
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether table sugar is a monosaccharide, disaccharide, or polysaccharide is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
On the basis of the structural differences carbohydrates are classified into three parts.
Monosaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy
Disaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Sucrose, lactose.
Polysaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing more than two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Cellulose, starch.
Answer to Problem 17.4E
Table sugar is a disaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
Table sugar is also known as sucrose. Sucrose on hydrolysis gives two monosaccharides, glucose and fructose which are linked through a glycosidic linkage. This shows that sucrose or table sugar is a disaccharide.
Table sugar is a disaccharide.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether the given carbohydrate is a monosaccharide, disaccharide, or polysaccharide is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
On the basis of the structural differences carbohydrates are classified into three parts.
Monosaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing only one aldehyde or ketone unit. For example: glucose and fructose.
Disaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Sucrose, lactose.
Polysaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing more than two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Cellulose, starch.
Answer to Problem 17.4E
The given carbohydrate is an example of monosaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The structural formula of the given carbohydrate is shown below.
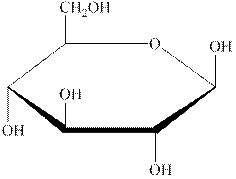
Figure 1
The above structure of carbohydrate shows that there is no glycosidic linkage through which another carbohydrate is linked. Therefore, the above carbohydrate is a monosaccharide.
The carbohydrate shown in Figure 1 is an example of monosaccharide.
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether starch is a monosaccharide, disaccharide, or polysaccharide is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
On the basis of the structural differences carbohydrates are classified into three parts.
Monosaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing only one aldehyde or ketone unit. For example: glucose and fructose.
Disaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Sucrose, lactose.
Polysaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing more than two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Cellulose, starch.
Answer to Problem 17.4E
Starch is a polysaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
Starch is the
Starch is an example of polysaccharide.
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether fructose is a monosaccharide, disaccharide, or polysaccharide is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
On the basis of the structural differences carbohydrates are classified into three parts.
Monosaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing only one aldehyde or ketone unit. For example: glucose and fructose.
Disaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Sucrose, lactose.
Polysaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing more than two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Cellulose, starch.
Answer to Problem 17.4E
Fructose is a monosaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
Hydrolysis of sucrose produces glucose and fructose which do not undergo further hydrolysis. Therefore, fructose comes under the category of monosaccharide.
Fructose is an example of monosaccharide.
(e)
Interpretation:
Whether cellulose is a monosaccharide, disaccharide, or polysaccharide is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
On the basis of the structural differences carbohydrates are classified into three parts.
Monosaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing only one aldehyde or ketone unit. For example: glucose and fructose.
Disaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Sucrose, lactose.
Polysaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing more than two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Cellulose, starch.
Answer to Problem 17.4E
Cellulose is a polysaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
Cellulose is a polymeric form of D-glucose because cellulose on hydrolysis gives a large number of glucose as monosaccharide. Each glucose is linked with
Cellulose on hydrolysis gives a large number of molecules of glucose. As a result, cellulose is a polysaccharide.
(f)
Interpretation:
Whether the given carbohydrate is a monosaccharide, disaccharide, or polysaccharide is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
On the basis of the structural differences carbohydrates are classified into three parts.
Monosaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing only one aldehyde or ketone unit. For example: glucose and fructose.
Disaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Sucrose, lactose.
Polysaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing more than two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Cellulose, starch.
Answer to Problem 17.4E
The given carbohydrate is a disaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The structural formula of the given carbohydrate is shown below.
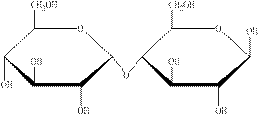
Figure 2
The above structure of carbohydrate shows that two monosaccharides are linked to each other through glycosidic linkage and results in the formation of a disaccharide. Therefore, the above carbohydrate is a disaccharide.
The carbohydrate shown in Figure 2 is an example of disaccharide.
(g)
Interpretation:
Whether glycogen is a monosaccharide, disaccharide, or polysaccharide is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
On the basis of the structural differences carbohydrates are classified into three parts.
Monosaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing only one aldehyde or ketone unit. For example: glucose and fructose.
Disaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Sucrose, lactose.
Polysaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing more than two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Cellulose, starch.
Answer to Problem 17.4E
Glycogen is a polysaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
Glycogen is a polymeric form of D-glucose which on hydrolysis gives glucose units. Each glucose unit is linked by
Glycogen on hydrolysis gives a large number of molecules of glucose. As a result, glycogen is a polysaccharide.
(h)
Interpretation:
Whether amulose is a monosaccharide, disaccharide, or polysaccharide is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
On the basis of the structural differences carbohydrates are classified into three parts.
Monosaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing only one aldehyde or ketone unit. For example: glucose and fructose.
Disaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Sucrose, lactose.
Polysaccharide: They are the polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing more than two aldehyde or ketone units. For example: Cellulose, starch.
Answer to Problem 17.4E
Amylose is a polysaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
Amylose is a polymeric form of
Amylose on hydrolysis gives a large number of glucose units. As a result, amylose is a polysaccharide.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Bundle: Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Biochemistry, Loose-Leaf Version, 9th + LMS Integrated OWLv2, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- Draw a tetramer of this alternating copolymer.arrow_forwardH I T H HH H -H C. H- Identify and select all structures below that represent a constitutional isomer(s) of the compound shown above. H- H CIH H H H HHHH H H 0 ·H H– 冊 CH CHI HH C- H- H H- H H A. H H C H H- -H HH H B. H- -H D. H H H H • H -H E. -H H H HICH T HHH F. H-arrow_forwardPolylactic acid (shown below) is a biodegradable polymer used for food packaging. Identify the monomer(s) used in the production of this polymer using a condensation process.arrow_forward
- Draw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore small byproducts that would evaporate pleasearrow_forwardPoly(ethylene adipate) is a biodegradable polyester (shown below). Identify the type of polymerization process used in the production of this polymer.arrow_forwardPolymers may be composed of thousands of monomers. draw two repeat units(dimer) of the polymer formed in this reaction. assume there are hydrogen atoms on the two ends of the dimer. ignore inorganic byproducts pleasearrow_forward
- Draw the product of the reaction shown below. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, Ignore inorganic byproductsarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction please. Ignore inorganic byproductsarrow_forwardOne of the pi molecular orbitals of 1,3-butadiene (CH2=CHCH=CH2) is shown below. Please identify the number of nodal planes perpendicular to the bonding axisarrow_forward
- Draw the monomers required to synthesize this condensation polymer please.arrow_forwardProvide the correct systematic name for the compound shown here. Please take into account the keyboard options belowarrow_forwardcurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s)arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





