Concept explainers
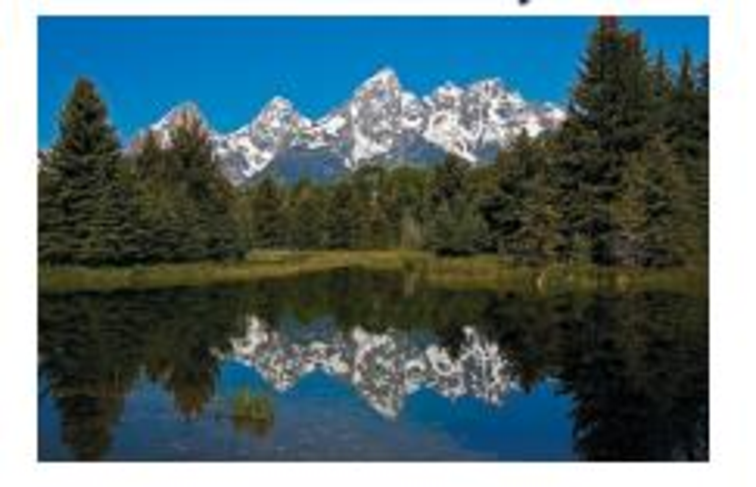
Light can pass easily through water and through air, but light will reflect from the surface of a lake. What does this tell you about the

To explain: Speed of light in air and water.
Explanation of Solution
As light passes from air to water, it changes from one medium to another. In terms of refractive index, water is denser than air.
Hence, the wave speed of light decreases in water. Therefore, some light waves undergo refraction, while some of them reflect back from the plane of water.
Conclusion:
Hence, the speed of light in air and water is described.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
- Which of the following is part of the interior of the Sun? photosphere the corona sunspots radiation zonearrow_forwardMost craters on the surface of the Moon are believed to be caused by which of the following? faults asteroids volcanoes meteoroidsarrow_forwardAn object is subjected to a friction force with magnitude 5.49 N, which acts against the object's velocity. What is the work (in J) needed to move the object at constant speed for the following routes? y (m) C B (5.00, 5.00) A x (m) © (a) the purple path O to A followed by a return purple path to O ] (b) the purple path O to C followed by a return blue path to O ] (c) the blue path O to C followed by a return blue path to O ] (d) Each of your three answers should be nonzero. What is the significance of this observation? ○ The force of friction is a conservative force. ○ The force of friction is a nonconservative force.arrow_forward
- A block of mass m = 2.50 kg is pushed d = 2.30 m along a frictionless horizontal table by a constant applied force of magnitude F = 10.0 N directed at an angle 25.0° below the horizontal as shown in the figure below. m (a) Determine the work done by the applied force. ] (b) Determine the work done by the normal force exerted by the table. ] (c) Determine the work done by the force of gravity. ] (d) Determine the work done by the net force on the block. ]arrow_forwardA man pushing a crate of mass m = 92.0 kg at a speed of v = 0.845 m/s encounters a rough horizontal surface of length = 0.65 m as in the figure below. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and rough surface is 0.357 and he exerts a constant horizontal force of 294 N on the crate. e (a) Find the magnitude and direction of the net force on the crate while it is on the rough surface. magnitude direction ---Select--- N (b) Find the net work done on the crate while it is on the rough surface. ] (c) Find the speed of the crate when it reaches the end of the rough surface. m/sarrow_forwardTwo blocks, A and B (with mass 45 kg and 120 kg, respectively), are connected by a string, as shown in the figure below. The pulley is frictionless and of negligible mass. The coefficient of kinetic friction between block A and the incline is μk = 0.26. Determine the change in the kinetic energy of block A as it moves from to, a distance of 15 m up the incline (and block B drops downward a distance of 15 m) if the system starts from rest. × J 37° Barrow_forward
- You are working for the Highway Department. In mountainous regions, highways sometimes include a runaway truck ramp, and you are asked to help with the design of such a ramp. A runaway truck ramp is often a lane of gravel adjacent to a long downhill section of roadway where trucks with failing brakes may need assistance to stop. Working with your supervisor, you develop a worst-case scenario: a truck with a mass of 6.00 × 104 kg enters a runaway truck lane traveling at 34.1 m/s. Assume that the maximum constant value for safe acceleration of the truck is -5.00 m/s². Any higher magnitude of acceleration increases the likelihood that semi-trailer rigs could jackknife. Your supervisor asks you to advise her on the required length (in m) of a runaway truck lane on a flat section of ground next to the roadway. marrow_forwardA large cruise ship of mass 6.20 × 107 kg has a speed of 10.2 m/s at some instant. (a) What is the ship's kinetic energy at this time? ] (b) How much work is required to stop it? (Give the work done on the ship. Include the sign of the value in your answer.) ] (c) What is the magnitude of the constant force required to stop it as it undergoes a displacement of 3.10 km? Narrow_forwardA 7.80 g bullet is initially moving at 660 m/s just before it penetrates a block of wood to a depth of 6.20 cm. (a) What is the magnitude of the average frictional force (in N) that is exerted on the bullet while it is moving through the block of wood? Use work and energy considerations to obtain your answer. N (b) Assuming the frictional force is constant, how much time (in s) elapses between the moment the bullet enters the block of wood and the moment it stops moving? Sarrow_forward
- Please don't use Chatgpt will upvote and give handwritten solutionarrow_forwardTwo blocks, A and B (with mass 45 kg and 120 kg, respectively), are connected by a string, as shown in the figure below. The pulley is frictionless and of negligible mass. The coefficient of kinetic friction between block A and the incline is μk = 0.26. Determine the change in the kinetic energy of block A as it moves from to ①, a distance of 15 m up the incline (and block B drops downward a distance of 15 m) if the system starts from rest. ] 37° A © Barrow_forwardA skateboarder with his board can be modeled as a particle of mass 80.0 kg, located at his center of mass. As shown in the figure below, the skateboarder starts from rest in a crouching position at one lip of a half-pipe (point). On his descent, the skateboarder moves without friction so that his center of mass moves through one quarter of a circle of radius 6.20 m. i (a) Find his speed at the bottom of the half-pipe (point Ⓡ). m/s (b) Immediately after passing point Ⓑ, he stands up and raises his arms, lifting his center of mass and essentially "pumping" energy into the system. Next, the skateboarder glides upward with his center of mass moving in a quarter circle of radius 5.71 m, reaching point D. As he passes through point ①, the speed of the skateboarder is 5.37 m/s. How much chemical potential energy in the body of the skateboarder was converted to mechanical energy when he stood up at point Ⓑ? ] (c) How high above point ① does he rise? marrow_forward
 An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning





