
Concept explainers
Knowing that at the instant shown the rod attached at A has an angular velocity of 5 rad/s counterclockwise and an angular acceleration of 2 rad/s2 clockwise, determine the angular velocity and the angular acceleration of the rod attached at B.
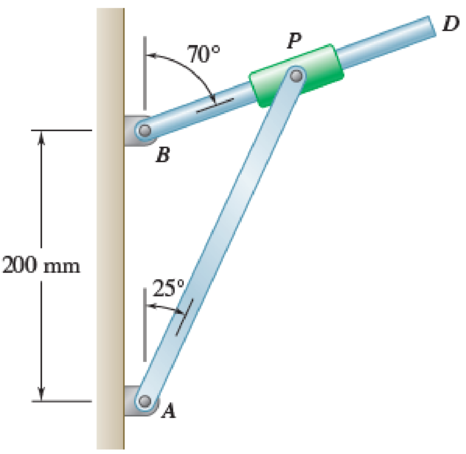
Fig. P15.176
The angular velocity and the angular acceleration of the rod at B.
Answer to Problem 15.176P
The angular velocity of the rod at B is
The angular acceleration of the rod at B is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The angular velocity of the rod at A is
The angular acceleration of the rod at A is
Calculation:
Consider the triangle ABP to get the values of AP and BP.
Calculate the angle ABP
Consider the sum of the angles is
Calculate the angle APB
Substitute
Apply law of sine for the triangle ABP as shown below.
Substitute
Calculate the position vectors
Position of P with respect to A.
Position of P with respect to B.
Provide the angular velocity of each link in vector form as shown below.
Provide the angular acceleration of each link in vector form as shown below.
Calculate the velocity of point P
Here,
Calculate the velocity the point P on the rod AP
Substitute
Calculate the acceleration at the point P
Substitute
Calculate the relative velocity component
Here, u is the velocity of the point P relative to BP.
The angle of relative velocity with respect to the rotating rod BP is
Resolve the relative velocity along x and y directions.
Calculate the relative acceleration component
Here,
Resolve the relative velocity along x and y directions.
Calculate the velocity component
Substitute
Calculate the angular velocity
Substitute
Resolving i and j components as shown below.
For i component.
For i component.
Solving Equations (3) and (4) to get the values as shown below.
Hence, the angular velocity of the rod at B is
Calculate the relative velocity
Substitute
Calculate the acceleration of the point P.
Calculate the acceleration component
Substitute
Calculate the Coriolis component of acceleration
Substitute
Calculate the angular acceleration
Substitute
Resolving i and j components as shown below.
For i component.
For j component.
Solving Equations (6) and (7) to get the values as shown below.
Hence, the angular acceleration of the rod at B is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
<LCPO> VECTOR MECH,STAT+DYNAMICS
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Concepts Of Programming Languages
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Modern Database Management
- Solve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardreading is 0.4 mas SHOWN. Assume h₁ = 0.4 m, h₂ = 0.5 m. (a) Do you know the specific weight of mercury? (b) Do you know the specific weight of gasoline? (c) Do you know the specific weight of oil? (a) YHg = 133,000 (b) Ygas = 6867 (c) Yoil = 8829 eTextbook and Media Part 2 N/m³ N/m³ N/m³ A+ Gasoline t +B Oil -Mercury Attempts: unlimited Did you calculate the pressure difference between two locations using the correct specific weight? Did you assume that the pressures in fluid are the same in a horizontal plane even though they are in different tubes? Are the calculated pressures in a column of fluid always higher at lower elevations? Did you account for the fact that the two horizontal tubes of the U-tube are above the ground? Concepts: The pressure in a fluid is a function of the specific weight of the fluid and the height relative to a reference. Pressure is constant in a horizontal plane of a continuous mass of fluid. (a) What is the initial pressure difference? (PA-PB) (b) What is…arrow_forward
- Find the solution of the following Differential Equations 1) "-4y+3y=0 3) "+16y=0 2) y"-16y=0 4) y"-y-6y=0 5) y"+2y=0 7) y"+y=0, (#0) 9) y"-y=0, y(0) = 6, y'(0) = -4 11) y"-4y+3y=0, y(0)=-1, 13) y'(0) = -5 "+2y+2y=0 15) y"-9y=0 17) y"-4y=0 6) y"-2y+2y=0 8) "+4y+5y=0 10) y"-9y=0, y(0) = 2, y'(0) = 0 12) y"-3y+2y= 0, y(0)=-1, y'(0) = 0 14) 4y+4y+y=0 16) "+6y+12y=0 18) 4y+4y+17y=0arrow_forwardAccess Pearson Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Course Home Scoresarrow_forwardAccess Pearson Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Course Home Scores Review Next >arrow_forward
- Access Pearson Course Home Scoresarrow_forwardAccess Pearson Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Course Home Scoresarrow_forwardAccess Pearson Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Course Home Scores ■Review Next >arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





