
(a)
Interpretation: The name of the following compound should be determined:
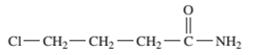
Concept Introduction: An organic compound in which carboxy
The reaction which results in the formation of amide along with water on heating acids with
So, in order to give the IUPAC name to the amides, the rules for naming carboxylic acid is followed and -oic acid of the carboxylic acid is replaced by amide.
In order to give the name to the amide group, the following steps are followed:
- The parent (longest)
alkane chain is named as for carboxylic acids. - The -oic acid in the name is changed to -amide.
- The numbering of the chain is done in such a way that amide group and substituents gets the smaller number.
- N-alkyl is used to show each alkyl group bonded to -N atom in the name for secondary and tertiary amides.
For number of carbons atoms chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec
In order to write the common name of the amides, the common of acids are written from which the amide has been formed by replacing -oic acid in name from -amide.
(b)
Interpretation: The name of the following compound should be determined:
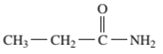
Concept Introduction: An organic compound in which carboxy functional group that is -COOH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be a carboxylic acid. The general formula for carboxylic acid is RCOOH or RCO2H. When -OH (hydroxyl group) of the carboxylic acid is replaced by nitrogen (-N) then it results in the formation of an amide.
The reaction which results in the formation of amide along with water on heating acids with amine or ammonia is said to be amidation.
So, in order to give the IUPAC name to the amides, the rules for naming carboxylic acid is followed and -oic acid of the carboxylic acid is replaced by amide.
In order to give the name to the amide group, the following steps are followed:
- The parent (longest) alkane chain is named as for carboxylic acids.
- The -oic acid in the name is changed to -amide.
- The numbering of the chain is done in such a way that amide group and substituents gets the smaller number.
- N-alkyl is used to show each alkyl group bonded to -N atom in the name for secondary and tertiary amides.
For number of carbons atoms chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec
In order to write the common name of the amides, the common of acids are written from which the amide has been formed by replacing -oic acid in name from -amide.
(c)
Interpretation: The name of the following compound should be determined:
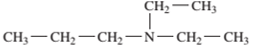
Concept Introduction: The group that contains a nitrogen atom attached to one or more carbon atoms is said to be an amine group, general representation of an amine group is R1R2R3-N.
The common name of amines are derived by naming the alkyl groups bonded to nitrogen atom in alphabetical order and then ending with word -amine.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 17 Solutions
Pearson eText Basic Chemistry -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
- Please complete the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardConsider the synthesis. What is compound Y? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the compound Y creates the product. The correct answer is D.arrow_forwardWhat would be the major product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include steps and a drawing to show this reaction proceeds and how the final product is formed. The correct answer is B. I put answer D and I don't really understand what is going on in the question.arrow_forward
- What is the product of the following reaction? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalysts to product the correct product. The correct answer is B.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2. Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediate and how it occurs and how the final product is former.arrow_forwardWhat would be the reagents and conditions above and below the arrow that will complete the proposed acetoacetic ester synthesis? If it cannot be done efficiently, then I will choose that answer. There could be 2 or 4 reagents involved. Please provide a detailed explanation and drawings showing how it would proceed with the correct reagents.arrow_forward
- For benzene, the ∆H° of vaporization is 30.72 kJ/mol and the ∆S° of vaporization is 86.97 J/mol・K. At 1.00 atm and 228.0 K, what is the ∆G° of vaporization for benzene, in kJ/mol?arrow_forwardThe reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reaction. it is spontaneous only at High T, it is spontaneous at low T it is nonspontaneous at all T it is spontanrous at all T. it is non spontaneous only at low T.arrow_forwardThe reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reactionarrow_forward
- Which of the following has the largest standard molar entropy, S° (298.15 K) He H2 NaCl KBr Hgarrow_forwardWhich of the following is true for a particular reaction if ∆G° is -40.0 kJ/mol at 290 K and –20.0 kJ/mol at 390 K?arrow_forwardWhat is the major product of the following reaction? O O OH OH 1. BH 2. H₂O₂, NaOH OH OHarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





