
Concept explainers
a)
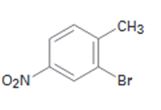
Interpretation:
Starting from benzene and assuming that the ortho and para isomers can be separated how the compound can be synthesized is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
The compound required is 2-bromo-4-nitrotoluene. Benzene can be converted into alkyl benzene by Friedal-Crafts alkylation. The alkylbenzene can be nitrated in the ortho and para positions as the alkyl groups are ortho and para directors. Nitro group is deactivating while alkyl group is activating in nature. Hence bromonation of the nitrotoluene will introduce the bromine in the ortho position to alkyl group.
To show:
Starting from benzene and assuming that the ortho and para isomers can be separated how 2-bromo-4-nitrotoluene can be synthesized.
b)
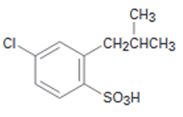
Interpretation:
Starting from benzene and assuming that the ortho and para isomers can be separated how the compound can be synthesized is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
The Friedal-Crafts acylation of benzene will yield an acyl benzene as the product. Chlorination of the acyl benzene will produce m-chloroacyl benzene as the acyl group is meta directing. Reduction of the acyl group to the corresponding alkyl group and sulfonation of the product will result in the product required.
To show:
Starting from benzene and assuming that the ortho and para isomers can be separated how the compound can be synthesized.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 16 Solutions
Student Value Bundle: Organic Chemistry, + OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card (NEW!!)
- 42. Which of the following halogenated compounds can be used successfully to prepare a Grignard reagent for alcohol synthesis by subsequent reaction with an aldehyde or ketone? Which ones cannot and why? H3C CH3 a. Br H OH b. Cl C. I H H d. Cl e. H OCH3 Br Harrow_forwardFor each reaction below, decide if the first stable organic product that forms in solution will create a new CC bond, and check the appropriate box. Next, for each reaction to which you answered "Yes" to in the table, draw this product in the drawing area below. Note for advanced students: for this problem, don't worry if you think this product will continue to react under the current conditions - just focus on the first stable product you expect to form in solution. ? Will the first MgBr product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? olo ? OH جمله O Yes Ⓒ No MgCl ? Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Yes No X ☐ : ☐ टे PHarrow_forwardAssign all the protonsarrow_forward
- 9 7 8 C 9 8 200 190 B 5 A -197.72 9 8 7 15 4 3 0: ང་ 200 190 180 147.52 134.98 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 90 OH 10 4 3 1 2 -143.04 140. 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 CI 3 5 1 2 141.89 140.07 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 ៖- 90 129. 126.25 80 70 60 -60 50 40 10 125.19 -129.21 80 70 3.0 20 20 -8 60 50 10 ppm -20 40 128.31 80 80 70 60 50 40 40 -70.27 3.0 20 10 ppm 00˚0-- 77.17 30 20 20 -45.36 10 ppm -0.00 26.48 22.32 ―30.10 ―-0.00arrow_forwardAssign all the carbonsarrow_forwardC 5 4 3 CI 2 the Righ B A 5 4 3 The Lich. OH 10 4 5 3 1 LOOP- -147.52 T 77.17 -45.36 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 ppm B -126.25 77.03 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 ppm 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 TO LL <-50.00 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 ppm 45.06 30.18 -26.45 22.36 --0.00 45.07 7.5 1.93 2.05 -30.24 -22.36 C A 7 8 5 ° 4 3 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 ppm 9 8 5 4 3 ཡི་ OH 10 2 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 5 4 3 2 that th 7 I 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 115 2.21 4.00 1.0 ppm 6.96 2.76 5.01 1.0 ppm 6.30 1.00arrow_forward
- Curved arrows were used to generate the significant resonance structure and labeled the most significant contribute. What are the errors in these resonance mechanisms. Draw out the correct resonance mechanisms with an brief explanation.arrow_forwardWhat are the: нсе * Moles of Hice while given: a) 10.0 ml 2.7M ? 6) 10.ome 12M ?arrow_forwardYou are asked to use curved arrows to generate the significant resonance structures for the following series of compounds and to label the most significant contributor. Identify the errors that would occur if you do not expand the Lewis structures or double-check the mechanisms. Also provide the correct answers.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning

