
a)
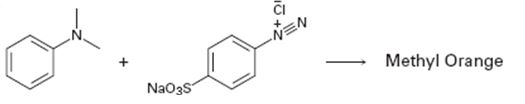
Interpretation:
A structure for methyl orange, an azo dye, produced when the two reactants shown react is to be drawn and the electron pushing mechanism for its formation is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
The diazonium cation can act as an electrophile and can attack
To draw:
The structure of methyl orange, an azo dye, produced when the two reactants shown react and to show the electron pushing mechanism for its formation.
b)
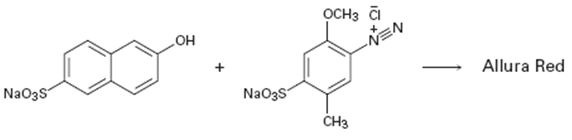
Interpretation:
A structure for allura red, an azo dye, produced when the two reactants shown react is to be drawn and the electron pushing mechanism for its formation is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
The diazonium cation can act as an electrophile and attack the aromatic rings. The dimethylamino group is an o- and p- directing group. Hence the diazonium cation can attack the ring at the p-position to yield a carbocation intermediate. The intermediate then can lose a proton to yield the desired product. This reaction is known as coupling reaction.
To draw:
The structure of allura red, an azo dye, produced when the two reactants shown react and to give the electron pushing mechanism for its formation.
c)
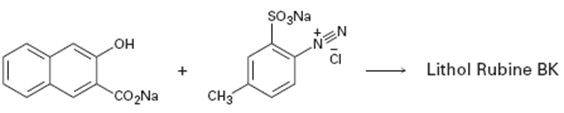
Interpretation:
A structure for lithol rubine BX, an azo dye, produced when the two reactants shown react is to be drawn and the electron pushing mechanism for its formation is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
The diazonium cation can act as an electrophile and attack the aromatic rings. The dimethylamino group is an o- and p- directing group. Hence the diazonium cation can attack the ring at the p-position to yield a carbocation intermediate. The intermediate then can lose a proton to yield the desired product. This reaction is known as coupling reaction.
To draw:
The structure of lithol rubine BX, an azo dye, produced when the two reactants shown react and to show the electron pushing mechanism for its formation.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 16 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - With Access (Custom)
- A mixture of C7H12O2, C9H9OCl, biphenyl and acetone was put together in a gas chromatography tube. Please decide from the GC resutls which correspond to the peak for C7,C9 and biphenyl and explain the reasoning based on GC results. Eliminate unnecessary peaks from Gas Chromatography results.arrow_forwardIs the molecule chiral, meso, or achiral? CI .CH3 H₂C CIarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP ! URGENT!arrow_forward
- Identify priority of the substituents: CH3arrow_forwardHow many chiral carbons are in the molecule? OH F CI Brarrow_forwardA mixture of three compounds Phen-A, Acet-B and Rin-C was analyzed using TLC with 1:9 ethanol: hexane as the mobile phase. The TLC plate showed three spots of R, 0.1 and 0.2 and 0.3. Which of the three compounds (Phen-A; Acet-B or Rin-C) would have the highest (Blank 1), middle (Blank 2) and lowest (Blank 3) spot respectively? 0 CH: 0 CH, 0 H.C OH H.CN OH Acet-B Rin-C phen-A A A <arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning



