaction of
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron rich chemical species that contains negative charge or lone pair of electrons are known as nucleophile. In nucleophilc acyl substitution reaction, nucleophile takes the position of leaving group.
Answer to Problem 18.46AP
No product is formed on reaction of
Explanation of Solution
The product on reaction of
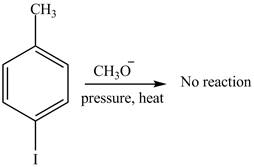
Figure 3
Aryl iodides cannot undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction. Aryl iodides neither undergo
There is no product formed on reaction of
(d)
Interpretation:
The product on reaction of
Concept introduction:
Grignard reagents are
Answer to Problem 18.46AP
The product on reaction of
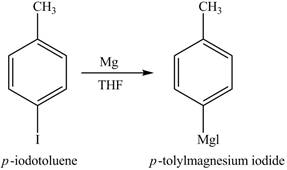
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
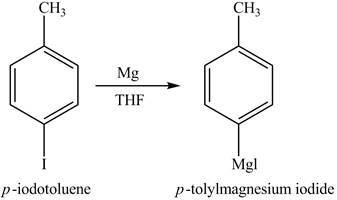
Figure 4
In the above reaction, magnesium gets inserted in the carbon-halogen bond to form a Grignard reagent. THF is used as the reaction should be done in anhydrous and inert condition. Therefore, the product formed on reaction of
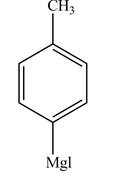
Figure 5
The reaction of
(e)
Interpretation:
The product on reaction of the product formed in part (d) with
Concept introduction:
Stille reaction is an example of coupling reaction. In Stille reaction, the triflate reacts with trimethylstannane in presence of
Answer to Problem 18.46AP
The product on reaction of the product formed in part (d) with
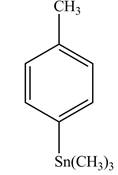
Explanation of Solution
The product formed in part (d) is shown below.
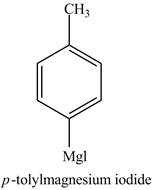
Figure 5
The reaction of the product formed in part (d) with
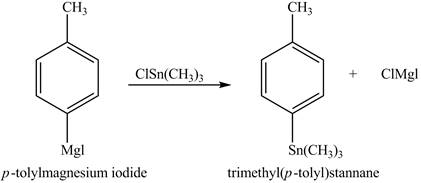
Figure 6
In the above reaction, a stannane compound is formed on reaction of a Grignard reagent with
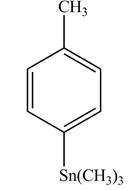
Figure 7
The product on reaction of the product formed in part (d) with
(f)
Interpretation:
The product on reaction of
Concept introduction:
Alkyl lithium is an organolithium reagent. It contains carbon-lithium bond. It is used in
Answer to Problem 18.46AP
The product on reaction of
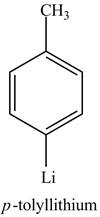
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
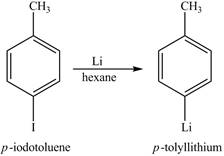
Figure 8
The above reaction is known as lithium-halogen exchange reaction. The reaction occurs under inert conditions. In this reaction, two moles of lithium react with
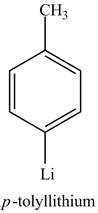
Figure 9
The product on reaction of
(g)
Interpretation:
The product on reaction of
Concept introduction:
The treatment of an organic halide with an
Answer to Problem 18.46AP
The product on reaction of
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
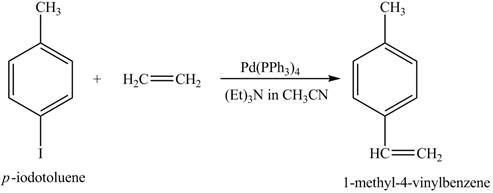
Figure 10
In the above reaction a coupled product is formed. The coupling takes place between ethene and
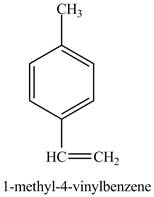
Figure 11
The product on reaction of
(h)
Interpretation:
The product on reaction of product of part (e) with phenyl triflate, excess
Concept introduction:
Stille reaction is an example of coupling reaction. In Stille reaction, the triflate reacts with trimethylstannane in presence of
Answer to Problem 18.46AP
The product on reaction of product of part (e) with phenyl triflate, excess
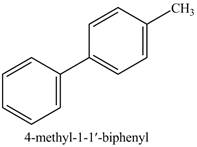
Explanation of Solution
The product formed in part (e) is shown below.
