
Concept explainers
FIFO method, equivalent units. Refer to the information in Exercise 17-24. Suppose the assembly division at Quality Time Pieces, Inc. uses the FIFO method of
Required
Compute equivalent units for direct materials and conversion costs. Show physical units in the first column of your schedule.
17-24 Weighted-average method, equivalent units. The assembly division of Quality Time Pieces, Inc. uses the weighted-average method of process costing. Consider the following data for the month of May 2017:
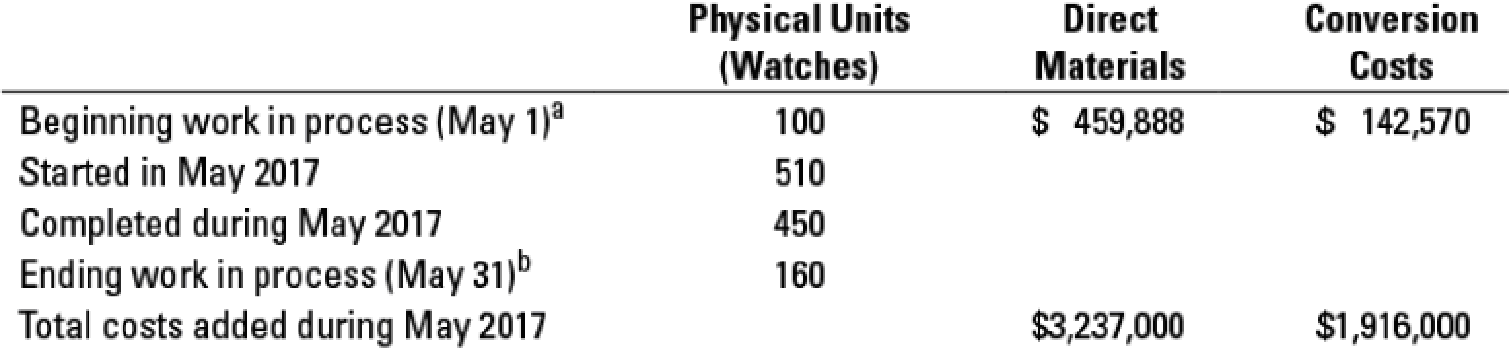
a Degree of completion: direct materials. 80%: conversion costs, 35%.
b Degree of completion: direct materials, 80%; conversion costs, 40%.
Compute equivalent units for direct materials and conversion costs. Show physical units in the first column of your schedule.
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 17 Solutions
EBK HORNGREN'S COST ACCOUNTING
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
Foundations Of Finance
Fundamentals of Management (10th Edition)
Corporate Finance (4th Edition) (Pearson Series in Finance) - Standalone book
Financial Accounting: Tools for Business Decision Making, 8th Edition
Horngren's Accounting (12th Edition)
- I need this question answer general Accountingarrow_forwardDiscuss the potential benefits and limitations of incorporating forward-looking information, such as budgets and forecasts, into traditional financial reporting. Explore the challenges accountants face in balancing the need for reliable historical data with the desire to provide more forward-looking and decision-useful information to stakeholders.arrow_forwardGeneral Accounting need answerarrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning  Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning



