
Concept explainers
a Draw a pH titration curve that represents the titration of 25.0 mL of 0.15 M propionic acid. CH3CH2COOH, by the addition of 0.15 M KOH from a buret. Label the axes and put a scale on each axis. Show where the equivalence point and the buffer region are on the titration curve. You should do calculations for the 0%, 50%, 60%, and 100% titration points. b Is the solution neutral, acidic, or basic at the equivalence point? Why?
(a)
Interpretation:
For titration of 25.0 mL of 0.15 M propionic acid,
A pH titration curve showing the equivalence point and buffer region has to be drawn
- (a) The pH of the titration points for the 0%, 50%, 60% and 100% has to be calculated
- (b) Whether the solution at the equivalence point is neutral, acidic or basic has to be explained
Concept Introduction:
Equivalence point:
The equivalence point in titration is the point where the amount of standard titrant solution (in moles) and the unknown concentration analyte solution (in moles) becomes equal.
In other words, the equivalence point is the point obtained in a titration once a stoichiometric amount of reactant has been added.
Relationship between pH and pOH:
Answer to Problem 16.120QP
A pH titration curve showing the equivalence point and buffer region is given in Figure 1 as follows,
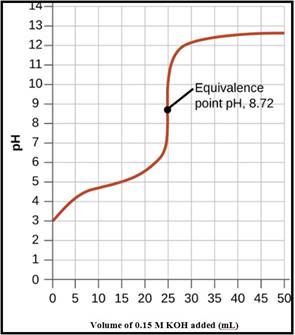
Figure 1
(a)
The pH at the 0% titration point is 2.85
The pH at the 50% titration point is 4.89
The pH at the 60% titration point is 5.06
The pH at the 100% titration point is 8.88
Explanation of Solution
To Draw: A pH titration curve showing the equivalence point and buffer region
The pH titration curve for the titration of 0.15 M propionic acid with 0.15 M
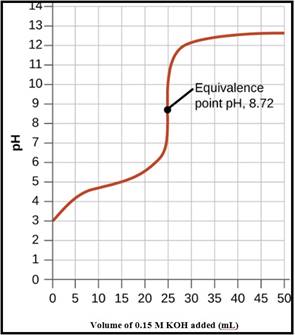
Figure 1
(a)
To Calculate: The pH of the titration points for the 0%, 50 %, 60% and 100%
Given data:
Titration of 0.15 M propionic acid with 0.15 M
pH at the 0% titration point:
Construct an equilibrium table with x as unknown concentration
Consider propionic acid as
|
|
|||
| Initial |
0.15
0.15-x |
0.00 | 0.00 |
| Change |
|
|
|
| Equilibrium |
x | x | |
Substitute equilibrium concentrations into the equilibrium-constant equation.
The
Assume x is negligible compared to 0.15 M
Therefore, the concentration of hydronium ion
In the end, pH is calculated as follows,
Therefore, the pH at the 0% titration point is 2.85
pH at the 50% titration point:
The pH is calculated as follows,
Therefore, the pH at the 50% titration point is 4.89
pH at the 60% titration point:
For convenience, express the concentrations as percents.
Substitute the concentrations into the equilibrium expression.
Therefore, the concentration of hydronium ion
In the end, pH is calculated as follows,
Therefore, the pH at the 60% titration point is 5.06
pH at the 100% titration point:
The salt that got produced has undergone a twofold dilution.
Therefore,
Construct an equilibrium table with x as unknown concentration
|
|
|||
| Initial |
0.0750
0.0750-x |
0.00 | 0.00 |
| Change |
|
|
|
| Equilibrium |
x | x | |
Now, calculate
Substitute into the equilibrium constant expression.
Here, x gives the concentration of hydroxide ion,
The pH is calculated as follows,
Therefore, the pH at the 100% titration point is 8.88
The pH at the 0% titration point was calculated as 2.85
The pH at the 50% titration point was calculated as 4.89
The pH at the 60% titration point was calculated as 5.06
The pH at the 100% titration point was calculated as 8.88
(b)
Interpretation:
For titration of 25.0 mL of 0.15 M propionic acid,
A pH titration curve showing the equivalence point and buffer region has to be drawn
- (a) The pH of the titration points for the 0%, 50%, 60% and 100% has to be calculated
- (b) Whether the solution at the equivalence point is neutral, acidic or basic has to be explained
Concept Introduction:
Equivalence point:
The equivalence point in titration is the point where the amount of standard titrant solution (in moles) and the unknown concentration analyte solution (in moles) becomes equal.
In other words, the equivalence point is the point obtained in a titration once a stoichiometric amount of reactant has been added.
Relationship between pH and pOH:
Answer to Problem 16.120QP
The solution at the equivalence point is basic
Explanation of Solution
To Explain: Whether the solution at the equivalence point is neutral, acidic or basic
As a result of titration Potassium propionate salt is produced.
Potassium propionate is the salt of a weak acid and a strong base.
Propionate ion reacts with water to produce hydroxide ions.
Therefore, the given solution is basic
The solution at the equivalence point was found as basic
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Bundle: General Chemistry, Loose-leaf Version, 11th + OWLv2, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- 3.2 32 Consider calibrating a calorimeter and measuring heat transferred. A sample of compound was burned in a calorimeter and a temperature change of 3.33°C recorded. When a 1.23 A current from a 12.0 V source was passed through a heater in the same calorimeter for 156 s, the temperature changed of 4.47°C was recorded. 3.2.1 Calculate the heat supplied by the heater. 3.2.2 Calculate the calorimeter constant. 3.2.3 Calculate the heat released by the combustion reaction.arrow_forward-.1 Consider the standard enthalpy of formation of gaseous water at 25°C as -241.82 kJ/mol and calculate the standard enthalpy of formation of gaseous water at 100°C.arrow_forward3.5 Complete the following sentences to make correct scientific meaning. 3.5.1 The entropy of a perfect gas. 3.5.2 when it expands isothermally. The change in entropy of a substance accompanying a change of state at its transition 3.5.3 temperature is calculated from its of transition. The increase in entropy when a substance is heated is calculated from itsarrow_forward
- 3.4 Consider the internal energy of a substance 3.4.1 Draw a graph showing the variation of internal energy with temperature at constant volume 3.4.2 Write the mathematical expression for the slope in your graph in 3.4.1arrow_forwardFor a system, the excited state decays to the ground state with a half-life of 15 ns, emitting radiation of 6000 Å. Determine the Einstein coefficients for stimulated absorption and spontaneous emission and the dipole moment of the transition. Data: epsilon 0 = 8.85419x10-12 C2m-1J-1arrow_forwardProblem a. The following compounds have the same molecular formula as benzene. How many monobrominated products could each form? 1. HC =CC=CCH2CH3 2. CH2=CHC = CCH=CH₂ b. How many dibrominated products could each of the preceding compounds form? (Do not include stereoisomers.)arrow_forward
- Don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward4.3 Explain the following terms: 4.3.1 Normal boiling point. 4.3.2 Cooling curve. 4.3.3 Congruent melting. 4.3.4 Ideal solution. 4.3.5 Phase diagram of a pure substance.arrow_forwardFor CO, an electronic transition occurs at 2x1015 Hz. If the dipole moment of the transition is of the order of 1 Debye, calculate:a) The Einstein coefficient of stimulated emissionb) The lifetime of the excited statec) The natural width (in Hz)Data: epsilon 0 = 8.85419x10-12 C2m-1J-1; 1 D = 3.33564x10-30 C m;arrow_forward
- A radiation of intensity l0 = 2.5x1010 photos s-1 cm2 affects a dispersion and produces a transmittance of 0.1122. How much incident radiation is absorbed by the music screen?arrow_forwardIf a radiation intensity l0 = 2.5x1010 fotones s-1 cm2 causes a dissolución and an absorbance of 0.95 will be recorded. How much incident radiation is absorbed by the music screen?arrow_forwardFrom the causes of the detection of a spectral band of a spectrum obtained by a signal in the gaseous phase that is indicated, you can avoid or minimize those that have their origin in:a) the Doppler effectb) collisionsc) the life time of the excited statearrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning





