
ENGR.MECH.: DYNAMICS-EBOOK>I<
14th Edition
ISBN: 9781292088785
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: INTER PEAR
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 16.3, Problem 13P
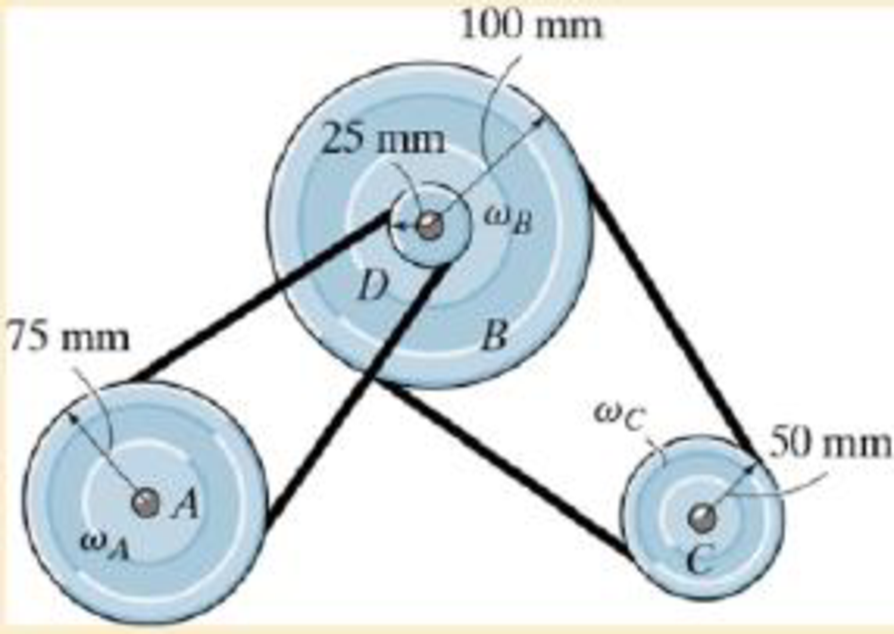
If the engine turns pulley A at ωA = 60 rad/s, determine the angular velocities of the generator pulley B and the air-conditioning pulley C, The hub at D is rigidly connected to B and turns with it.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Problem 4.
A homogeneous disk with radius and mass m is mounted on an axle OG with length L and a
negligible mass. The axle is pivoted at the fixed-point O, and the disk is constrained to roll on a
horizontal surface. The disk rotates counterclockwise at the constant rate o₁ about the axle. (mg
must be included into your calculation)
(a). Calculate the linear velocity of G and indicate it on the figure.
(b). Calculate ₂ (constant), which is the angular velocity of the
axle OG around the vertical axis.
(c). Calculate the linear acceleration ā of G and indicate it on the
figure.
(d). Determine the force (assumed vertical) exerted by the floor on
the disk
(e). Determine the reaction at the pivot O.
1
Answers: N = mg +mr(r/L)² @² |j
mr w
IIG
C
R
L
i+
2L
=
Problem 2.
The homogeneous disk of weight W = 6 lb rotates at the constant rate co₁ = 16 rad/s with respect
to arm ABC, which is welded to a shaft DCE rotating at the constant rate 2 = 8 rad/s. Assume
the rod weight is negligible compared to the disk. Determine the dynamic reactions at D and E
(ignore mg).
Answers:
D=-7.12ĵ+4.47k lb
r-8 in.
9 in.
B
D
E=-1.822+4.47 lb
9 in.
E
12 in.
12 in.
x
Problem 3.
Each of the right angle rods has a mass of 120 g and is welded to the shaft, which rotates at a steady
speed of 3600 rpm. Ignore the weight of the shaft AB. Find the bearing dynamic reaction at A
due to the dynamic imbalance of the shaft. (ignore mgs)
100
N
A
100
100
100
100
100
(Dimensions in millimeters)
Answer: A=-8521-426j N
B
Chapter 16 Solutions
ENGR.MECH.: DYNAMICS-EBOOK>I<
Ch. 16.3 - Determine its constant angular acceleration and...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the angular acceleration when it has...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the time it takes to achieve an angular...Ch. 16.3 - If the angular displacement of the wheel is =...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitude of the velocity and...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the velocity of the cylinder and the...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitudes of the velocity and...Ch. 16.3 - If the disk is originally rotating at 0 = 12...Ch. 16.3 - It it is subjected to a constant angular...Ch. 16.3 - If it is subjected to a constant angular...
Ch. 16.3 - Determine the number of revolutions, the angular...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the number of revolutions it must...Ch. 16.3 - Also, find the number of revolutions of gear D to...Ch. 16.3 - Gears A, B, C, and D have radii of 15 mm, 50 mm,...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitude of acceleration of point B...Ch. 16.3 - pulley A is given a constant angular acceleration...Ch. 16.3 - Starting from rest, determine the angular...Ch. 16.3 - If the engine turns pulley A at A = (20t + 40)...Ch. 16.3 - If the engine turns pulley A at A = 60 rad/s,...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the angular velocity of the disk and its...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitudes of the normal and...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitudes of the normal and...Ch. 16.3 - If this gear is initially turning at A = 15 rad/s,...Ch. 16.3 - If this gear is initially turning at A = 15 rad/s,...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the brushs angular velocity when t = 4...Ch. 16.3 - If this gear is initially turning at (A)0 = 20...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitudes of the velocity and the n...Ch. 16.3 - If the motor turns gear A with an angular...Ch. 16.3 - If the motor turns gear A with an angular...Ch. 16.3 - and the meshed pinion gear B on the propeller...Ch. 16.3 - determine the magnitude of the velocity and...Ch. 16.3 - If the gears A and have the dimensions shown,...Ch. 16.3 - and the meshed pinion gear B on the propeller...Ch. 16.3 - and the meshed pinion gear B on the propeller...Ch. 16.3 - If the canisters are centered 200 mm apart on the...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the largest angular velocity of gear B...Ch. 16.3 - The shaft of the motor M turns with an angular...Ch. 16.3 - If A has a constant angular acceleration of A = 30...Ch. 16.3 - If the angular displacement of A it A = (5t3 +...Ch. 16.3 - This gear is connected to gear B, which is fixed...Ch. 16.3 - Express the result in Cartesian vector form.Ch. 16.3 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of point D...Ch. 16.3 - At the instant shown it is rotating about the y...Ch. 16.3 - Determine the magnitudes of the velocity and...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the angular acceleration and angular...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the angular acceleration and angular...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the angular velocity of the connecting...Ch. 16.4 - The cam rotates with a constant counterclockwise...Ch. 16.4 - The pin connection at O does not cause an...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the velocity of the follower rod AB as...Ch. 16.4 - The pin connection at O does not cause an...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of the peg...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of block...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.4 - If the slotted arm is causing A to move downward...Ch. 16.4 - If the wedge moves to the left with a constant...Ch. 16.4 - If the rollers do not slip, determine their...Ch. 16.4 - If no slipping occurs between the disk D and the...Ch. 16.4 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of...Ch. 16.5 - If roller A moves to the right with a constant...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the magnitude of the velocity of point B...Ch. 16.5 - The cable wraps around the inner core, and the...Ch. 16.5 - If crank OA rotates with an angular velocity of =...Ch. 16.5 - If rod AB slides along the horizontal slot with a...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of the peg at B at this...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of point B at this instant.Ch. 16.5 - If the block at C is moving downward at 4 ft/s,...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of block C and the angular...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the angular velocities of links A B and...Ch. 16.5 - Also, sketch the position of link BC when = 55,...Ch. 16.5 - Link BC rotates clockwise with an angular velocity...Ch. 16.5 - If the angular velocity of link AB is AB = 3...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of the gear rack C.Ch. 16.5 - If B is moving to the right at 8 ft/s and C is...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the angular velocity of the gear and the...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of point A on the rim of...Ch. 16.5 - Link CB is horizontal at this instant.Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of the slider C at the...Ch. 16.5 - Determine the velocity of block C and the angular...Ch. 16.5 - If AB has an angular velocity AB = 8 rad/s,...Ch. 16.5 - If the slider block A is moving downward at vA = 4...Ch. 16.5 - If the slider block A is moving downward at A = 4...Ch. 16.5 - This gear has an inner hub C which is fixed to B...Ch. 16.5 - If link AB is rotating at AB =3 rad/s, determine...Ch. 16.5 - If link CD is rotating at CD = 5 rad/s, determine...Ch. 16.5 - By locking or releasing certain gears, it has the...Ch. 16.5 - If the ring gear A rotates clockwise with an...Ch. 16.5 - It consists of a driving piston A, three links,...Ch. 16.5 - Because of the rotational motion of lint AB and...Ch. 16.6 - Establish the location of the instantaneous center...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of the rod and the...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of link BC and...Ch. 16.6 - The gear rack B is fixed.Ch. 16.6 - If cable AB is unwound with a speed of 3 m/s, and...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of link BC and the...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of links BC and CD...Ch. 16.6 - Assume the geometry is known.Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of link AB at the...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of the link CB at...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocities of the cylinders center C...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocities of points A and B on the...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocities of points A and B.Ch. 16.6 - If rod CD is rotating with an angular velocity CD...Ch. 16.6 - If bar AB has an angular velocity AB = 6 rad/s,...Ch. 16.6 - Under these conditions, what is the speed at A if...Ch. 16.6 - Due to slipping, points A and B on the rim of the...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocities of the center point C and...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocity of point D and the angular...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocity of point P, and the angular...Ch. 16.6 - If connected bar CD is rotating with an angular...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the speeds of points A, B, and C caused...Ch. 16.6 - Determine the velocity of the gear rack C.Ch. 16.6 - If the hub gear H and ring gear R have angular...Ch. 16.6 - What is the angular velocity of the spur gear?Ch. 16.6 - Determine the angular velocity of rod CD at the...Ch. 16.6 - If bar CD is rotating with an angular velocity of...Ch. 16.6 - If the link rotates about the fixed point B at 4...Ch. 16.7 - if the sun gear D is rotating clockwise at D = 5...Ch. 16.7 - The angular velocity is given.Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of the rod and...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the acceleration of point A.Ch. 16.7 - At the instant shown, the center O of the gear...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of the gear at...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of link BC at...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of link BC and...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the velocity sod acceleration of the...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the acceleration of the top of the...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the acceleration of the bottom A of the...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of the...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of the...Ch. 16.7 - At the instant shown, point A has the motion...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of link AB and...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of link CD if...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of point A...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of point B...Ch. 16.7 - If it is pulled with a constant velocity v,...Ch. 16.7 - If it does not slip at A, determine the...Ch. 16.7 - If it does not slip at A, determine the...Ch. 16.7 - As cord CF unwinds from the inner rim of the...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of point B...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.7 - If link DE has the angular motion shown, determine...Ch. 16.7 - If member AB has the angular motion shown,...Ch. 16.7 - If member AB has the angular motion shown,...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the acceleration of points A and B on...Ch. 16.7 - At a given instant, A has a velocity of vA = 4...Ch. 16.7 - Determine the angular acceleration of rod AB at...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the acceleration of A at the instant...Ch. 16.8 - If at the same instant the disk has the angular...Ch. 16.8 - At the same instant, the boom is extending with a...Ch. 16.8 - Prob. 131PCh. 16.8 - Prob. 132PCh. 16.8 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of a water...Ch. 16.8 - At the instant shown, the cord is pulled down...Ch. 16.8 - Prob. 135PCh. 16.8 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of point C...Ch. 16.8 - Prob. 137PCh. 16.8 - Determine the magnitudes of the velocity and...Ch. 16.8 - If link AD is rotating at a constant rate of AD =...