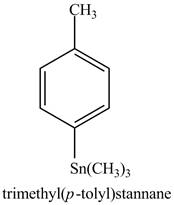
Figure 7
The reaction of above compound with phenyl triflate, excess
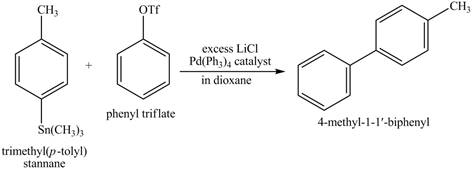
Figure 12
The above reaction is an example of Stille coupling reaction. In this reaction a triflate reacts with stannane compound in presence of
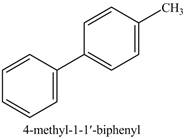
Figure 13
The product on reaction of product of part (e) with phenyl triflate, excess
(i)
Interpretation:
The product on reaction of
Concept introduction:
The Suzuki coupling reaction is a reaction in which an aryl or vinylic boronic acid is coupled to an aryl or vinylic iodide or bromide. It is a
Answer to Problem 18.46AP
The product on reaction of
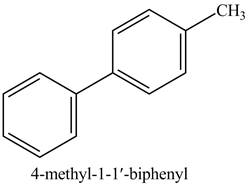
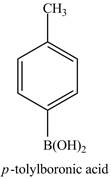
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
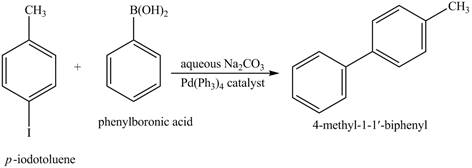
Figure 14
In the above reaction,
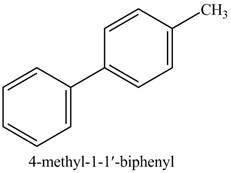
Figure 15
The product on reaction of
(j)
Interpretation:
The product on reaction of product of part (d) with
Concept introduction:
The Suzuki coupling reaction in which an aryl or vinylic boronic acid is coupled to an aryl or vinylic iodide or bromide. It is a
Answer to Problem 18.46AP
The product of part (d) with
Explanation of Solution
The product of part (d) is shown below.
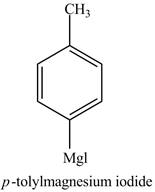
Figure 5
The reaction of product of part (d) with
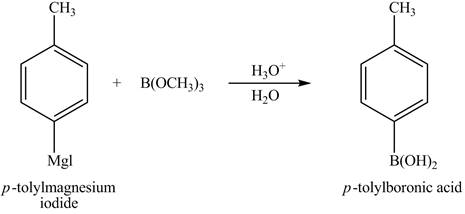
Figure 16
In the above reaction,
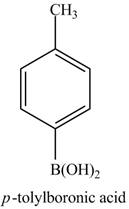
Figure 17
The product of part (d) with
(k)
Interpretation:
The product on reaction of product of part (j) with
Concept introduction:
The Suzuki coupling reaction in which an aryl or vinylic boronic acid is coupled to an aryl or vinylic iodide or bromide. It is a
Answer to Problem 18.46AP
The product on reaction of product of part (j) with
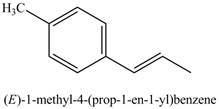
Explanation of Solution
The product of part (j) is shown below.
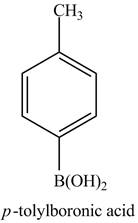
Figure 17
The reaction of product of part (j) with
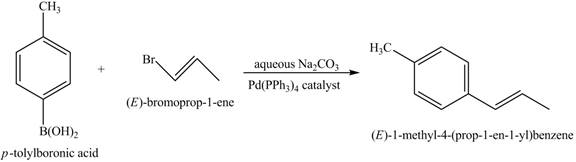
Figure 18
The above reaction is Suzuki coupling reaction. In this reaction,
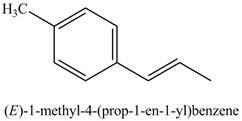
Figure 19
The product on reaction of product of part (j) with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- What are the major products of the following reaction? Please provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the reaction proceeds.arrow_forwardWhat are the major products of the following enolate alkylation reaction? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing as to how the reaction proceeds.arrow_forwardA block of zinc has an initial temperature of 94.2 degrees celcius and is immererd in 105 g of water at 21.90 degrees celcius. At thermal equilibrium, the final temperature is 25.20 degrees celcius. What is the mass of the zinc block? Cs(Zn) = 0.390 J/gxdegrees celcius Cs(H2O) = 4.18 J/gx degrees celcusarrow_forward
- Potential Energy (kJ) 1. Consider these three reactions as the elementary steps in the mechanism for a chemical reaction. AH = -950 kJ AH = 575 kJ (i) Cl₂ (g) + Pt (s) 2C1 (g) + Pt (s) Ea = 1550 kJ (ii) Cl (g)+ CO (g) + Pt (s) → CICO (g) + Pt (s) (iii) Cl (g) + CICO (g) → Cl₂CO (g) Ea = 2240 kJ Ea = 2350 kJ AH = -825 kJ 2600 2400 2200 2000 1800 1600 1400 1200 1000 a. Draw the potential energy diagram for the reaction. Label the data points for clarity. The potential energy of the reactants is 600 kJ 800 600 400 200 0 -200- -400 -600- -800- Reaction Progressarrow_forwardCan u help me figure out the reaction mechanisms for these, idk where to even startarrow_forwardHi, I need your help with the drawing, please. I have attached the question along with my lab instructions. Please use the reaction from the lab only, as we are not allowed to use outside sources. Thank you!arrow_forward
- Hi, I need your help i dont know which one to draw please. I’ve attached the question along with my lab instructions. Please use the reaction from the lab only, as we are not allowed to use outside sources. Thank you!arrow_forward5. Write the formation reaction of the following complex compounds from the following reactants: 6. AgNO₃ + K₂CrO₂ + NH₄OH → 7. HgNO₃ + excess KI → 8. Al(NO₃)₃ + excess NaOH →arrow_forwardIndicate whether the product formed in the reaction exhibits tautomerism. If so, draw the structure of the tautomers. CO₂C2H5 + CH3-NH-NH,arrow_forward
- Draw the major product of this reaction N-(cyclohex-1-en-1-yl)-1-(pyrrolidino) reacts with CH2=CHCHO, heat, H3O+arrow_forwardDraw the starting material that would be needed to make this product through an intramolecular Dieckmann reactionarrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Nitropropane reacts + pent-3-en-2-one reacts with NaOCH2CH3, CH3CHOHarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
