
Basic Chemistry
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780134878119
Author: Timberlake, Karen C. , William
Publisher: Pearson,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 16, Problem 51UTC
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The new nucleus after the emission of a positron needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
A proton is turned into a neutron and a positron (with a positive charge) leaves the nucleus.
Positron emission happens when a nucleus emits a positron
Expert Solution & Answer
Answer to Problem 51UTC
Solution:
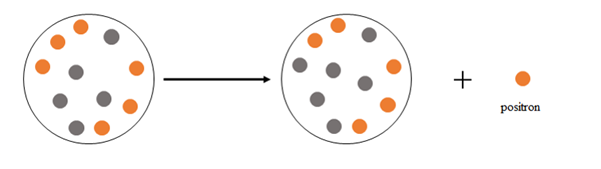
Explanation of Solution
Positron emission happens when a nucleus emits a positron
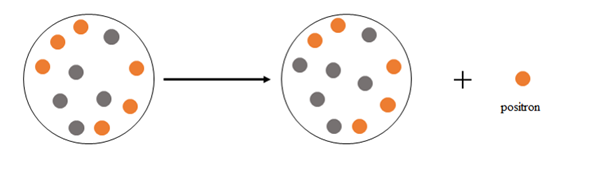
At the beginning there are 6 protons and 5 neutrons, after the emission there are 5 protons and 6 neutrons.
Conclusion
Thus, positron emission happens when a nucleus emits a positron
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Subscribe now to access step-by-step solutions to millions of textbook problems written by subject matter experts!
Students have asked these similar questions
Construct a molecular orbital energy-level diagram for BeH2. Sketch the MO pictures (schematic
representation) for the HOMO and LUMO of BeH2 [Orbital Potential Energies, H (1s): -13.6 eV; Be (2s):
-9.3 eV, Be (2p): -6.0 eV]
Indicate the isomers of the A(H2O)6Cl3 complex. State the type of isomerism they exhibit and explain it briefly.
State the formula of the compound potassium
μ-dihydroxydicobaltate (III) tetraoxalate.
Chapter 16 Solutions
Basic Chemistry
Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 1PPCh. 16.1 - Prob. 2PPCh. 16.1 - Naturally occurring potassium consists of three...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 4PPCh. 16.1 - Prob. 5PPCh. 16.1 - Prob. 6PPCh. 16.1 - Prob. 7PPCh. 16.1 - Prob. 8PPCh. 16.1 - Supply the missing information in the following...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 10PP
Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 11PPCh. 16.1 - Prob. 12PPCh. 16.2 - Prob. 13PPCh. 16.2 - Prob. 14PPCh. 16.2 - Prob. 15PPCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16PPCh. 16.2 - Prob. 17PPCh. 16.2 - Prob. 18PPCh. 16.2 - Prob. 19PPCh. 16.2 - Prob. 20PPCh. 16.2 - Prob. 21PPCh. 16.2 - Prob. 22PPCh. 16.3 - Prob. 23PPCh. 16.3 - Prob. 24PPCh. 16.3 - Prob. 25PPCh. 16.3 - Prob. 26PPCh. 16.3 - Prob. 27PPCh. 16.3 - Prob. 28PPCh. 16.4 - Prob. 29PPCh. 16.4 - Prob. 30PPCh. 16.4 - Prob. 31PPCh. 16.4 - Prob. 32PPCh. 16.4 - Prob. 33PPCh. 16.4 - Prob. 34PPCh. 16.5 - Prob. 35PPCh. 16.5 - Prob. 36PPCh. 16.5 - Prob. 37PPCh. 16.5 - Prob. 38PPCh. 16.5 - Prob. 39PPCh. 16.5 - Prob. 40PPCh. 16.6 - Prob. 41PPCh. 16.6 - Prob. 42PPCh. 16.6 - Prob. 43PPCh. 16.6 - Prob. 44PPCh. 16.6 - Prob. 45PPCh. 16.6 - Prob. 46PPCh. 16.6 - Prob. 47PPCh. 16.6 - Prob. 48PPCh. 16.6 - Prob. 49PPCh. 16.6 - Prob. 50PPCh. 16 - Prob. 51UTCCh. 16 - Prob. 52UTCCh. 16 - The chapter sections to review are shown in...Ch. 16 - Prob. 54UTCCh. 16 - Prob. 55UTCCh. 16 - Prob. 56UTCCh. 16 - Prob. 57APPCh. 16 - Prob. 58APPCh. 16 - Prob. 59APPCh. 16 - Prob. 60APPCh. 16 - Prob. 61APPCh. 16 - Prob. 62APPCh. 16 - Prob. 63APPCh. 16 - Prob. 64APPCh. 16 - Prob. 65APPCh. 16 - Prob. 66APPCh. 16 - Prob. 67APPCh. 16 - Prob. 68APPCh. 16 - Prob. 69APPCh. 16 - Prob. 70APPCh. 16 - Prob. 71APPCh. 16 - Prob. 72APPCh. 16 - Prob. 73APPCh. 16 - Prob. 74APPCh. 16 - Prob. 75APPCh. 16 - Prob. 76APPCh. 16 - Prob. 77APPCh. 16 - Prob. 78APPCh. 16 - Prob. 79CPCh. 16 - Prob. 80CPCh. 16 - Prob. 81CPCh. 16 - Prob. 82CPCh. 16 - Prob. 83CPCh. 16 - Prob. 84CPCh. 16 - Prob. 85CPCh. 16 - Prob. 86CPCh. 16 - Prob. 87CPCh. 16 - Prob. 88CPCh. 16 - Prob. 89CPCh. 16 - Prob. 90CPCh. 16 - Consider the reaction of sodium oxalate (Na2C2O4)...Ch. 16 - Prob. 34CICh. 16 - Prob. 35CICh. 16 - Prob. 36CICh. 16 - Prob. 37CICh. 16 - Prob. 38CICh. 16 - Prob. 39CICh. 16 - Prob. 40CI
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the reaction of the cyclopentanone derivative shown below. i) NaOCH2CH3 CH3CH2OH, 25°C ii) CH3!arrow_forwardWhat constitutes a 'reference material', and why does its utilization play a critical role in the chemical analysis of food products? Provide examples.arrow_forwardExplain what calibration is and why it is essential in relation to food analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forward
- The cobalt mu-hydroxide complex cobaltate(III) of potassium is a dinuclear complex. Correct?arrow_forwardThe cobalt mi-hydroxide complex cobaltate(III) of potassium is a dinuclear complex. Correct?arrow_forward3. Arrange the different acids in Exercise B # 2 from the strongest (1) to the weakest acid (10). 1. 2. (strongest) 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10 10. (weakest)arrow_forward
- Name Section Score Date EXERCISE B pH, pOH, pка, AND PKD CALCULATIONS 1. Complete the following table. Solution [H+] [OH-] PH РОН Nature of Solution A 2 x 10-8 M B 1 x 10-7 M C D 12.3 6.8 2. The following table contains the names, formulas, ka or pka for some common acids. Fill in the blanks in the table. (17 Points) Acid Name Formula Dissociation reaction Ka pka Phosphoric acid H₂PO₁ H3PO4 H++ H₂PO 7.08 x 10-3 Dihydrogen H₂PO H₂PO H+ HPO 6.31 x 10-6 phosphate Hydrogen HPO₁ 12.4 phosphate Carbonic acid H2CO3 Hydrogen HCO 6.35 10.3 carbonate or bicarbonate Acetic acid CH,COOH 4.76 Lactic acid CH₂CHOH- COOH 1.38 x 10 Ammonium NH 5.63 x 10-10 Phenol CH₂OH 1 x 10-10 Protonated form CH3NH3* 3.16 x 10-11 of methylaminearrow_forwardIndicate whether it is true that Co(III) complexes are very stable.arrow_forwardMnO2 acts as an oxidant in the chlorine synthesis reaction.arrow_forward
- In Potassium mu-dihydroxydicobaltate (III) tetraoxalate K4[Co2(C2O4)4(OH)2], indicate whether the OH ligand type is bidentate.arrow_forwardImagine an electrochemical cell based on these two half reactions with electrolyte concentrations as given below: Oxidation: Pb(s) → Pb2+(aq, 0.10 M) + 2 e– Reduction: MnO4–(aq, 1.50 M) + 4 H+(aq, 2.0 M) + 3 e– → MnO2(s) + 2 H2O(l) Calculate Ecell (assuming temperature is standard 25 °C).arrow_forward: ☐ + Draw the Fischer projection of the most common naturally-occurring form of aspartate, with the acid group at the top and the side chain at the bottom. Important: be sure your structure shows the molecule as it would exist at physiological pH. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ✓arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co