
(a)
Interpretation:
Average rate over the entire experiment has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Relative rates and stoichiometry: During a
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The reaction given is:
The average rate of the chemical reaction:
Substituting in the equation (1) as follows,
Therefore, the average rate over the entire experiment was
(b)
Interpretation:
Average rate between
Concept introduction:
Relative rates and stoichiometry: During a chemical reaction, amounts of reactant decrease with time and amounts of products increases.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The reaction given is:
The average rate of the chemical reaction:
Substituting in the equation (1) as follows,
Therefore, the average rate between
(c)
Interpretation:
Initial reaction rate has to be calculated using graphical method.
Concept introduction:
Rate law or rate equation: The relationship between the reactant concentrations and reaction rate is expressed by an equation.
Order of a reaction: The order of a reaction with respect to a particular reactant is the exponent of its concentration term in the rate law expression, and the overall reaction order is the sum of the exponents on all concentration terms.
Rate constant, k: It is a proportionality constant that relates rate and concentration at a given temperature.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
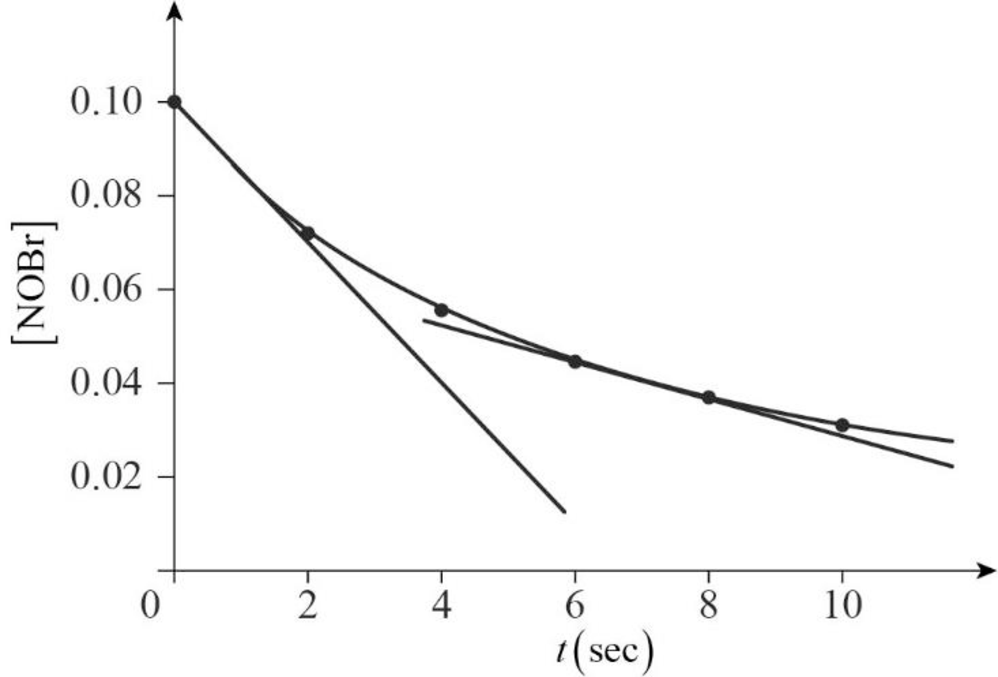
Figure.1
Using the given values, the graph has been plotted as shown above.
The initial reaction rate is calculated as shown below,
Therefore, the initial reaction rate obtained as
(d)
Interpretation:
Concept introduction:
Rate law or rate equation: The relationship between the reactant concentrations and reaction rate is expressed by an equation.
Order of a reaction: The order of a reaction with respect to a particular reactant is the exponent of its concentration term in the rate law expression, and the overall reaction order is the sum of the exponents on all concentration terms.
Rate constant, k: It is a proportionality constant that relates rate and concentration at a given temperature.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The reaction rate at
Therefore, the reaction rate at
(e)
Interpretation:
Particular time the instantaneous rate equal the average rate over the entire experiment has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Rate law or rate equation: The relationship between the reactant concentrations and reaction rate is expressed by an equation.
Order of a reaction: The order of a reaction with respect to a particular reactant is the exponent of its concentration term in the rate law expression, and the overall reaction order is the sum of the exponents on all concentration terms.
Rate constant, k: It is a proportionality constant that relates rate and concentration at a given temperature.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The average between
Rate of reaction at
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change - Standalone book
- Can I please get help with this.arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





