
Concept explainers
Three recent college graduates have formed a
a. Draw the precedence diagram.
b. What is the probability that the project can be completed in 24 days or less? In 21 days or less?
c. Suppose it is now the end of the seventh day and that activities A and B have been completed while activity D is 50 percent completed. Time estimates for the completion of activity D are 5, 6, and 7. Activities C and H are ready to begin. Determine the probability of finishing the project by day 24 and the probability of finishing by day 21.
d. The partners have decided that shortening the project by two days would be beneficial, as long as it doesn’t cost more than about $20,000. They have estimated the daily crashing costs for each activity in thousands, as shown in the following table. Which activities should be crashed, and what further analysis would they probably want to do?
a)
To draw: A precedence diagram.
Answer to Problem 7P
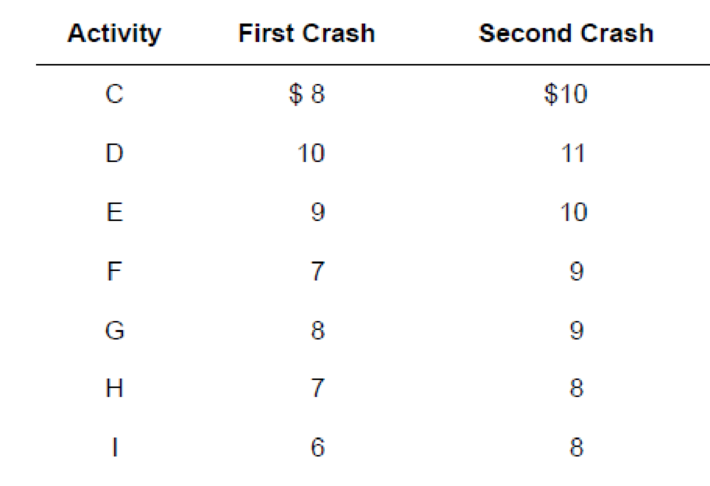
Precedence diagram:
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Activity | Immediate Predecessor | Optimistic time | Most likely time | Pessimistic time |
| A | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| B | 8 | 8 | 11 | |
| C | A | 6 | 8 | 11 |
| D | 9 | 12 | 15 | |
| E | C | 5 | 6 | 9 |
| F | D | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| G | F | 2 | 3 | 7 |
| H | B | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| I | H | 5 | 7 | 8 |
| End | E, G, I |
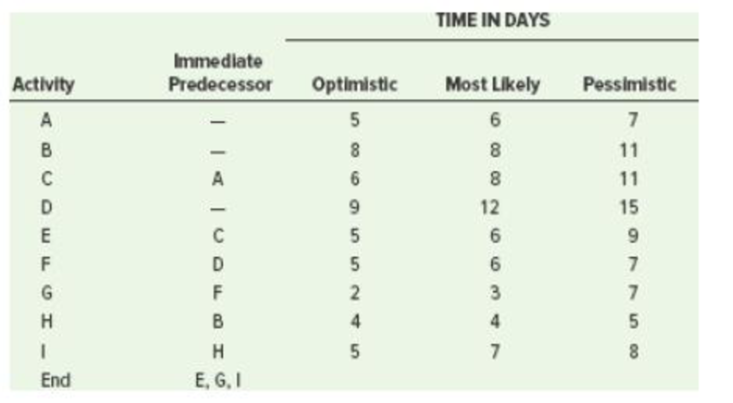
| Activity | First crash | Second crash |
| C | $ 8.00 | $ 10.00 |
| D | $ 10.00 | $ 11.00 |
| E | $ 9.00 | $ 10.00 |
| F | $ 7.00 | $ 9.00 |
| G | $ 8.00 | $ 9.00 |
| H | $ 7.00 | $ 8.00 |
| I | $ 6.00 | $ 8.00 |
Precedence diagram:

The precedence diagram is drawn from the first task till the last task. The activities are placed from left to right. The directions are represented with arrows to indicate the relationship between activities. The arrows are represented with the activity name.
b)
To determine: The probability at which the projected can be completed in 24 days or less and 21 days or less.
Answer to Problem 7P
24 days or less = 0.9686
21 days or less = 0.2350
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Activity | Immediate Predecessor | Optimistic time | Most likely time | Pessimistic time |
| A | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| B | 8 | 8 | 11 | |
| C | A | 6 | 8 | 11 |
| D | 9 | 12 | 15 | |
| E | C | 5 | 6 | 9 |
| F | D | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| G | F | 2 | 3 | 7 |
| H | B | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| I | H | 5 | 7 | 8 |
| End | E, G, I |
| Activity | First crash | Second crash |
| C | $ 8.00 | $ 10.00 |
| D | $ 10.00 | $ 11.00 |
| E | $ 9.00 | $ 10.00 |
| F | $ 7.00 | $ 9.00 |
| G | $ 8.00 | $ 9.00 |
| H | $ 7.00 | $ 8.00 |
| I | $ 6.00 | $ 8.00 |
Formula to calculate expected time and variance:
Calculation of expected time and variance:
| Activity | Optimistic time | Most likely time | Pessimistic time | Expected time | Standard deviation | Variance |
| A | B | C | (A+(4*B)+C)/6 | (C-A)/6 | (C-A)^2/6^2 | |
| A | 5 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 0.333 | 0.111 |
| B | 8 | 8 | 11 | 8.5 | 0.500 | 0.250 |
| C | 6 | 8 | 11 | 8.17 | 0.833 | 0.694 |
| D | 9 | 12 | 15 | 12 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| E | 5 | 6 | 9 | 6.33 | 0.667 | 0.444 |
| F | 5 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 0.333 | 0.111 |
| G | 2 | 3 | 7 | 3.5 | 0.833 | 0.694 |
| H | 4 | 4 | 5 | 4.17 | 0.167 | 0.028 |
| I | 5 | 7 | 8 | 6.83 | 0.500 | 0.250 |
Calculation of expected duration, variance and standard deviation for each path:
A-C-E:
D-F-G:
B-H-I:
Calculation of z value for all paths:
Formula:
24 days or less:
A-C-E:
Since z value is greater than +3.00, probability of completion is 1.00.
D-F-G:
From the standard normal distribution table,
The probability value for (z = 1.86) is 0.9686.
B-H-I:
Since z value is greater than +3.00, probability of completion is 1.00.
Probability of completion in 24 days or less:
The probability at which the project can be completed in 24 days or less is 0.9686.
21 days or less:
A-C-E:
From the standard normal distribution table,
The probability value for (z = 0.45) is 0.6736.
D-F-G:
From the standard normal distribution table,
The probability value for (z = -0.37) is 0.3557.
B-H-I:
From the standard normal distribution table,
The probability value for (z = 2.07) is 0.9808.
Probability of completion in 21 days or less:
The probability at which the project can be completed in 21 days or less is 0.2350.
c)
To determine: The probability of completing the project by day 24 and day 21.
Answer to Problem 7P
Day 24 = 0.9328
Day 21 = 0.0186
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
- At the end of 7th day activities A and B are completed and D is 50% completed.
- Time estimates of activity D completion are 5, 6 and 7.
- Activities C and H are ready to begin.
| Activity | Immediate Predecessor | Optimistic time | Most likely time | Pessimistic time |
| A | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| B | 8 | 8 | 11 | |
| C | A | 6 | 8 | 11 |
| D | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| E | C | 5 | 6 | 9 |
| F | D | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| G | F | 2 | 3 | 7 |
| H | B | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| I | H | 5 | 7 | 8 |
| End | E, G, I |
| Activity | First crash | Second crash |
| C | $ 8.00 | $ 10.00 |
| D | $ 10.00 | $ 11.00 |
| E | $ 9.00 | $ 10.00 |
| F | $ 7.00 | $ 9.00 |
| G | $ 8.00 | $ 9.00 |
| H | $ 7.00 | $ 8.00 |
| I | $ 6.00 | $ 8.00 |
Formula to calculate expected time and variance:
Calculation of expected time and variance:
| Activity | Optimistic time | Most likely time | Pessimistic time | Expected time | Standard deviation | Variance |
| A | B | C | (A+(4*B)+C)/6 | (C-A)/6 | (C-A)^2/6^2 | |
| A | 5 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 0.333 | 0.111 |
| B | 8 | 8 | 11 | 8.5 | 0.500 | 0.250 |
| C | 6 | 8 | 11 | 8.17 | 0.833 | 0.694 |
| D | 5 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 0.333 | 0.111 |
| E | 5 | 6 | 9 | 6.33 | 0.667 | 0.444 |
| F | 5 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 0.333 | 0.111 |
| G | 2 | 3 | 7 | 3.5 | 0.833 | 0.694 |
| H | 4 | 4 | 5 | 4.17 | 0.167 | 0.028 |
| I | 5 | 7 | 8 | 6.83 | 0.500 | 0.250 |
Revised project diagram:
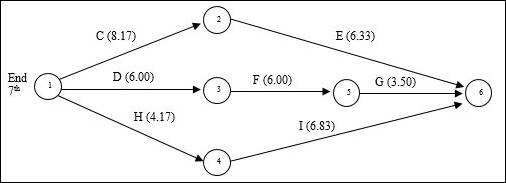
Calculation of expected duration, variance and standard deviation for each path:
C-E:
D-F-G:
H-I:
Calculation of z value for all paths:
Formula:
24 days or less:
C-E:
From the standard normal distribution table,
The probability value for (z = 2.34) is 0.9904.
D-F-G:
From the standard normal distribution table,
The probability value for (z = 1.57) is 0.9418.
H-I:
Since z value is greater than +3.00, probability of completion is 1.00.
Probability of completion in 24 days or less:
The probability at which the project can be completed in 24 days is 0.9328.
21 days or less:
C-E:
From the standard normal distribution table,
The probability value for (z = -0.47) is 0.3192.
D-F-G:
From the standard normal distribution table,
The probability value for (z = -1.57) is 0.0582.
H-I:
Since z value is greater than +3.00, probability of completion is 1.00.
Probability of completion in 21 days or less:
The probability at which the project can be completed in 21 days is 0.0186.
d)
To determine: The activities that should be crashed and further analysis.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
- The partners want to shorten the project by 2 days as long as the cost is not more than $20,000.
| Activity | Immediate Predecessor | Optimistic time | Most likely time | Pessimistic time |
| A | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| B | 8 | 8 | 11 | |
| C | A | 6 | 8 | 11 |
| D | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| E | C | 5 | 6 | 9 |
| F | D | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| G | F | 2 | 3 | 7 |
| H | B | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| I | H | 5 | 7 | 8 |
| End | E, G, I |
| Activity | First crash | Second crash |
| C | $ 8.00 | $ 10.00 |
| D | $ 10.00 | $ 11.00 |
| E | $ 9.00 | $ 10.00 |
| F | $ 7.00 | $ 9.00 |
| G | $ 8.00 | $ 9.00 |
| H | $ 7.00 | $ 8.00 |
| I | $ 6.00 | $ 8.00 |
Paths and expected duration:
| Paths | Expected Duration |
| C-E | 21.50 |
| D-F-G | 22.50 |
| H-I | 18.00 |
The critical path is D – F – G.
The activities are crashed based on the cost of crash given.
| Activity | Cost |
| F | $7 |
| G | $8 |
| D | $10 |
Step 1:
Activity F has the lowest crashing cost ($7,000) and will be crashed first for 1 day. The expected duration of D-F-G will be 21.50 days.
Step 2:
| Path | Expected Duration |
| C-E | 21.50 |
| D-F-G | 21.50 |
| H-I | 18.00 |
Now there are two critical paths C-E and D-F-G.
The critical activities are arranged in the order of low crash costs.
| Path | Activity | Cost |
| C-E | C | $8 |
| F | $9 |
| Path | Activity | Cost |
| D-F-G | D | $8 |
| F | $9 | |
| G | $10 |
One activity in each path is chosen to crash.
Activity C is crashed for 1 day since it has the lowest crashing cost ($8,000) on path C-E. The expected duration of path C-E is now 20.50 days.
Activity G is crashed for 1 day since it has the lowest crashing cost ($8,000) on path D-F-G. The expected duration of path D-F-G is now 20.50 days.
Calculation of total crashing cost:
The total cost of crashing is over the budget of $20,000 ($23,000 > $20,000). Hence, the partners will have to determine if crashing the project by 1 day or 2 days is really beneficial or not.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Operations Management (McGraw-Hill Series in Operations and Decision Sciences)
- How can a local tourism and hospitality company successfully enter international markets?arrow_forwardHow was Circuit City Company collapsed? And what was the sequence of time and events or problems? How to solve the issues, and could you help identify positions or titles. Sanitize all names and use only fictitious data. What is synthesize the qualitative research methodology of Case Study research? Please give some examples. How to use the practical of Lean Six Sigma to develop a business-facing DMAIC-based case studyarrow_forwardBUSINESS MODEL CANVAS: U.S ARMY key partners: Key activities: Key Resources: Value Propositions: Buy-in & Support: Deployment: Benficiaries: Mission budget/cost: Mission Achievement/ Impact factors: Please at least 4 for each categoryarrow_forward
- how you would best conduct a performance evaluation meeting with a subordinate (where an employee would receive their performance evaluation from their supervisor). Importantly, detail how a supervisor can best gain the concurrence from an employee on the evaluation itself, and to ensure that the employee’s performance will be modified as a result of appraisal meeting.arrow_forwardI need answer typing clear urjent no chatgpt used pls i will give 5 Upvotes.arrow_forwardassume that you are police commander which leads and supervises the department’s internal affairs division. Your goal is to reduce civilian complainants against personnel in the department. Using what you have learned and at least three scholarly sources, document two changes you see the department can implement, whether it be training, planning, mitigating, and resolving, to improve police/community relations.arrow_forward
- Ness Engineering is a private limited company mainly engaged in the continuous production and assembly of domestic products. The annual turnover is $900,000,000. The largest area of expenditure is raw materials and components where the annual spend is approximately $450,000,000. The Managing Director, Bill, considers that profit margins are too small and has asked you to suggest how profitability might be increased. Bill suggests that this might be done by appointing additional sales staff and by an advertising campaign, which would, hopefully, increase turnover and thereby reduce overhead cost per item. You find that purchasing is little more than a post-office function. Specifications are received from the design or user departments and sent either to supplies designated by the directors or to the supplier providing the cheapest quotation. The company does, in fact, deal with many suppliers and issues many orders for low-cost items. All purchasing is done by manual means. None of the…arrow_forwardThe oasis outpost of Abu Ilan, in the heart of the Negev desert, has a population of 20 Bedouin tribesmen and 20 Farima tribesmen. El Kamin, a nearby oasis, has a population of 32 Bedouins and 8 Farima. A lost Israeli soldier, accidentally separated from his army unit, is wandering through the desert and arrives at the edge of one of the oases. The soldier has no idea which oasis he has found, but the first person he spots at a distance is a Bedouin. 1. What is the probability that he wandered into Abu Ilan? 2. What is the probability that he is in El Kamin?arrow_forward2-22 The lost Israeli soldier mentioned in Problem 2-21 decides to rest for a few minutes before entering the desert oasis he has just found. Closing his eyes, he dozes off for 15 minutes, wakes, and walks toward the center of the oasis. The first person he spots this time he again recognizes as a Bedouin. What is the posterior probability that he is in El Kamin?*Note* 2-21 The oasis outpost of Abu Ilan, in the heart of the Negev desert, has a population of 20 Bedouin tribesmen and 20 Farima tribesmen. El Kamin, a nearby oasis, has a population of 32 Bedouins and 8 Farima. A lost Israeli soldier, accidentally separated from his army unit, is wandering through the desert and arrives at the edge of one of the oases. The soldier has no idea which oasis he has found, but the first person he spots at a distance is a Bedouin. What is the probability that he has wandered into Abu Ilan? What is the probability that he is in El Kamin?arrow_forward
- Hello, please make an excel of this. Show all the cells thanks. some replied with a paper answer thank you I just cant understand the way the did it. Can someone show me all screenshots o fthis problem solved and in excel? i need to solver too for the constraints. I seen multiple times across other platforms that one of the chairs optimal solutions is 0 but they both have to be higher than 1 The Heinrich Company manufactures two types of plastic hangerracks (Foldaways and Straightaways) especially suited for mountingnear clothes dryers. Because permanent press clothing must be hungon hangers immediately after removal from the dryer, these items havebeen especially popular. However, there is some concern that thePreppie movement (popularized by its own handbook) will extinguishpolyester clothing; Heinrich is terribly interested in doing the best withthe resources it has while its products are still in demand. The firsttype of hanger rack, the Foldaway, requires 10 ounces of…arrow_forwardReview the Profit Ratio by Product chart again. What information is uncovered when the data is less aggregated than the data in Profit Ratio by Category chart?arrow_forwardWhat is the correlation between Measure A and Measure B in this example?arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Management, Loose-Leaf VersionManagementISBN:9781305969308Author:Richard L. DaftPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Management, Loose-Leaf VersionManagementISBN:9781305969308Author:Richard L. DaftPublisher:South-Western College Pub


