
CHEMISTRY THE CENTRAL SCIENCE >EBOOK<
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780136873891
Author: Brown
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 17, Problem 33E
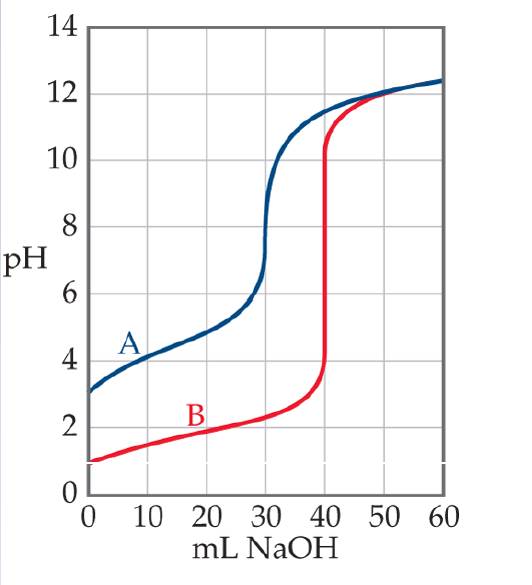
The accompanying graph shows the titration curves for two monoprotic acids.
a. Which curve is that of a strong acid?
b. What is the approximate pH at the equivalence point of each titration?
c. 40.0 mL of each acid was titrated with a 0.100 M base. Which acid is more concentrated?
d. Estimate the pKa of the weak acid.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Two 25.0-mL samples, one 0.100 M HCl and the other 0.100 M HF, are titrated with 0.200 M KOH.a. What is the volume of added base at the equivalence point for each titration?b. Is the pH at the equivalence point for each titration acidic, basic, or neutral?c. Which titration curve has the lower initial pH?d. Sketch each titration curve.
Two 20.0-mL samples, one 0.200 M KOH and the other
0.200 M CH,NH2, are titrated with 0.100 M HI.
a. What is the volume of added acid at the equivalence point
for each titration?
b. Is the pH at the equivalence point for each titration acidic,
basic, or neutral?
c. Which titration curve has the lower initial pH?
d. Sketch each titration curve.
Consider the titration of 20.00 mL of 0.1145 M sodium azide (NaN3) with 0.1250 M HCl. The Ka of HN3 is 2.2 x 10 –5 .
a. What is the pH after 15.00 mL of HCl have been added?
b. What is the pH at the equivalence point?
c. What is the pH 2.00 mL past the equivalence point volume?
Chapter 17 Solutions
CHEMISTRY THE CENTRAL SCIENCE >EBOOK<
Ch. 17.1 - For the generic equilibrium HA(aq)H+(aq)+A(aq) ,...Ch. 17.1 - Practice Exercise 2 Calculate the pH of a solution...Ch. 17.1 - Calculate the concentration of the lactate ion in...Ch. 17.1 - Practice Exercise 2 Calculate the format ion...Ch. 17.2 - Practice Exercise 1 If the pH of a buffer solution...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.3.2PECh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.4.1PECh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.4.2PECh. 17.2 - Calculate the number of grams of ammonium chloride...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.5.2PE
Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.6.1PECh. 17.2 - Determine The pH of the original buffer described...Ch. 17.3 - An acid-base titration is performed: 250.0 mL of...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.7.2PECh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.8.1PECh. 17.3 - Calculate the pH in the solution formed by adding...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.9.1PECh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.9.2PECh. 17.4 - Which of these expressions correctly expresses the...Ch. 17.4 - Prob. 17.10.2PECh. 17.4 - You add 10.0 grams of solid copper(II) phosphate,...Ch. 17.4 - Prob. 17.11.2PECh. 17.4 - Prob. 17.12.1PECh. 17.4 - Prob. 17.12.2PECh. 17.5 - Consider a saturated solution of the salt MA3, in...Ch. 17.5 - Prob. 17.13.2PECh. 17.5 - Prob. 17.14.1PECh. 17.5 - Prob. 17.14.2PECh. 17.5 - Prob. 17.15.1PECh. 17.5 - Prob. 17.15.2PECh. 17.6 - An insoluble salt MA has a Kap of 1.0 × 10-10. Two...Ch. 17.6 - Does a precipitate form when 0.050 L of 2.0 × 10-2...Ch. 17.6 - Under what conditions does an ionic compound...Ch. 17.6 - Prob. 17.17.2PECh. 17 - Prob. 1DECh. 17 - The following boxes represent aqueos solutions...Ch. 17 - Prob. 2ECh. 17 - Prob. 3ECh. 17 - Prob. 4ECh. 17 - Prob. 5ECh. 17 - Prob. 6ECh. 17 - Prob. 7ECh. 17 - Prob. 8ECh. 17 - 17.9 The following graphs represent the behavior...Ch. 17 - Prob. 10ECh. 17 - 17.11 The graph below shows the solubility of a...Ch. 17 - 17.12 Three cations, Ni+2, Cu+2, and Ag+, are...Ch. 17 - Prob. 13ECh. 17 - Prob. 14ECh. 17 - Prob. 15ECh. 17 - Use information from Appendix D to calculate the...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17ECh. 17 - a. calculate the percent ionization of 0.125 M...Ch. 17 - Prob. 19ECh. 17 - 17.20 Which of the following solutions is a...Ch. 17 - Prob. 21ECh. 17 - Calculate the pH of a buffer that is 0.105n M in...Ch. 17 - Prob. 23ECh. 17 - A buffer is prepared by adding 10.0 g of ammonium...Ch. 17 - You are asked to prepare a pH = 3.00 buffer...Ch. 17 - You are asked to prepare an pH = 4.00 buffer...Ch. 17 - Prob. 27ECh. 17 - Prob. 28ECh. 17 - Prob. 29ECh. 17 - Prob. 30ECh. 17 - Prob. 31ECh. 17 - Prob. 32ECh. 17 - The accompanying graph shows the titration curves...Ch. 17 - Prob. 34ECh. 17 - 17.35 The samples of nitric and acetic acids shows...Ch. 17 - 17.36 Determine whether each of the following...Ch. 17 - Prob. 37ECh. 17 - Prob. 38ECh. 17 - Prob. 39ECh. 17 - Assume that 30.0 mL of a M solution of a week base...Ch. 17 - Prob. 41ECh. 17 - Prob. 42ECh. 17 - Prob. 43ECh. 17 - Prob. 44ECh. 17 - Prob. 45ECh. 17 - Consider the titration of 30.0 mL of 0.050 M NH3...Ch. 17 - Prob. 47ECh. 17 - Prob. 48ECh. 17 - 17.49 for each statement, incate whether it is...Ch. 17 - The solubility of two slighty soluble salts of...Ch. 17 - Prob. 51ECh. 17 - 17.52
a. true or false: solubility and...Ch. 17 - If the molar solubility CaF2 at 35 C is 1.24 *10-3...Ch. 17 - Prob. 54ECh. 17 - Prob. 55ECh. 17 - Prob. 56ECh. 17 - using calculate the molar solubility of AgBr in a....Ch. 17 - calculate the solubility of LaF3 in grams per...Ch. 17 - Prob. 59ECh. 17 - Consider a beaker containing a saturated solution...Ch. 17 - Calculate the solubility of Mn (OH) 2 in grams per...Ch. 17 - Calculate the molar solubility of Ni (OH) 2 when...Ch. 17 - 17.63 Which of the following salts will be...Ch. 17 - For each of the following slightly soluble salts,...Ch. 17 - Prob. 65ECh. 17 - Prob. 66ECh. 17 - Use values of Kap for Agl and Kf for Ag (CN) 2- to...Ch. 17 - Prob. 68ECh. 17 - Prob. 69ECh. 17 - Prob. 70ECh. 17 - Calculate the minimum pH needed to precipitate Mn...Ch. 17 - Prob. 72ECh. 17 - Prob. 73ECh. 17 - Prob. 74ECh. 17 - Prob. 75ECh. 17 - Prob. 76ECh. 17 - A solution containing several metal ions is...Ch. 17 - An unknown solid is entirely soluble in water. On...Ch. 17 - Prob. 79ECh. 17 - Prob. 80ECh. 17 - 17.81
Precipitation of the group 4 cautions of...Ch. 17 - Prob. 82ECh. 17 - Prob. 83AECh. 17 - Prob. 84AECh. 17 - Furoic acid (HC5H3O3) has a K value of 6.76 x 10-4...Ch. 17 - Prob. 86AECh. 17 - Equal quantities of 0.010 M solution of an acid HA...Ch. 17 - Prob. 88AECh. 17 - 17.89 A biochemist needs 750 ml of an acetic...Ch. 17 - A sample of 0.2140 g of an unknown monophonic acid...Ch. 17 - A sample of 0.1687 g of an unknown monoprotic acid...Ch. 17 - Prob. 92AECh. 17 - Prob. 93AECh. 17 - What is the pH of a solution made by mixing 0.30...Ch. 17 - Suppose you want to do a physiological experiment...Ch. 17 - Prob. 96AECh. 17 - Prob. 97AECh. 17 - For each pair of compounds, use Kap values to...Ch. 17 - Prob. 99AECh. 17 - Tooth enamel is composed of hydroxyapatite, whose...Ch. 17 - Salts containing the phosphate ion are added to...Ch. 17 - Prob. 102AECh. 17 - 17.103 The solubility –product constant for barium...Ch. 17 - Prob. 104AECh. 17 - Prob. 105AECh. 17 - A buffer of what pH is needed to give a Mg2+...Ch. 17 - The value of Kap for Mg3(AsO4)2 is 2.1 10-20 ....Ch. 17 - Prob. 108AECh. 17 - Prob. 109AECh. 17 - Prob. 110IECh. 17 - Prob. 111IECh. 17 - Prob. 112IECh. 17 - Prob. 113IECh. 17 - Prob. 114IECh. 17 - Prob. 115IECh. 17 - Prob. 116IECh. 17 - A concentration of 10-100 parts per billion (by...Ch. 17 - Prob. 118IECh. 17 - Prob. 119IECh. 17 - In nonaqueous solvents, it is possible to react HF...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The titration curves for two acids with the same base are shown on this graph. (a) Which is the curve for the weaker acid? Explain your choice. (b) Give the approximate pH at the equivalence point for the titration of each acid. (c) Explain why the pH at the equivalence point differs for each acid. (d) Explain why the starting pH values of the two acids differ. (e) Which indicator or indicators, phenolphthalein, bromthymol blue, or methyl red, could be used for the titration of Acid 1? For the titration of Acid 2? Explain your choices.arrow_forwardA 0.2481 M solution of KOH is used to titrate 30.00 mL of 0.269 M hydrobromic acid. Assume that volumes are additive. (a) Write a balanced net ionic equation for the reaction that takes place during the titration. (b) What are the species present at the equivalence point? (c) What volume of KOH is required to reach the equivalence point? (d) What is the pH of the solution 1. before any KOH is added? 2. halfway to the equivalence point? 3. at the equivalence point?arrow_forwardWhich of these buffers involving a weak acid HA has the greater resistance to change in pH? Explain your answer. (i) [HA] =0.100 M = [A] (ii) [HA] = 0.300 M = [A]arrow_forward
- The following plot shows the pH curves for the titrations of various acids by 0.10 M NaOH (all of the acids were 50.0-mL samples of 0.10 M concentration). a. Which pH curve corresponds to the weakest acid? b. Which pH curve corresponds to the strongest acid? Which point on the pH curve would you examine to see if this acid is a strong acid or a weak acid (assuming you did not know the initial concentration of the acid)? c. Which pH curve corresponds to an acid with Ka 1 106?arrow_forwardConsider the titration of 100.0 mL of 0.200 M HONH2 by 0.100 M HCI. (Kb for HONH2 = 1.1 108.) a. Calculate the pH after 0.0 mL of HCl has been added. b. Calculate the pH after 25.0 mL of HCl has been added. c. Calculate the pH after 70.0 mL of HCl has been added. d. Calculate the pH at the equivalence point. e. Calculate the pH after 300.0 mL of HCl has been added. f. At what volume of HCl added does the pH = 6.04?arrow_forwardFifty cm3 of 1.000 M nitrous acid is titrated with 0.850 M NaOH. What is the pH of the solution (a) before any NaOH is added? (b) at half-neutralization? (c) at the equivalence point? (d) when 0.10 mL less than the volume of NaOH to reach the equivalence point is added? (e) when 0.10 mL more than the volume of NaOH to reach the equivalence point is added? (f) Use your data to construct a plot similar to that shown in Figure 14.10 (pH versus volume NaOH added).arrow_forward
- A weak acid with pKa = 4.35 is titrated with 0.10 M NaOH. Which of the following is true about the pH of the solution at the equivalence point in this titration? A. The pH at the equivalence point is equal to 7. B. The pH at the equivalence point is above 7. C. The pH at the equivalence point is below 7.arrow_forwarda. The pH at the equivalence point of an acid-base titration depends on the hydrolysis of the neutralization reaction. formed in the b. The pH at the equivalence point for strong acid-strong base titration is c. The pH at the equivalence point for a weak acid-strong base titration is d. The pH at the equivalence point for a strong acid-weak base titration is 3.arrow_forwardA titration is carried out to determine the molecular weight of oxalic acid. In this experiment, 0.617g of oxalic acid was dissolved in water and 18.3 mL of 0.75 M NaOH were used to reach the equivalence point of the titration. However, each mol of oxalic acid reacts with 2 mols of NaOH. A.What is the molecular weight of oxalic acid? B. What is the concentration of oxalic acid in the original solution if the total volume was 100mLarrow_forward
- 3arrow_forward1. A 100 mL solution of 0.10 M weak base NH3 (Kb = 1.8 10-5) is titrated with 1.0 M strong acid titrant HCl. NH3 + H2O → NH4+ + OH- A.What is the acid and base pH before titration? B. How much acid is required to achieve the equivalence point and the midway point where pH = pKa? C. Write your own titration curve,include pH after 50 mL of acid is added, at the equivalence point, and after 60 mL of acid is added.arrow_forwardWhich of the following is true about the titration curves of solutions of weak acids? A. The pH for optimal buffering power of a weak acid is 7.00. B. You can calculate the pKa of an acid, given the pH and the molar ratio of the acid and its conjugate base. C. The pKa of a weak acid is the pH at which the acid is completely dissociated. D. At a pH below the pKa of a weak acid, its conjugate base will predominate.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Acid-Base Titration | Acids, Bases & Alkalis | Chemistry | FuseSchool; Author: FuseSchool - Global Education;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yFqx6_Y6c2M;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY