
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133915389
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 16.4, Problem 39P
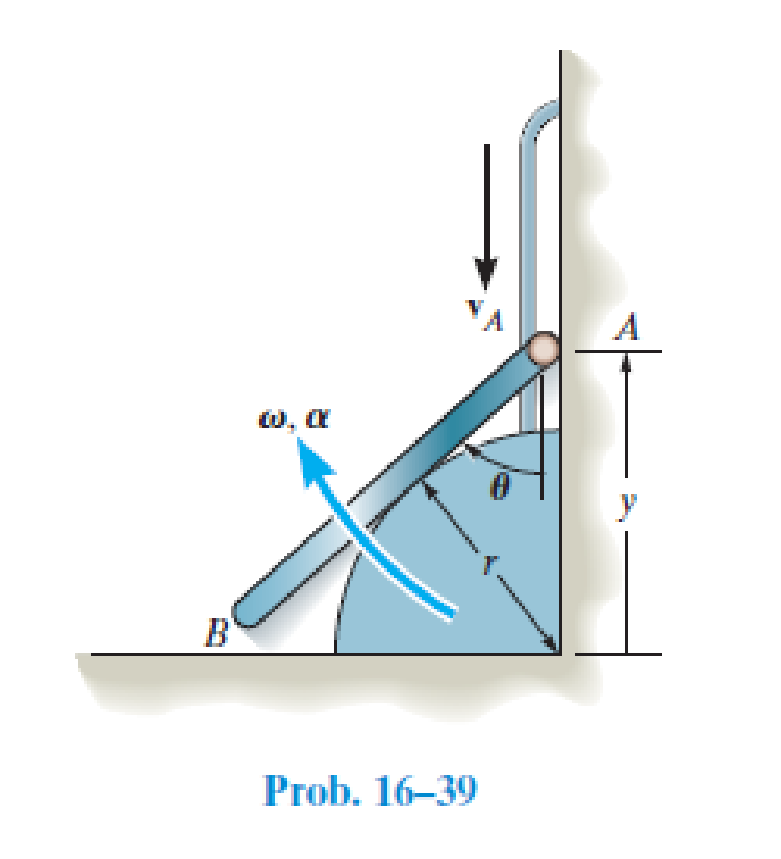
Determine the angular velocity ω and angular acceleration α of the bar as a function of its position y.
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule09:24
Students have asked these similar questions
3 kN
3 kN
1.8 kN/m
80 mm
B
300 mm
D
an
1.5 m-1.5 m--1.5 m-
PROBLEM 5.47
Using the method of Sec. 5.2, solve Prob. 5.16
PROBLEM 5.16 For the beam and loading shown, determine the
maximum normal stress due to bending on a transverse section at C.
300 mm
3 kN
3 kN
450 N-m
D
E
200 mm
300 mm
PROBLEM 5.12
Draw the shear and bending-moment diagrams for the beam and loading
shown, and determine the maximum absolute value (a) of the shear,
(b) of the bending moment.
CORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. I REALLY NEED FBD.
The cantilevered spandrel beam shown whose depth tapers from d1 to d2, has a constant width of 120mm. It carries a triangularly distributed end reaction.Given: d1 = 600 mm, d2 = 120 mm, L = 1 m, w = 100 kN/m1. Calculate the maximum flexural stress at the support, in kN-m.2. Determine the distance (m), from the free end, of the section with maximum flexural stress.3. Determine the maximum flexural stress in the beam, in MPa.ANSWERS: (1) 4.630 MPa; (2) 905.8688 m; (3) 4.65 MPa
Chapter 16 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
Ch. 16.3 - Determine its constant angular acceleration and...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the angular acceleration when it has...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the time it takes to achieve an angular...Ch. 16.3 - If the angular displacement of the wheel is =...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitude of the velocity and...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the velocity of the cylinder and the...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitudes of the velocity and...Ch. 16.3 - If the disk is originally rotating at 0 = 12...Ch. 16.3 - It it is subjected to a constant angular...Ch. 16.3 - If it is subjected to a constant angular...
Ch. 16.3 - Determine the number of revolutions, the angular...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the number of revolutions it must...Ch. 16.3 - Also, find the number of revolutions of gear D to...Ch. 16.3 - Gears A, B, C, and D have radii of 15 mm, 50 mm,...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitude of acceleration of point B...Ch. 16.3 - pulley A is given a constant angular acceleration...Ch. 16.3 - Starting from rest, determine the angular...Ch. 16.3 - If the engine turns pulley A at A = (20t + 40)...Ch. 16.3 - If the engine turns pulley A at A = 60 rad/s,...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the angular velocity of the disk and its...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitudes of the normal and...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitudes of the normal and...Ch. 16.3 - If this gear is initially turning at A = 15 rad/s,...Ch. 16.3 - If this gear is initially turning at A = 15 rad/s,...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the brushs angular velocity when t = 4...Ch. 16.3 - If this gear is initially turning at (A)0 = 20...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitudes of the velocity and the n...Ch. 16.3 - If the motor turns gear A with an angular...Ch. 16.3 - If the motor turns gear A with an angular...Ch. 16.3 - and the meshed pinion gear B on the propeller...Ch. 16.3 - determine the magnitude of the velocity and...Ch. 16.3 - If the gears A and have the dimensions shown,...Ch. 16.3 - and the meshed pinion gear B on the propeller...Ch. 16.3 - and the meshed pinion gear B on the propeller...Ch. 16.3 - If the canisters are centered 200 mm apart on the...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the largest angular velocity of gear B...Ch. 16.3 - The shaft of the motor M turns with an angular...Ch. 16.3 - If A has a constant angular acceleration of A = 30...Ch. 16.3 - If the angular displacement of A it A = (5t3 +...Ch. 16.3 - This gear is connected to gear B, which is fixed...Ch. 16.3 - Express the result in Cartesian vector form.Ch. 16.3 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of point D...Ch. 16.3 - At the instant shown it is rotating about the y...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitudes of the velocity and...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the angular acceleration and angular...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the angular acceleration and angular...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the angular velocity of the connecting...Ch. 16.4 - The cam rotates with a constant counterclockwise...Ch. 16.4 - The pin connection at O does not cause an...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the velocity of the follower rod AB as...Ch. 16.4 - The pin connection at O does not cause an...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of the peg...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of block...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.4 - If the slotted arm is causing A to move downward...Ch. 16.4 - If the wedge moves to the left with a constant...Ch. 16.4 - If the rollers do not slip, determine their...Ch. 16.4 - If no slipping occurs between the disk D and the...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of...Ch. 16.5 - If roller A moves to the right with a constant...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the magnitude of the velocity of point B...Ch. 16.5 - The cable wraps around the inner core, and the...Ch. 16.5 - If crank OA rotates with an angular velocity of =...Ch. 16.5 - If rod AB slides along the horizontal slot with a...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of the peg at B at this...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of point B at this instant.Ch. 16.5 - If the block at C is moving downward at 4 ft/s,...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of block C and the angular...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the angular velocities of links A B and...Ch. 16.5 - Also, sketch the position of link BC when = 55,...Ch. 16.5 - Link BC rotates clockwise with an angular velocity...Ch. 16.5 - If the angular velocity of link AB is AB = 3...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of the gear rack C.Ch. 16.5 - If B is moving to the right at 8 ft/s and C is...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the angular velocity of the gear and the...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of point A on the rim of...Ch. 16.5 - Link CB is horizontal at this instant.Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of the slider C at the...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of block C and the angular...Ch. 16.5 - If AB has an angular velocity AB = 8 rad/s,...Ch. 16.5 - If the slider block A is moving downward at vA = 4...Ch. 16.5 - If the slider block A is moving downward at A = 4...Ch. 16.5 - This gear has an inner hub C which is fixed to B...Ch. 16.5 - If link AB is rotating at AB =3 rad/s, determine...Ch. 16.5 - If link CD is rotating at CD = 5 rad/s, determine...Ch. 16.5 - By locking or releasing certain gears, it has the...Ch. 16.5 - If the ring gear A rotates clockwise with an...Ch. 16.5 - It consists of a driving piston A, three links,...Ch. 16.5 - Because of the rotational motion of lint AB and...Ch. 16.6 - Establish the location of the instantaneous center...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of the rod and the...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of link BC and...Ch. 16.6 - The gear rack B is fixed.Ch. 16.6 - If cable AB is unwound with a speed of 3 m/s, and...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of link BC and the...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of links BC and CD...Ch. 16.6 - Assume the geometry is known.Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of link AB at the...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of the link CB at...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocities of the cylinders center C...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocities of points A and B on the...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocities of points A and B.Ch. 16.6 - If rod CD is rotating with an angular velocity CD...Ch. 16.6 - If bar AB has an angular velocity AB = 6 rad/s,...Ch. 16.6 - Under these conditions, what is the speed at A if...Ch. 16.6 - Due to slipping, points A and B on the rim of the...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocities of the center point C and...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocity of point D and the angular...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocity of point P, and the angular...Ch. 16.6 - If connected bar CD is rotating with an angular...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the speeds of points A, B, and C caused...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocity of the gear rack C.Ch. 16.6 - If the hub gear H and ring gear R have angular...Ch. 16.6 - What is the angular velocity of the spur gear?Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of rod CD at the...Ch. 16.6 - If bar CD is rotating with an angular velocity of...Ch. 16.6 - If the link rotates about the fixed point B at 4...Ch. 16.7 - if the sun gear D is rotating clockwise at D = 5...Ch. 16.7 - The angular velocity is given.Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of the rod and...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the acceleration of point A.Ch. 16.7 - At the instant shown, the center O of the gear...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of the gear at...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of link BC at...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of link BC and...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the velocity sod acceleration of the...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the acceleration of the top of the...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the acceleration of the bottom A of the...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of the...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of the...Ch. 16.7 - At the instant shown, point A has the motion...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of link AB and...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of link CD if...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of point A...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of point B...Ch. 16.7 - If it is pulled with a constant velocity v,...Ch. 16.7 - If it does not slip at A, determine the...Ch. 16.7 - If it does not slip at A, determine the...Ch. 16.7 - As cord CF unwinds from the inner rim of the...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of point B...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.7 - If link DE has the angular motion shown, determine...Ch. 16.7 - If member AB has the angular motion shown,...Ch. 16.7 - If member AB has the angular motion shown,...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the acceleration of points A and B on...Ch. 16.7 - At a given instant, A has a velocity of vA = 4...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of rod AB at...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the acceleration of A at the instant...Ch. 16.8 - If at the same instant the disk has the angular...Ch. 16.8 - At the same instant, the boom is extending with a...Ch. 16.8 - Prob. 131PCh. 16.8 - Prob. 132PCh. 16.8 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of a water...Ch. 16.8 - At the instant shown, the cord is pulled down...Ch. 16.8 - Prob. 135PCh. 16.8 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of point C...Ch. 16.8 - Prob. 137PCh. 16.8 - Determine the magnitudes of the velocity and...Ch. 16.8 - If link AD is rotating at a constant rate of AD =...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.8 - If rod AB has an angular velocity of 2 rad/s and...Ch. 16.8 - Prob. 142PCh. 16.8 - If the gears center O moves with the velocity and...Ch. 16.8 - Prob. 144PCh. 16.8 - Prob. 145PCh. 16.8 - Also at this instant the car mounted at the end of...Ch. 16.8 - If the slider block C is fixed to the disk that...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of car A...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of car B...Ch. 16.8 - Link AB has a pin at B which is confined to move...Ch. 16.8 - Prob. 151PCh. 16.8 - The star wheel A makes one sixth of a revolution...Ch. 16.8 - If the tires do not slip on the pavement,...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the velocity and deceleration of the...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the speed of block B when it has risen s...Ch. 16.8 - At the instant shown, it has an acceleration of...Ch. 16.8 - If bar AB has an angular velocity AB = 6 rad/s,...Ch. 16.8 - If the cable does not slip on the pulley's...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the acceleration of the pin at C and the...Ch. 16.8 - If it does not slip at A, determine the...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of the...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Explain the problems that denormalized tables may have for insert, update, and delete actions.
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
// Assume inputFile references a Scanner object, try { input = inputFile.nextlnt(); } finally { inputFile.close...
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
What is the difference between application software and utility software?
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Write a program to read in three nonnegative integers from the keyboard. Display the integers in increasing ord...
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
The data that you retrieve from an Entry widget is always of the int data type.
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
In Exercises 1 through 52, determine the output produced by the lines of code. DimdtlAsDate=2/1/20162016wasalea...
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- CORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. I REALLY NEED FBD A concrete wall retains water as shown. Assume that the wall is fixed at the base. Given: H = 3 m, t = 0.5m, Concrete unit weight = 23 kN/m3Unit weight of water = 9.81 kN/m3(Hint: The pressure of water is linearly increasing from the surface to the bottom with intensity 9.81d.)1. Find the maximum compressive stress (MPa) at the base of the wall if the water reaches the top.2. If the maximum compressive stress at the base of the wall is not to exceed 0.40 MPa, what is the maximum allowable depth(m) of the water?3. If the tensile stress at the base is zero, what is the maximum allowable depth (m) of the water?ANSWERS: (1) 1.13 MPa, (2) 2.0 m, (3) 1.20 marrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. I NEED FBD A short plate is attached to the center of the shaft as shown. The bottom of the shaft is fixed to the ground.Given: a = 75 mm, h = 125 mm, D = 38 mmP1 = 24 kN, P2 = 28 kN1. Calculate the maximum torsional stress in the shaft, in MPa.2. Calculate the maximum flexural stress in the shaft, in MPa.3. Calculate the maximum horizontal shear stress in the shaft, in MPa.ANSWERS: (1) 167.07 MPa; (2) 679.77 MPa; (3) 28.22 MPaarrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. I REALLY NEED FBD. The roof truss shown carries roof loads, where P = 10 kN. The truss is consisting of circular arcs top andbottom chords with radii R + h and R, respectively.Given: h = 1.2 m, R = 10 m, s = 2 m.Allowable member stresses:Tension = 250 MPaCompression = 180 MPa1. If member KL has square section, determine the minimum dimension (mm).2. If member KL has circular section, determine the minimum diameter (mm).3. If member GH has circular section, determine the minimum diameter (mm).ANSWERS: (1) 31.73 mm; (2) 35.81 mm; (3) 18.49 mmarrow_forward
- PROBLEM 3.23 3.23 Under normal operating condi- tions a motor exerts a torque of magnitude TF at F. The shafts are made of a steel for which the allowable shearing stress is 82 MPa and have diameters of dCDE=24 mm and dFGH = 20 mm. Knowing that rp = 165 mm and rg114 mm, deter- mine the largest torque TF which may be exerted at F. TF F rG- rp B CH TE Earrow_forward1. (16%) (a) If a ductile material fails under pure torsion, please explain the failure mode and describe the observed plane of failure. (b) Suppose a prismatic beam is subjected to equal and opposite couples as shown in Fig. 1. Please sketch the deformation and the stress distribution of the cross section. M M Fig. 1 (c) Describe the definition of the neutral axis. (d) Describe the definition of the modular ratio.arrow_forwardusing the theorem of three moments, find all the moments, I only need concise calculations with minimal explanations. The correct answers are provided at the bottomarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY