
Concept explainers
Azo dyes are organic dyes that are used for many applications, such as the coloring of fabrics. Many azo dyes are derivatives of the organic substance azobenzene, Cl2H10N2. A closely related substance is hydrazobenzene, Cl2H12N2. The Lewis structures of these two substances are
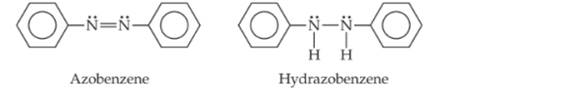
(Recall the shorthand notation used for benzene.)
a. What is the hybridization at the N atom in each of the substances?
b. How many unhybridized atomic orbitals are there on the N and the C atoms in each of the substances?
c. Predict the N-N-C angles in each of the substances.
d. Azobenzene is said to have greater delocalization of its p electrons than hydrazobenzene. Discuss this statement in light of your answers to (a) and (b).
e. All the atoms of azobenzene lie in one plane, whereas those of hydrazobenzene do not. Is this observation consistent with the statement in part (d)?
f. Azobenzene is an intense red-orange color, whereas hydrazobenzene is nearly colorless. Which molecule would be a better one to use in a solar energy conversion device? (See the "Chemistry Put to Work" box for more information about solar cells.)
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 17 Solutions
Chemistry: The Central Science (13th Edition)
- ASP please....arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardConsider the structure of 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane. Part 1 of 2 Draw the Newman projection for the anti conformation of 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane, viewed down the C1-C2 bond. ✡ ぬ Part 2 of 2 H H F Br H H ☑ Draw the Newman projection for the gauche conformation of 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane, viewed down the C1-C2 bond. H F Br H Harrow_forward
- Please help me answer this question. I don't understand how or where the different reagents will attach and it's mostly due to the wedge bond because I haven't seen a problem like this before. Please provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how it can happen and what the final product will look like.arrow_forwardWhich of the following compounds is the most acidic in the gas phase? Group of answer choices H2O SiH4 HBr H2Sarrow_forwardWhich of the following is the most acidic transition metal cation? Group of answer choices Fe3+ Sc3+ Mn4+ Zn2+arrow_forward
- Based on the thermodynamics of acetic acid dissociation discussed in Lecture 2-5, what can you conclude about the standard enthalpy change (ΔHo) of acid dissociation for HCl? Group of answer choices You cannot arrive at any of the other three conclusions It is a positive value It is more negative than −0.4 kJ/mol It equals −0.4 kJ/molarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP URGENT!arrow_forwardDraw the skeletal structure corresponding to the following IUPAC name: 7-isopropyl-3-methyldecanearrow_forward
- Which of the following oxyacids is the weakest? Group of answer choices H2SeO3 Si(OH)4 H2SO4 H3PO4arrow_forwardAdd conditions above and below the arrow that turn the reactant below into the product below in a single transformation. + More... If you need to write reagents above and below the arrow that have complex hydrocarbon groups in them, there is a set of standard abbreviations you can use. More... T H,N NC Datarrow_forwardIndicate the order of basicity of primary, secondary and tertiary amines.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,
Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,