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 16.8 - If rod AB has an angular velocity of 2 rad/s and...Ch. 16.8 - Prob. 142PCh. 16.8 - If the gears center O moves with the velocity and...Ch. 16.8 - Prob. 144PCh. 16.8 - Prob. 145PCh. 16.8 - Also at this instant the car mounted at the end of...Ch. 16.8 - If the slider block C is fixed to the disk that...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of car A...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of car B...Ch. 16.8 - Link AB has a pin at B which is confined to move...Ch. 16.8 - Prob. 151PCh. 16.8 - The star wheel A makes one sixth of a revolution...Ch. 16.8 - If the tires do not slip on the pavement,...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the velocity and deceleration of the...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the speed of block B when it has risen s...Ch. 16.8 - At the instant shown, it has an acceleration of...Ch. 16.8 - If bar AB has an angular velocity AB = 6 rad/s,...Ch. 16.8 - If the cable does not slip on the pulley's...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the acceleration of the pin at C and the...Ch. 16.8 - If it does not slip at A, determine the...Ch. 16.8 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Thermodynamics. Need help solving this. Step by step with unitsarrow_forwardQuiz/An eccentrically loaded bracket is welded to the support as shown in Figure below. The load is static. The weld size for weld w1 is h1 = 4mm, for w2 h2=6mm, and for w3 is h3 -6.5 mm. Determine the safety factor (S.f) for the welds. F=29 kN. Use an AWS Electrode type (E100xx). 163 mm 133 mm 140 mm w3 wiarrow_forwardE W X FO FB F10 F11 F12 Home Q: Consider the square of Figure below.The left face is maintained at 100°C and the top face at 500°C, while the other two faces are exposed to an environment at1 00°C, h=10 W/m². C and k=10 W/m.°C. The block is 1 m square. Compute the temperature of the various nodes as indicated in Figure below and the heat flows at the boundaries. T= 500°C Alt Explain to me in detail how to calculate the matrix in the Casio calculator type (fx-991ES plus) T= 100°C 1 2 4 7 1 m- 3 1 m 5 6 T= 100°C 8 9arrow_forward
- Which of the following sequences converge and which diverge? 1) a₁ = 2+(0.1)" 1-2n 2) a = 1+2n 1/n 3 16) a = n In n 17) an = n 1/n 1-5n4 3) an = n² +8n³ 18) an = √4" n n² -2n+1 n! 20) a = 4) an = 106 5) n-1 a₁ =1+(-1)" n+1 a-(+) (1-4) 6) = 7) a = 2n (-1)"+1 2n-1 21) an = n -A" 1/(Inn) 3n+1 22) a = 3n-1 1/n x" 23) a = , x>0 2n+1 3" x 6" 24) a = 2™" xn! 2n 8) a = n+1 πT 1 9) a„ = sin +- 2 n sin n 10) an = n 25) a = tanh(n) 26) a = 2n-1 27) a = tan(n) 1 -sin n n 11) a = 2" 28) an == " 1 + 2" In(n+1) 12) a = n (In n) 200 29) a = n 13) a = 8/n 14) a 1+ =(1+²)" 15) an 7 n = 10n 30) an-√√n²-n 1"1 31) adx nixarrow_forwardA steel alloy contains 95.7 wt% Fe, 4.0 wt% W, and 0.3 wt% C.arrow_forwardb. A horizontal cantilever of effective length 3a, carries two concentrated loads W at a distance a from the fixed end and W' at a distance a from the free end. Obtain a formula for the maximum deflection due to this loading using Mohr's method. If the cantilever is 250 mm by 150mm steel I beam, 3 m long having a second moment of area I as 8500 cm4, determine W and W'to give a maximum deflection of 6 mm when the maximum stress due to bending is 90 Mpa. Take Young's modulus of material E as 185 Gpa.arrow_forward
- Which of the following sequences converge and which diverge? 1/n 1) a₁ = 2+(0.1)" 3 16) a = n 1-2n 2) a = In n 1+2n 17) an = 1/n n 1-5n4 3) an = n² +8n³ 18) an = √4" n n! n² -2n+1 20) a = 4) an = 106 5) n-1 a₁ =1+(-1)" n+1 a-(+) (1-4) 6) = 7) a = 2n (-1)"+1 2n-1 21) an = n -A" 1/(Inn) 3n+1 22) a = 3n-1 1/n x" 23) a = , x>0 2n+1 3" x 6" 24) a = 2™" xn! 2n 8) a = n+1 πT 1 9) a„ = sin +- 2 n sin n 10) an = n 25) a = tanh(n) 26) a = 2n-1 27) a = tan(n) 1 -sin n n 11) a = 2" 28) an == " 1 + 2" In(n+1) 12) a = n (In n) 200 29) a = n 13) a = 8/n 14) a 1+ =(1+²)" 15) an 7 n = 10n 30) an-√√n²-n 1"1 31) adx nixarrow_forwardCalculate the angle of incidence of beam radiation on a collector located at (Latitude 17.40S) on June 15 at 1030hrs solar time. The collector is tilted at an angle of 200, with a surface azimuth angle of 150.arrow_forwardMechanical engineering, please don't use chatgpt. Strict warningarrow_forward
- Compute the mass fraction of eutectoid cementite in an iron-carbon alloy that contains 1.00 wt% C.arrow_forwardCompute the mass fraction of eutectoid cementite in an iron-carbon alloy that contains 1.00 wt% C.arrow_forward! Required information Mechanical engineering, don't use chatgpt. Thanks A 60-kip-in. torque T is applied to each of the cylinders shown. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. 3 in. 4 in. (a) (b) Determine the inner diameter of the 4-in. diameter hollow cylinder shown, for which the maximum stress is the same as in part a. The inner diameter is in.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY