
Chemistry
12th Edition
ISBN: 9780078021510
Author: Raymond Chang Dr., Kenneth Goldsby Professor
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 15.8, Problem 1RC
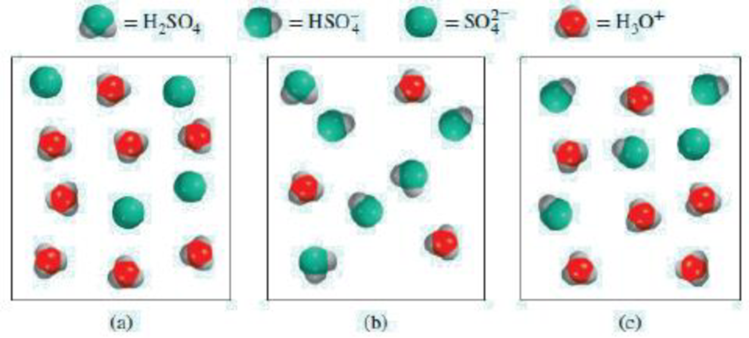
Which of the diagrams (a)–(c) represents a solution of sulfuric acid? Water molecules have been omitted for clarity.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Where are the chiral centers in this molecule? Also is this compound meso yes or no?
PLEASE HELP! URGENT!
Where are the chiral centers in this molecule? Also is this compound meso yes or no?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Chemistry
Ch. 15.1 - Identify the conjugate acid-base pairs for the...Ch. 15.1 - Which of the following does not constitute a...Ch. 15.2 - Prob. 2PECh. 15.2 - Prob. 1RCCh. 15.3 - Nitric acid (HNO3) is used in the production of...Ch. 15.3 - The pH of a certain orange juice is 3.33....Ch. 15.3 - Prob. 5PECh. 15.3 - Which is more acidic: a solution where [H+] =2.5 ...Ch. 15.4 - Prob. 6PECh. 15.4 - Predict whether the equilibrium constant for the...
Ch. 15.4 - Prob. 1RCCh. 15.5 - What is the pH of a 0.122 M monoprotic acid whose...Ch. 15.5 - The pH of a 0.060 M weak monoprotic acid is 3.44....Ch. 15.5 - The concentration of water is 55.5 M. Calculate...Ch. 15.6 - Calculate the pH of a 0.26 M methylamine solution...Ch. 15.6 - Consider the following three solutions of equal...Ch. 15.7 - Consider the following two acids and their...Ch. 15.8 - Calculate the concentrations of H2C2O4, HC2O4,...Ch. 15.8 - Which of the diagrams (a)(c) represents a solution...Ch. 15.9 - Which of the following acids is weaker: HClO2 or...Ch. 15.10 - Calculate the pH of a 0.24 M sodium formate...Ch. 15.10 - Prob. 14PECh. 15.10 - The diagrams shown here represent solutions of...Ch. 15.11 - Prob. 1RCCh. 15.12 - Identify the Lewis acid and Lewis base in the...Ch. 15.12 - Prob. 1RCCh. 15 - Define Brnsted acids and bases. Give an example of...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.2QPCh. 15 - Classify each of the following species as a...Ch. 15 - Write the formulas of the conjugate bases of the...Ch. 15 - Identify the acid-base conjugate pairs in each of...Ch. 15 - Write the formula for the conjugate acid of each...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.7QPCh. 15 - Write the formula for the conjugate base of each...Ch. 15 - What is the ion-product constant for water?Ch. 15 - Write an equation relating [H+] and [OH] in...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.12QPCh. 15 - The pH of a solution is 6.7. From this statement...Ch. 15 - Define pOH. Write the equation relating pH and...Ch. 15 - Calculate the concentration of OH ions in a 1.4 ...Ch. 15 - Calculate the concentration of H+ ions in a 0.62 M...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH of each of the following...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH of each of the following...Ch. 15 - Calculate the hydrogen ion concentration in mol/L...Ch. 15 - Calculate the hydrogen ion concentration in mol/L...Ch. 15 - Complete the following table for a solution: pH...Ch. 15 - Fill in the word acidic, basic, or neutral for the...Ch. 15 - The pOH of a strong base solution is 1.88 at 25C....Ch. 15 - Calculate the number of moles of KOH in 5.50 mL of...Ch. 15 - How much NaOH (in grams) is needed to prepare 546...Ch. 15 - A solution is made by dissolving 18.4 g of HCl in...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.27QPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.28QPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.29QPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.30QPCh. 15 - Which of the following diagrams best represents a...Ch. 15 - (1) Which of the following diagrams represents a...Ch. 15 - Classify each of the following species as a weak...Ch. 15 - Classify each of the following species as a weak...Ch. 15 - Which of the following statements is/are true for...Ch. 15 - Which of the following statements is/are true...Ch. 15 - Predict the direction that predominates in this...Ch. 15 - Predict whether the following reaction will...Ch. 15 - What does the ionization constant tell us about...Ch. 15 - List the factors on which the Ka of a weak acid...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.41QPCh. 15 - Which of the following solutions has the highest...Ch. 15 - The Ka for benzoic acid is 6.5 105. Calculate the...Ch. 15 - A 0.0560-g quantity of acetic acid is dissolved in...Ch. 15 - The pH of an acid solution is 6.20. Calculate the...Ch. 15 - What is the original molarity of a solution of...Ch. 15 - Calculate the percent ionization of benzoic acid...Ch. 15 - Calculate the percent ionization of hydrofluoric...Ch. 15 - A 0.040 M solution of a monoprotic acid is 14...Ch. 15 - (a) Calculate the percent ionization of a 0.20 M...Ch. 15 - Use NH3 to illustrate what we mean by the strength...Ch. 15 - Which of the following has a higher pH: (a) 0.20 M...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH of a 0.24 M solution of a weak...Ch. 15 - The diagrams here represent three different weak...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH for each of the following...Ch. 15 - The pH of a 0.30 M solution of a weak base is...Ch. 15 - What is the original molarity of a solution of...Ch. 15 - In a 0.080 M NH3 solution, what percent of the NH3...Ch. 15 - Write the equation relating Ka for a weak acid and...Ch. 15 - From the relationship KaKb = Kw, what can you...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.61QPCh. 15 - Write all the species (except water) that are...Ch. 15 - The first and second ionization constants of a...Ch. 15 - Compare the pH of a 0.040 M HCl solution with that...Ch. 15 - What are the concentrations of HSO4, SO42 and H+...Ch. 15 - Calculate the concentrations of H+, HCO3, and CO32...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.67QPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.68QPCh. 15 - Predict the acid strengths of the following...Ch. 15 - Compare the strengths of the following pairs of...Ch. 15 - Which of the following is the stronger acid:...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.72QPCh. 15 - Define salt hydrolysis. Categorize salts according...Ch. 15 - Explain why small, highly charged metal ions are...Ch. 15 - Al3+ is not a Brnsted acid but is Al(H2O)63+....Ch. 15 - Specify which of the following salts will undergo...Ch. 15 - Predict the pH ( 7, 7, or 7) of aqueous...Ch. 15 - Predict whether the following solutions are...Ch. 15 - A certain salt, MX (containing the M+ and X ions),...Ch. 15 - In a certain experiment a student finds that the...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH of a 0.36 M CH3COONa solution.Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH of a 0.42 M NH4Cl solution.Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.83QPCh. 15 - Predict whether a solution containing the salt...Ch. 15 - Classify the following oxides as acidic, basic,...Ch. 15 - Write equations for the reactions between (a) CO2...Ch. 15 - Explain why metal oxides tend to be basic if the...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.88QPCh. 15 - Zn(OH)2 is an amphoteric hydroxide. Write balanced...Ch. 15 - Al(OH)3 is an insoluble compound. It dissolves in...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.91QPCh. 15 - In terms of orbitals and electron arrangements,...Ch. 15 - Classify each of the following species as a Lewis...Ch. 15 - Describe the following reaction in terms of the...Ch. 15 - Which would be considered a stronger Lewis acid:...Ch. 15 - All Brnsted acids are Lewis acids, but the reverse...Ch. 15 - Determine the concentration of a NaNO2 solution...Ch. 15 - Determine the concentration of a NH4Cl solution...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.99QPCh. 15 - A typical reaction between an antacid and the...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.101QPCh. 15 - The pH of a 0.0642 M solution of a monoprotic acid...Ch. 15 - Like water, liquid ammonia undergoes...Ch. 15 - HA and HB are both weak acids although HB is the...Ch. 15 - A solution contains a weak monoprotic acid HA and...Ch. 15 - The three common chromium oxides are CrO, Cr2O3,...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.107QPCh. 15 - Use the data in Table 15.3 to calculate the...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.109QPCh. 15 - Calculate the pH of a 0.20 M ammonium acetate...Ch. 15 - Novocaine, used as a local anesthetic by dentists,...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.112QPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.113QPCh. 15 - The ion product of D2O is 1.35 1015 at 25C. (a)...Ch. 15 - Give an example of the following: (a) a weak acid...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.116QPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.117QPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.118QPCh. 15 - When chlorine reacts with water, the resulting...Ch. 15 - When the concentration of a strong acid is not...Ch. 15 - Calculate the pH of a 2.00 M NH4CN solution.Ch. 15 - Calculate the concentrations of all species in a...Ch. 15 - Identify the Lewis acid and Lewis base that lead...Ch. 15 - Very concentrated NaOH solutions should not be...Ch. 15 - In the vapor phase, acetic acid molecules...Ch. 15 - Calculate the concentrations of all the species in...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.127QPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.128QPCh. 15 - How many grams of NaCN would you need to dissolve...Ch. 15 - A solution of formic acid (HCOOH) has a pH of...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.131QPCh. 15 - A 1.87-g sample of Mg reacts with 80.0 mL of a HCl...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.133QPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.134QPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.135QPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.136QPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.137QPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.138QPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.139QPCh. 15 - The atmospheric sulfur dioxide (SO2) concentration...Ch. 15 - Calcium hypochlorite [Ca(OCl)2] is used as a...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.142QPCh. 15 - About half of the hydrochloric acid produced...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.144QPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.145QPCh. 15 - How many milliliters of a strong monoprotic acid...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.147QPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.148QPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.149QPCh. 15 - A 1.294-g sample of a metal carbonate (MCO3) is...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.151QPCh. 15 - Calculate the pH of a solution that is 1.00 M HCN...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.153QPCh. 15 - Use the vant Hoff equation (see Problem 14.119.)...Ch. 15 - At 28C and 0.982 atm, gaseous compound HA has a...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.156QPCh. 15 - Calculate the pH of a 0.20 M NaHCO3...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.158QPCh. 15 - In this chapter, HCl, HBr, and HI are all listed...Ch. 15 - Use the data in Appendix 2 to calculate the for...Ch. 15 - Malonic acid [CH2(COOH)2] is a diprotic acid....Ch. 15 - Look up the contents of a Tums tablet. How many...Ch. 15 - Phosphorous acid, H3PO3(aq), is a diprotic acid...Ch. 15 - Chicken egg shells are composed primarily of...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A mixture of C7H12O2, C9H9OCl, biphenyl and acetone was put together in a gas chromatography tube. Please decide from the GC resutls which correspond to the peak for C7,C9 and biphenyl and explain the reasoning based on GC results. Eliminate unnecessary peaks from Gas Chromatography results.arrow_forwardIs the molecule chiral, meso, or achiral? CI .CH3 H₂C CIarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP ! URGENT!arrow_forward
- Identify priority of the substituents: CH3arrow_forwardHow many chiral carbons are in the molecule? OH F CI Brarrow_forwardA mixture of three compounds Phen-A, Acet-B and Rin-C was analyzed using TLC with 1:9 ethanol: hexane as the mobile phase. The TLC plate showed three spots of R, 0.1 and 0.2 and 0.3. Which of the three compounds (Phen-A; Acet-B or Rin-C) would have the highest (Blank 1), middle (Blank 2) and lowest (Blank 3) spot respectively? 0 CH: 0 CH, 0 H.C OH H.CN OH Acet-B Rin-C phen-A A A <arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Chemistry
ISBN:9781559539418
Author:Angelica Stacy
Publisher:MAC HIGHER
Solutions: Crash Course Chemistry #27; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9h2f1Bjr0p4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY