
Concept explainers
Write chemical equations, showing all necessary reagents, for the preparation of
by each of the following methods:
Hydroboration–oxidation of an
Use of a Grignard reagent
Use of a Grignard reagent in a way different from part (b)
Reduction of a
Hydrogenation of an
Reduction with sodium borohydride
Interpretation:
The chemical equations showing all necessary reagents for the preparation of
Concept introduction:
Hydroboration-oxidation of an alkene results in overall addition of water molecule across the double bond with a regioselectivity opposite to that of Markovnikov’s rule.
In the overall reaction, a hydrogen atom gets attached to the double bonded carbon atom having fewer hydrogens and the hydroxyl group gets attached to the carbon atom having greater number of hydrogens.
When a Grignard reagent reacts with formaldehyde primary alcohols are produced.
Grignard reagents are nucleophilic and react with oxiranes producing alcohols.
Aldehydes are reduced to the corresponding primary alcohols by using
By a suitable reducing agent like lithium aluminum hydride, carboxylic acids are reduced to the corresponding primary alcohols.
Answer to Problem 16P
Solution:
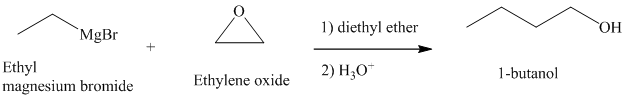

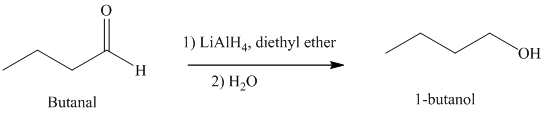
Explanation of Solution
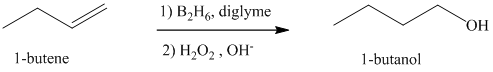
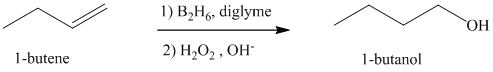
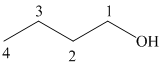
a) Hydroboration-oxidation of an alkene to form
The structure of
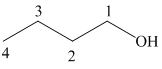
The hydroxyl group is attached to the C1 carbon atom. This alcohol is produced by hydroboration-oxidaton of an alkene. So in the alkene, the C1 carbon atom must be double bonded to the the C2 carbon atom. Thus, the alkene must be
The regioselectivity of hydroboration-oxidation is such that the hydrogen atom will get attached to the C2 carbon atom while the hydroxyl group will get attached to the C1 carbon atom producing
The reaction is shown below:
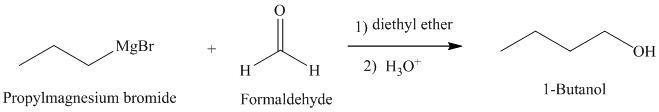
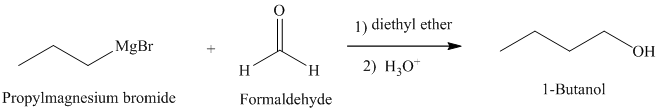
b) Grignard reagent is used to prepare
The structure of
Grignard reagents are nucleophilic and react with carbonyl groups forming a new carbon-carbon bond. An aqueous acid is used to convert the intermediate alkoxy ion to the corresponding alcohol.
In
The reaction is shown below:
c) Different Grignard reagent is used to prepare
The structure of
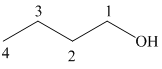
It is a primary alcohol. The hydroxyl group is attached to the C1 carbon atom.
Grignard reagents reacts with ethylene oxide to produce primary alcohol containing two more carbon atoms than the alkyl halide.
Thus, ethyl magnesium bromide, upon reaction with ethylene oxide, will produce
The reaction is shown below:
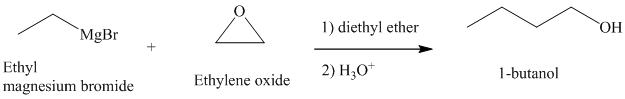
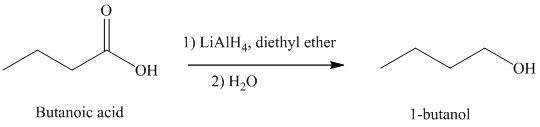
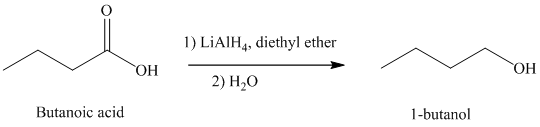
d) The reduction of carboxylic acid to produce

Carboxylic acids, upon reduction, produce the correspionding primary alcohols.
Thus, reduction of butanoic acid with Lithium aluminum hydride will produce
The reaction is shown below:
e) Hydrogenation of an aldehyde to form

Reduction of aldehydes with a suitable reducing agent produces the corresponding primary alcohols.
Thus, reduction of butanal in the presence of Lithium aluminum hydride will produce
The reaction is shown below:
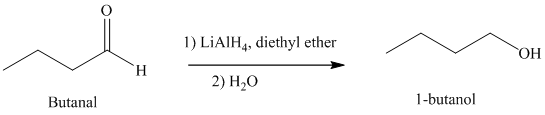
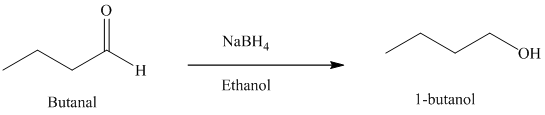
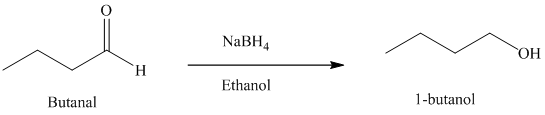
f) Reduction of an aldehyde to form

Sodium borohydride is used for the reduction of aldehydes and ketones to primary and secondary alcohols respectively.
Thus, reduction of butanal with sodium borohydride will produce
The reaction is shown below:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LOOSELEAF)-PACKAGE
- Indicate if the aldehyde shown reacts with the provided nucleophiles in acid or base conditions. a NaBH4 be Li eli -NH2 P(Ph3) f KCN g OH excess h CH3OH i NaCHCCH3arrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following organic reaction: + A ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. C © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centearrow_forwardPolar solutes are most likely to dissolve into _____, and _____ are most likely to dissolve into nonpolar solvents. A. nonpolar solutes; polar solvents B. nonpolar solvents; polar solvents C. polar solvents; nonpolar solutes D. polar solutes; nonpolar solventsarrow_forward
- Deducing the Peactants Can the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ? Δ If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Xarrow_forwardDraw all 8 stereoisomers, circling each pair of enantiomer(s)/ mirror image compound(s)arrow_forwardBookmarks Profiles Tab Window Help Chemical Formula - Aktiv Che X + → C 11 a app.aktiv.com Google Chrome isn't your default browser Set as default Question 12 of 16 Q Fri Feb 2 Verify it's you New Chrome availabl- Write the balanced molecular chemical equation for the reaction in aqueous solution for mercury(I) nitrate and chromium(VI) sulfate. If no reaction occurs, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. 3 Hg(NO3)2(aq) + Cг2(SO4)3(aq) → 3 Hg₂SO (s) + 2 Cr(NO3), (aq) ean Ui mate co ence an climate bility inc ulnerabili women, main critic CLIMATE-INI ernational + 10 O 2 W FEB 1 + 4- 3- 2- 2 2 ( 3 4 NS 28 2 ty 56 + 2+ 3+ 4+ 7 8 9 0 5 (s) (1) Ch O 8 9 (g) (aq) Hg NR CI Cr x H₂O A 80 Q A DII A F2 F3 FA F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 #3 EA $ do 50 % 6 CO & 7 E R T Y U 8 ( 9 0 F10 34 F11 川 F12 Subr + delete 0 { P }arrow_forward
- Deducing the reactants of a Diels-Alder reaction n the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ? Δ • If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. • If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. >arrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following organic reaction: + Some important notes: A ? • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardif the answer is no reaction than state that and please hand draw!arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning


