![OWLv2 for Bettelheim/Brown/Campbell/Farrell/Torres' Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry, 11th Edition, [Instant Access], 1 term (6 months)](https://s3.amazonaws.com/compass-isbn-assets/textbook_empty_images/large_textbook_empty.svg)
OWLv2 for Bettelheim/Brown/Campbell/Farrell/Torres' Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry, 11th Edition, [Instant Access], 1 term (6 months)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305106734
Author: Frederick A. Bettelheim; William H. Brown; Mary K. Campbell; Shawn O. Farrell; Omar Torres
Publisher: Cengage Learning US
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 16, Problem 16.26P
16-26 The p/fb of amphetamine is approximately 3.2
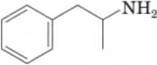
Amphetamine
(a) Which form of amphetamine (the free base or its conjugate acid) would you expect to be present at pH 1.0, the pH of stomach acid?
(b ) Which form of amphetamine would you expect to be present at pH 7.40, the pH of blood plasma?
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Where are the chiral centers in this molecule? Also is this compound meso yes or no?
PLEASE HELP! URGENT!
Where are the chiral centers in this molecule? Also is this compound meso yes or no?
Chapter 16 Solutions
OWLv2 for Bettelheim/Brown/Campbell/Farrell/Torres' Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry, 11th Edition, [Instant Access], 1 term (6 months)
Ch. 16.1 - Problem 16-1 How many hydrogen atoms does...Ch. 16.2 - Problem 16-2 Write a structural formula for each...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.3PCh. 16.4 - Problem 16-4 Select the stronger base from each...Ch. 16.5 - Prob. 16.5PCh. 16 - 16-6 Answer true or false. te/7-Butylamine is a 3°...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.7PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.8PCh. 16 - 16-9 In what way are pyridine and pyrimidine...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.10P
Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.11PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.12PCh. 16 - 16-13 Classify each amino group as primary,...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.14PCh. 16 - 16-15 There are eight primary amines with the...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.16PCh. 16 - 16-17 Propylamine (bp 48°C), ethylmethylamine (bp...Ch. 16 - 16-18 Account for the fact that 1-butanamine (bp...Ch. 16 - 16-19 2-Me thy 1 propane (bp -12°C), 2-propanol...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.20PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.21PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.22PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.23PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.24PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.25PCh. 16 - 16-26 The p/fb of amphetamine is approximately 3.2...Ch. 16 - 16-27 Guanidine, p/Ca 13.6, is a very strong base,...Ch. 16 - 16-28 Following is the structural formula of...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.29PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.30PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.31PCh. 16 - 16*32 Many tumors of the breast are correlated...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.33PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.34PCh. 16 - 16-35 (Chemical Connections 16B ) What is an...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.36PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.37PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.38PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.39PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.40PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.41PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.42PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.43PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.44PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.45PCh. 16 - 16-46 Arrange these three compounds in order of...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.47PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.48PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.49PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.50PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.51PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.52PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.53PCh. 16 - 16-54 Several poisonous plants, including Atropa...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.55PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.56PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.57PCh. 16 - 16-58 Following is a structural formula of...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.59P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A mixture of C7H12O2, C9H9OCl, biphenyl and acetone was put together in a gas chromatography tube. Please decide from the GC resutls which correspond to the peak for C7,C9 and biphenyl and explain the reasoning based on GC results. Eliminate unnecessary peaks from Gas Chromatography results.arrow_forwardIs the molecule chiral, meso, or achiral? CI .CH3 H₂C CIarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP ! URGENT!arrow_forward
- Identify priority of the substituents: CH3arrow_forwardHow many chiral carbons are in the molecule? OH F CI Brarrow_forwardA mixture of three compounds Phen-A, Acet-B and Rin-C was analyzed using TLC with 1:9 ethanol: hexane as the mobile phase. The TLC plate showed three spots of R, 0.1 and 0.2 and 0.3. Which of the three compounds (Phen-A; Acet-B or Rin-C) would have the highest (Blank 1), middle (Blank 2) and lowest (Blank 3) spot respectively? 0 CH: 0 CH, 0 H.C OH H.CN OH Acet-B Rin-C phen-A A A <arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry | Acids & Bases; Author: Ninja Nerd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AOr_5tbgfQ0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY