
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780130970695
Author: Peter S. Shaffer, Lillian C. McDermott
Publisher: Addison Wesley
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 15.5, Problem 4dTH
A bicycle coasts up a hill while a car drives up the hill at constant speed. The strobe diagram shows their positions at instants 1−4, separated by equal time intervals. The bicycle comes to rest relative to the road at instant 4.
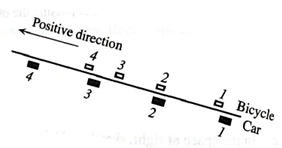
-
d. In the frame of the car, is the bicycle
speeding up, slowing down, or
moving with constant speed:
- At instant 2?
- At instant 3?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Statistical thermodynamics. The number of imaginary replicas of a system of N particlesa) cannot be greater than Avogadro's numberb) must always be greater than Avogadro's number.c) has no relation to Avogadro's number.
Lab-Based Section
Use the following information to answer the lab based scenario.
A student performed an experiment in an attempt to determine the index of refraction of glass.
The student used a laser and a protractor to measure a variety of angles of incidence and
refraction through a semi-circular glass prism. The design of the experiment and the student's
results are shown below.
Angle of
Incidence (°)
Angle of
Refraction (º)
20
11
30
19
40
26
50
31
60
36
70
38
2a) By hand (i.e., without using computer software), create a linear graph on graph paper
using the student's data. Note: You will have to manipulate the data in order to achieve a
linear function.
2b) Graphically determine the index of refraction of the semi-circular glass prism, rounding your
answer to the nearest hundredth.
Use the following information to answer the next two questions.
A laser is directed at a prism made of zircon (n = 1.92) at an incident angle of 35.0°, as shown in
the diagram.
3a) Determine the critical angle of zircon.
35.0°
70°
55
55°
3b) Determine the angle of refraction when the laser beam leaves the prism.
Chapter 15 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Ch. 15.1 - Describe the motion. During which periods of time,...Ch. 15.1 - Find the object’s instantaneous velocity at each...Ch. 15.1 - For each of the following intervals, find the...Ch. 15.1 - In which of the cased from part c, if any, is the...Ch. 15.1 - In the interval from t=0s to t=6s , does the...Ch. 15.1 - In the small box on the graph above is a portion...Ch. 15.1 - Next, we expand the section of the previous graph...Ch. 15.1 - All three graphs are representations of the same...Ch. 15.1 - Suppose that the object is speeding up. Which of...Ch. 15.1 - Suppose that the object is slowing down. Which of...
Ch. 15.1 - Describe how you could use these devices to...Ch. 15.1 - Describe how you could use these devices to...Ch. 15.2 - In each of the following exercises, a motion will...Ch. 15.2 - In each of the following exercises, a motion will...Ch. 15.2 - In each of the following exercises, a motion will...Ch. 15.2 - In each of the following exercises, a motion will...Ch. 15.2 - In each of the following exercises, a motion will...Ch. 15.2 - In each of the following exercises, a motion will...Ch. 15.2 - In each of the following exercises, a motion will...Ch. 15.2 - In each of the following exercises, a motion will...Ch. 15.2 - There are several answers for most of the...Ch. 15.2 - There are several answers for most of the...Ch. 15.2 - There are several answers for most of the...Ch. 15.3 - A ball rolls up, then down an incline. Sketch an...Ch. 15.3 - Sketch x versus t, v versus t, and a versus t...Ch. 15.3 - Sketch x versus t, v versus t, and a versus t...Ch. 15.3 - Sketch x versus t, v versus t, and a versus t...Ch. 15.3 - Describe the motion of an object: For which the...Ch. 15.3 - Describe the motion of an object: b. For which the...Ch. 15.3 - Describe the motion of an object: c. For which the...Ch. 15.3 - Describe the motion of an object: d. For which the...Ch. 15.3 - Two carts roll toward each other on a level table....Ch. 15.3 - Two carts roll toward each other on a level table....Ch. 15.3 - Two carts roll toward each other on a level table....Ch. 15.3 - In this problem, a Cart moves in various ways on a...Ch. 15.3 - In this problem, a Cart moves in various ways on a...Ch. 15.3 - In this problem, a Cart moves in various ways on a...Ch. 15.3 - Carts A and B move along a horizontal track. The...Ch. 15.3 - Carts A and B move along a horizontal track. The...Ch. 15.3 - Carts A and B move along a horizontal track. The...Ch. 15.3 - Carts A and B move along a horizontal track. The...Ch. 15.3 - Two cars, C and D, travel in the same direction on...Ch. 15.3 - Two cars, P and Q, travel in the same direction on...Ch. 15.3 - Two cars, P and Q, travel in the same direction on...Ch. 15.4 - Prob. 1aTHCh. 15.4 - Prob. 1bTHCh. 15.4 - Describe how you would determine the acceleration...Ch. 15.4 - Copy vG and vH (placed “tailtotail”) in the space...Ch. 15.4 - Generalize your results above and from tutorial to...Ch. 15.4 - For each instant, state whether the object is...Ch. 15.4 - The diagram at right illustrates how the...Ch. 15.4 - For each of the instants 14, compare your...Ch. 15.4 - Choose a point about 1/8th of the way around the...Ch. 15.4 - Prob. 3bTHCh. 15.4 - How would you characterize the direction of v as...Ch. 15.4 - Each of the following statements in incorrect....Ch. 15.4 - On the diagram at right, draw vectors that...Ch. 15.4 - On the diagram at right, draw vectors that...Ch. 15.4 - Draw arrows on the diagram at points AG to...Ch. 15.4 - Next to each of the labeled points, state whether...Ch. 15.4 - Draw arrows on the diagram below to show the...Ch. 15.4 - On the diagram at right, draw velocity vectors for...Ch. 15.4 - On the diagram at right, draw the acceleration...Ch. 15.4 - How does the magnitude of the acceleration at E...Ch. 15.5 - Reference frame of boat B: Complete the upper...Ch. 15.5 - Reference frame of boat A: Complete the diagram at...Ch. 15.5 - Is the speed of the kayak in the frame of boat A...Ch. 15.5 - Rank the following quantities in order of...Ch. 15.5 - A third riverboat, boat C, moves downstream so as...Ch. 15.5 - Prob. 2aTHCh. 15.5 - A car, a truck, and a traffic cone are on a...Ch. 15.5 - The relationship vcar,cone=vcar,truck+vtruck,cone...Ch. 15.5 - Car P moves to the west with constant speed v0...Ch. 15.5 - Car P moves to the west with constant speed v0...Ch. 15.5 - Car P moves to the west with constant speed v0...Ch. 15.5 - Car P moves to the west with constant speed v0...Ch. 15.5 - Car P moves to the west with constant speed v0...Ch. 15.5 - A bicycle coasts up a hill while a car drives up...Ch. 15.5 - A bicycle coasts up a hill while a car drives up...Ch. 15.5 - A bicycle coasts up a hill while a car drives up...Ch. 15.5 - A bicycle coasts up a hill while a car drives up...Ch. 15.5 - A bicycle coasts up a hill while a car drives up...Ch. 15.5 - A bicycle coasts up a hill while a car drives up...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Your bore cells, muscle cells, and skin cells look different because a. different kinds of genes are present in...
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
What is the difference between cellular respiration and external respiration?
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
DRAW IT Pea plants heterozygous for flower position and stem length (AaTt) are allowed to self-pollinate, and ...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. Based on computer models, when is plan...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
How can 1H NMR distinguish between the compounds in each of the following pairs?
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
10.71 Identify each of the following as an acid or a base: (10.1)
H2SO4
RbOH
Ca(OH)2
HI
...
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Use the following information to answer the next two questions. A laser is directed at a prism made of zircon (n = 1.92) at an incident angle of 35.0°, as shown in the diagram. 3a) Determine the critical angle of zircon. 35.0° 70° 55 55° 3b) Determine the angle of refraction when the laser beam leaves the prism.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardA beam of alpha-particles of energy 7.3MeV is used.The protons emitted at an angle of zero degree are found to have energy of 9.34MeV.Find the Q-value of this reaction .arrow_forward
- An aluminum rod and a copper rod have the same length of 100cm at 5C. At what temperatures would one of the rods be 0.5 mm longer than the other? Which rod is longer at such temperature?arrow_forwardROTATIONAL DYNAMICS Question 01 A solid circular cylinder and a solid spherical ball of the same mass and radius are rolling together down the same inclined. Calculate the ratio of their kinetic energy. Assume pure rolling motion Question 02 A sphere and cylinder of the same mass and radius start from ret at the same point and more down the same plane inclined at 30° to the horizontal Which body gets the bottom first and what is its acceleration b) What angle of inclination of the plane is needed to give the slower body the same acceleration Question 03 i) Define the angular velocity of a rotating body and give its SI unit A car wheel has its angular velocity changing from 2rads to 30 rads seconds. If the radius of the wheel is 400mm. calculate ii) The angular acceleration iii) The tangential linear acceleration of a point on the rim of the wheel Question 04 in 20arrow_forwardQuestion B3 Consider the following FLRW spacetime: t2 ds² = -dt² + (dx² + dy²+ dz²), t2 where t is a constant. a) State whether this universe is spatially open, closed or flat. [2 marks] b) Determine the Hubble factor H(t), and represent it in a (roughly drawn) plot as a function of time t, starting at t = 0. [3 marks] c) Taking galaxy A to be located at (x, y, z) = (0,0,0), determine the proper distance to galaxy B located at (x, y, z) = (L, 0, 0). Determine the recessional velocity of galaxy B with respect to galaxy A. d) The Friedmann equations are 2 k 8πG а 4πG + a² (p+3p). 3 a 3 [5 marks] Use these equations to determine the energy density p(t) and the pressure p(t) for the FLRW spacetime specified at the top of the page. [5 marks] e) Given the result of question B3.d, state whether the FLRW universe in question is (i) radiation-dominated, (ii) matter-dominated, (iii) cosmological-constant-dominated, or (iv) none of the previous. Justify your answer. f) [5 marks] A conformally…arrow_forward
- SECTION B Answer ONLY TWO questions in Section B [Expect to use one single-sided A4 page for each Section-B sub question.] Question B1 Consider the line element where w is a constant. ds²=-dt²+e2wt dx², a) Determine the components of the metric and of the inverse metric. [2 marks] b) Determine the Christoffel symbols. [See the Appendix of this document.] [10 marks] c) Write down the geodesic equations. [5 marks] d) Show that e2wt it is a constant of geodesic motion. [4 marks] e) Solve the geodesic equations for null geodesics. [4 marks]arrow_forwardPage 2 SECTION A Answer ALL questions in Section A [Expect to use one single-sided A4 page for each Section-A sub question.] Question A1 SPA6308 (2024) Consider Minkowski spacetime in Cartesian coordinates th = (t, x, y, z), such that ds² = dt² + dx² + dy² + dz². (a) Consider the vector with components V" = (1,-1,0,0). Determine V and V. V. (b) Consider now the coordinate system x' (u, v, y, z) such that u =t-x, v=t+x. [2 marks] Write down the line element, the metric, the Christoffel symbols and the Riemann curvature tensor in the new coordinates. [See the Appendix of this document.] [5 marks] (c) Determine V", that is, write the object in question A1.a in the coordinate system x'. Verify explicitly that V. V is invariant under the coordinate transformation. Question A2 [5 marks] Suppose that A, is a covector field, and consider the object Fv=AAμ. (a) Show explicitly that F is a tensor, that is, show that it transforms appropriately under a coordinate transformation. [5 marks] (b)…arrow_forwardHow does boiling point of water decreases as the altitude increases?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Time Dilation - Einstein's Theory Of Relativity Explained!; Author: Science ABC;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yuD34tEpRFw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY