
(a)
Interpretation:
The number of expected
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 16.62P
The number of expected
Explanation of Solution
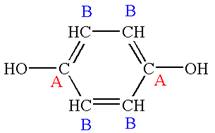
The structure of the given molecule is
The molecule has a plane of symmetry, which divides the molecule in two equal halves, and thus it has two distinct carbons indicated as
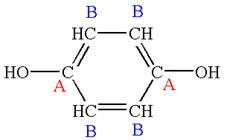
Every chemically distinct carbon atom in a molecule produces one
(b)
Interpretation:
The number of expected
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 16.62P
The number of expected
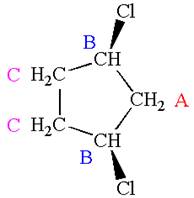
Explanation of Solution
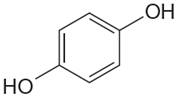
The structure of the given molecule is
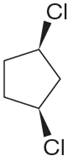
The molecule has a plane of symmetry, which divides the molecule in two equal halves, and thus it has three distinct carbons indicated as
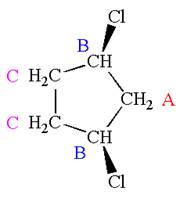
Every chemically distinct carbon atom in a molecule produces one
(c)
Interpretation:
The number of expected
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 16.62P
The number of expected
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given molecule is
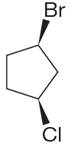
The molecule has ring with two different substituents, and thus all five carbons are distinctly indicated as
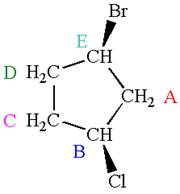
Every chemically distinct carbon atom in a molecule produces one
(d)
Interpretation:
The number of expected
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 16.62P
The number of expected
Explanation of Solution
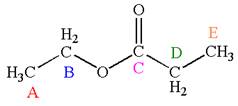
The structure of the given molecule is
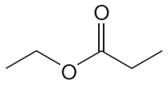
The molecule has one carbonyl carbon, two methylene carbons, and two methyl carbons. The two methylene carbons are in different chemical environment as one is bonded to oxygen and another to carbonyl carbon; thus they are distinct carbons. Therefore, the methyl carbons bonded to these methylene carbons are also distinct. Hence the molecule has total five distinct carbons indicated as
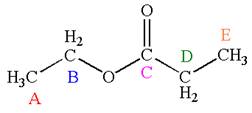
Every chemically distinct carbon atom in a molecule produces one
(e)
Interpretation:
The number of expected
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 16.62P
The number of expected
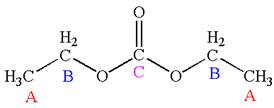
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given molecule is
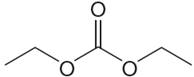
It has a plane of symmetry passing through
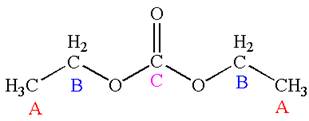
Every chemically distinct carbon atom in a molecule produces one
(f)
Interpretation:
The number of expected
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 16.62P
The number of expected
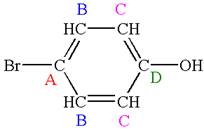
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given molecule is
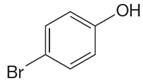
As the molecule is para disubstituted, it has a plane of symmetry passing through
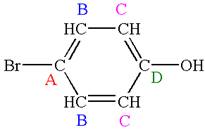
Every chemically distinct carbon atom in a molecule produces one
(g)
Interpretation:
The number of expected
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 16.62P
The number of expected
Explanation of Solution
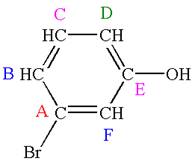
The structure of the given molecule is
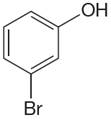
The molecule is meta disubstituted with different substituents and has no plane of symmetry; thus all carbons are chemically non-equivalent. Hence it has six chemically distinct carbons indicated as

Every chemically distinct carbon atom in a molecule produces one
(h)
Interpretation:
The number of expected
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 16.62P
The number of expected
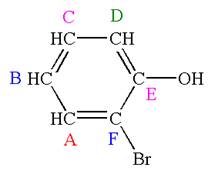
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given molecule is
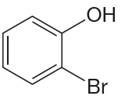
The molecule is ortho disubstituted with different substituents and has no plane of symmetry; thus all carbons are chemically non-equivalent. Hence it has six chemically distinct carbons indicated as
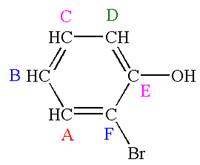
Every chemically distinct carbon atom in a molecule produces one
(i)
Interpretation:
The number of expected
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 16.62P
The number of expected
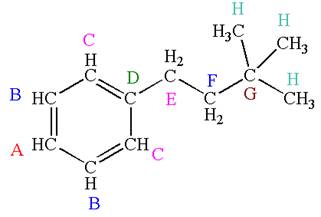
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given molecule is:\
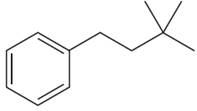
The molecule is monosubstituted benzene; thus there are four types of

Every chemically distinct carbon atom in a molecule produces one
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
EBK GET READY FOR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Predict the organic reactant of X and Y that are involved in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactant. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardPredict the major organic product for this reaction.arrow_forwardPredict the major organic product for this reaction.arrow_forward
- Predict the major organic product for this reaction.arrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forwardPlease provide the complete mechanism for the reaction below and include all appropriate arrows, formal charges, and intermediates. Please draw out the answerarrow_forward
- 3) The following molecule, chloral is a common precursor to chloral hydrate, an acetal type molecule that was a first-generation anesthetic. Draw a mechanism that accounts for tis formation and speculate why it does not require the use of an acid catalyst, like most hemiacetal and acetal reaction: (10 pts) H H₂Oarrow_forwardYou are a Quality Manager for a very well-known food ingredient company that produces umami powder, and you are responsible for setting specification limits. The net weight (in grams) of bags of unami powder is monitored by taking samples of six bags on an hourly basis during production. The label on every bag reports a contents of 1KG umami powder. The process mean is μ = 1012 g, and when the process is properly adjusted, it varies with σ = 11 g. QUESTION: Your organisation strives to ensure that >99.97% of bags of umami powder produced conforms to specification. What performance process index value is required to achieve this process yield? Calculate PPK using the following formula: Ppk = (USL – mean)/3 σ Ppk = (mean -LSL)/ 3 σarrow_forwardYou are a Quality Manager for a very well-known food ingredient company that produces umami powder, and you are responsible for setting specification limits. The net weight (in grams) of bags of unami powder is monitored by taking samples of six bags on an hourly basis during production. The label on every bag reports a contents of 1KG umami powder. The process mean is μ = 1012 g, and when the process is properly adjusted, it varies with σ = 11 g. QUESTION: Provide a valid and full justification as to whether you would advise your manager that the process is satisfactory when it is properly adjusted, or would you seek their approval to improve the process?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





