
Concept explainers
1.
Compute the basic earnings per share for Company M.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Earnings per share (EPS):
The amount of net income available to each shareholder per common share outstanding is referred to as earnings per share (EPS).
Compute the basic earnings per share for Company M.
Working notes:
(1) Calculation of weighted average shares outstanding:
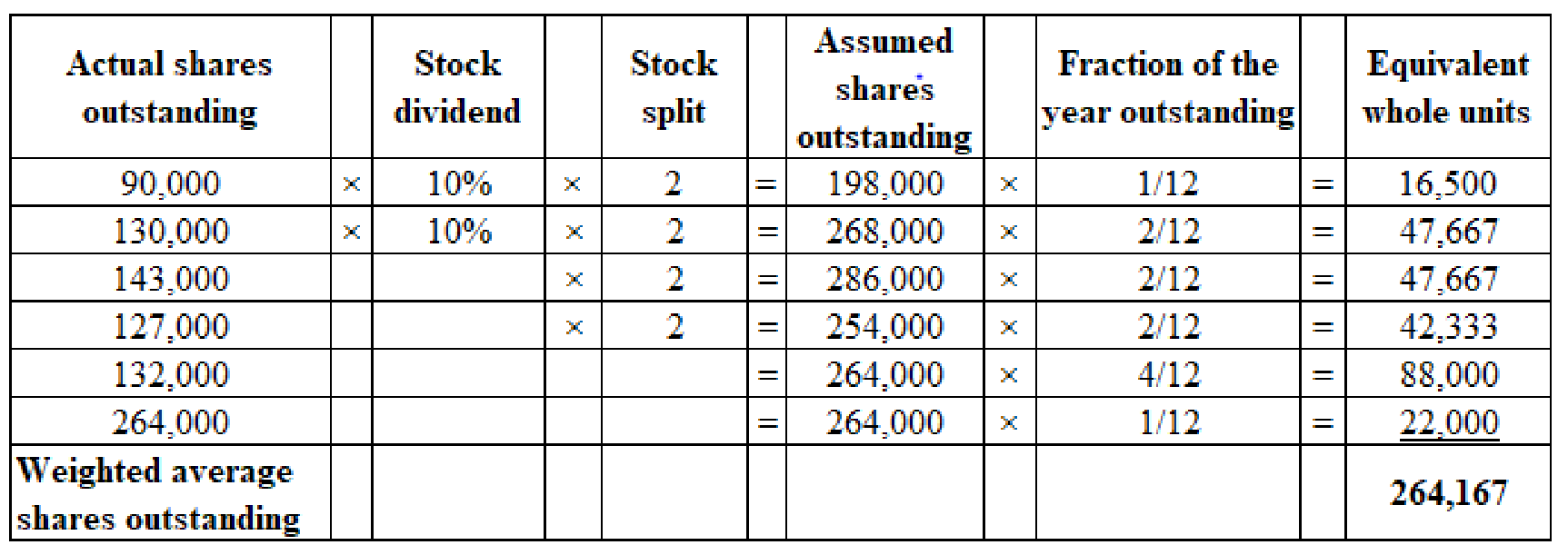
(Figure 1)
2.
Compute the tentative and incremental dilutive earnings per share for each dilutive security.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Compute tentative diluted EPS for stock options.
Compute the incremental diluted EPS for stock options.
Compute the incremental diluted EPS for convertible bonds.
Compute the incremental diluted EPS of convertible preferred stock.
Compute tentative diluted EPS assuming for 12% convertible preferred stock.
Compute tentative diluted EPS assuming, exercisable options, 9% convertible bonds, and 12% convertible preferred stock.
Working notes:
(1) Calculate the value of exercisable options:
(2) Compute the number of shares required:
(3) Compute the total weighted average number of common shares.
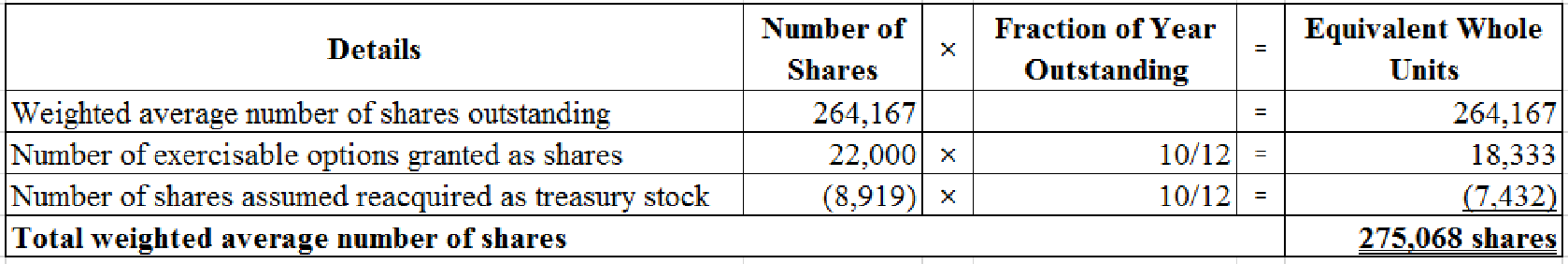
(Figure 2)
(4) Compute the amount of interest expense, net of income tax on 9% bonds.
(5) Compute the number of common shares due to conversion of 9% bonds.
(6) Compute the number of common shares due to conversion of preferred shares.
3.
Identify the amount that will be reported as basic and diluted earnings per share for the year 2019.
3.
Explanation of Solution
The Company M must report an amount of $1.95 as basic earnings per share and $1.64 as diluted earnings per share in its 2019 income statement.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
- Calculate the times-interest-earned ratios for PEPSI CO, Given the following informationarrow_forwardCalculate the times-interest-earned ratios for Coca Cola in 2020. Explain if the times-interest-earned ratios is adequate? Is the times-interest-earned ratio greater than or less than 2.5? What does that mean for the companies' income? Can the company afford the interest expense on a new loan?arrow_forwardWhich of the following is a temporary account?A. EquipmentB. Accounts PayableC. Utilities ExpenseD. Common Stockarrow_forward
- Unearned revenue becomes revenue when:A. A sale is madeB. Cash is receivedC. The service is performedD. The revenue is recordedarrow_forwardWhat is the effect of a debit to an expense account?A. Decreases expensesB. Increases equityC. Increases expensesD. Decreases assetsarrow_forwardIf total debits exceed total credits on a trial balance, the difference is most likely:A. A net lossB. A recording errorC. A net incomeD. An overstatement of assetsarrow_forward
- Which of the following accounts would be found on the post-closing trial balance?A. Service RevenueB. Salaries ExpenseC. Retained EarningsD. Dividendsarrow_forwardNeed answer What type of account is Service Revenue?A. AssetB. LiabilityC. EquityD. Revenuearrow_forwardNo chatgpt What type of account is Service Revenue?A. AssetB. LiabilityC. EquityD. Revenuearrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial & Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781285866307Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial & Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781285866307Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning



