
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The products should be identified by the reaction of 2-heptanone with
Concept Introduction:
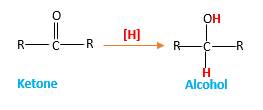
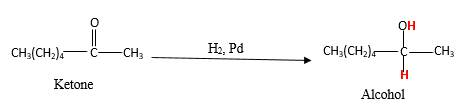
Addition of H2gas to a multiple bond is known as hydrogenation. In the presence of palladium metal as the catalyst, H2 molecules react with
Answer to Problem 16.87P
Explanation of Solution
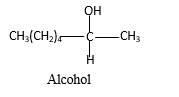
When a ketone reacts with H2 gas in the presence of palladium metal resulting product is the secondary alcohol of the initial ketone molecule. Palladium metal act as a catalyst to the reaction that provides a surface to bind both the H2 and carbonyl compound which reduce the activation energy of the reaction.
Hydrogen atoms in the alcohol molecule shown below, which are indicated in red color are the added H during the hydrogenation reaction.
(b)
Interpretation:
The products should be identified by the reaction of 2-heptanone with
Concept Introduction:
Addition of an O atom in to a molecule is known as oxidation. If a carbonyl atom consists of a hydrogen atom directly connected to the carbonyl C, it will be oxidized in the presence of an oxidizing agent such as
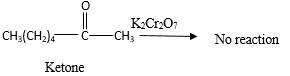
Answer to Problem 16.87P
No reaction.
Explanation of Solution
Addition of an O atom in to a molecule is known as oxidation. If a carbonyl atom consists of a hydrogen atom directly connected to the carbonyl C, it will be oxidized in the presence of an oxidizing agent such as
Hence, during the reaction no color change can be observed.
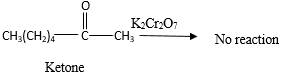
(c)
Interpretation:
The products should be identified by the reaction of 2-heptanone with
Concept Introduction:
Addition of an O atom in to a molecule is known as oxidation. If a carbonyl atom consists of a hydrogen atom directly connected to the carbonyl C, it will be oxidized in the presence of an oxidizing agent such as (
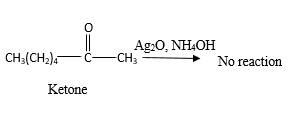
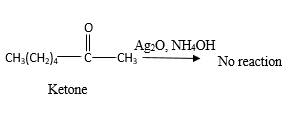
Answer to Problem 16.87P
No reaction.
Explanation of Solution
Addition of an O atom in to a molecule is known as oxidation. If a carbonyl atom consists of a hydrogen atom directly connected to the carbonyl C, it will be oxidized in the presence of an oxidizing agent such as
Hence, during the reaction is no silver mirror can be observed.
(d)
Interpretation:
The products should be identified by the reaction of 2-heptanone with
Concept Introduction:
Inthe presence of alcohol in the acidic medium, ketones undergo addition reactions and give acetal in two steps.
Hydrogen atom and CH3 groups in the acetal and hemiacetal molecules shown below, which are indicated in red color are the added molecules during the reaction.
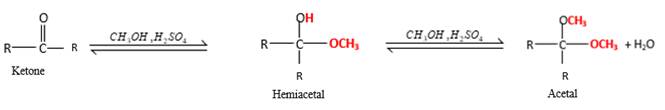
Answer to Problem 16.87P
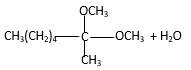
Explanation of Solution
In the presence of alcohol in the acidic medium, ketones undergo addition reactions and give acetal in two steps. In the first step ketones form hemiacetals and during the second step it converts to an acetal molecule of the respective ketone molecule.
Addition of one molecule of alcohol in to a ketone forms a hemiacetal, one bond of the
Hydrogen atom, CH3 and OCH3 groups in the acetal and hemiacetal molecules shown below, which are indicated in red color are the added molecules during the reaction.
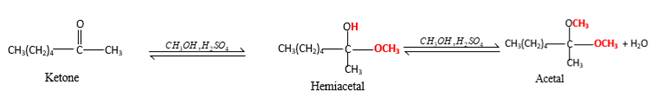
(e)
Interpretation:
The products should be identified by the reaction of 2-heptanone with
Concept Introduction:
In the presence of alcohol in the acidic medium,
Hydrogen atom and CH2CH3 groups in the acetal and hemiacetal molecules shown below, which are indicated in red color are the added molecules during the reaction.
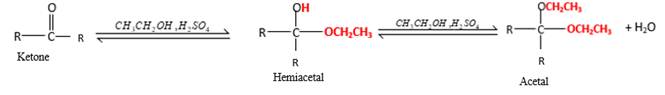
Answer to Problem 16.87P
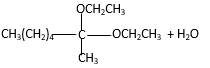
Explanation of Solution
In the presence of alcohol in the acidic medium, ketones undergo addition reactions and give acetal in two steps. In the first step ketones form hemiacetals and during the second step it converts to an acetal molecule of the respective ketone molecule.
Addition of one molecule of alcohol in to aketone forms a hemiacetal, one bond of the
Hydrogen atom, CH2CH3 and OCH2CH3 groups in the acetal and hemiacetal molecules shown below, which are indicated in red color are the added molecules during the reaction.
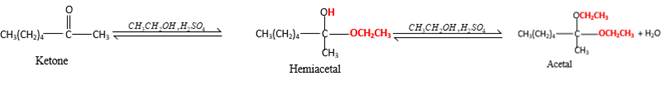
(f)
Interpretation:
The products should be identified by the reaction of
Concept Introduction:
In the presence of waterandacid, acetals undergo hydrolysis reaction and produce aldehydes.
OR' groups in the acetal molecule shown below, which are indicated in red color are the molecules which becomes alcohol molecules during the hydrolysis.
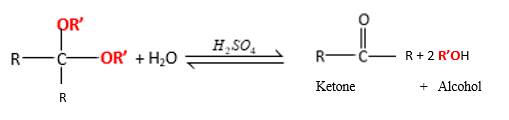
Answer to Problem 16.87P
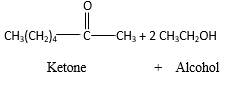
Explanation of Solution
Acetals are stable molecules, but their bonds can cleave by a reaction with water and produce aldehydes.
In the acetal molecule, two bonds of the
CH2CH3 groups in the acetal molecule shown below, which are indicated in red color are the molecules which becomes alcohol molecules during the hydrolysis.
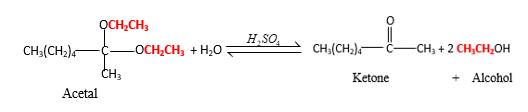
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
ALEKS 360 ACCESS CARD F/GEN. ORG.CHEM
- (a) 21.8 Name the following compounds. & (b) Br (e) O₂N. (h) H (c) Br (d) NH2 ☑N Br H ہیں Ph (g) OMe бл .0-0.e 21.9 Draw a structural formula for each compound. (a) 2,3-Dinitrotoluene (c) Diphenylmethanol (e) p-Nitroaniline (b) 3-Propylanisole (d) m-Propylphenol (f) Pentabromobenzenearrow_forwardIs this the major product of this reaction?arrow_forwardPlease helparrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





