
Concept explainers
The elliptical exercise machine has fixed axes of rotation at points A and E. Knowing that at the instant shown the flywheel AB has a constant angular velocity of 6 rad/s clockwise, determine (a) the angular acceleration of bar DEF, (b) the acceleration of point F.
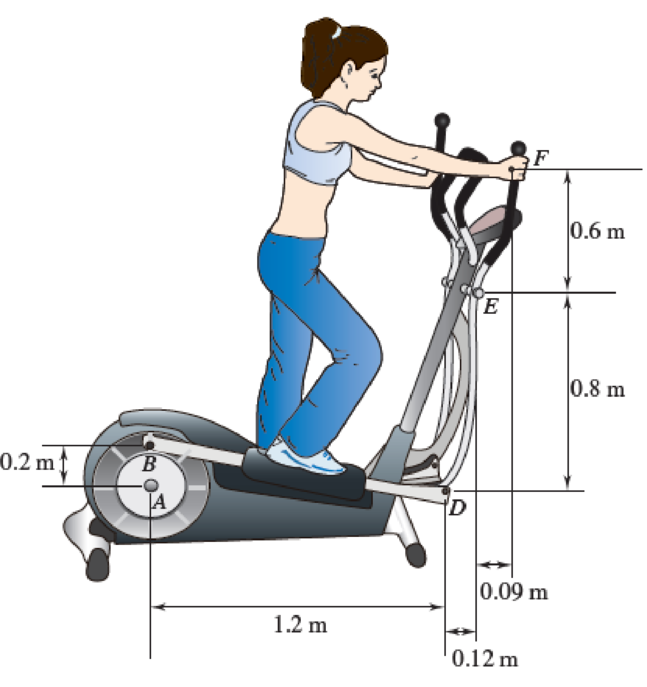
Fig. P15.127 and P15.128
(a)
Find the angular acceleration of the bar DEF.
Answer to Problem 15.128P
The angular acceleration of the bar DEF is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Consider the angular acceleration of the bar DEF is denoted by
The constant angular acceleration of the flywheel AB is
The angular acceleration of the flywheel AB is
Consider the position of the point B with respect to point A is denoted by
Consider the position of the point D with respect to point B is denoted by
Consider the position of the point D with respect to point E is denoted by
The axis of rotation points A and E are fixed. Then,
The velocity at the point A and E are
Show the relation between the velocity of the point B and A as follows:
Show the relation between the velocity of the point B and D as follows:
Modify Equation (2) using Equation (1).
Show the relation between the velocity of the point E and D as follows:
Equate Equation (3) and (4).
Substitute
Equate j component of the Equation (5).
Equate i component of the Equation (5).
Substitute
Substitute
The axis of rotation points A and E are fixed. Then,
The acceleration at the point A and E are
Show the relation between the acceleration of the point B and A as follows:
Show the relation between the acceleration of the point B and D as follows:
Modify Equation (2) using Equation (1).
Show the relation between the acceleration of the point E and D as follows:
Equate Equation (9) and (10).
Substitute
Equate j component of the Equation (5).
Equate i component of the Equation (5).
Substitute
Thus, the angular acceleration of the rod DEF is
(b)
Find the acceleration at point F.
Answer to Problem 15.128P
The acceleration at F is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Calculation:
Consider the position of the point F with respect to the point E is
Calculate the acceleration at F using the relation:
Substitute
Calculate the magnitude of the acceleration at D as follows:
Calculate the direction of the acceleration at D as follows:
Thus, the acceleration at F is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
VECTOR MECHANIC
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Concepts Of Programming Languages
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
- The flow rate is 12.275 Liters/s and the diameter is 6.266 cm.arrow_forwardAn experimental setup is being built to study the flow in a large water main (i.e., a large pipe). The water main is expected to convey a discharge (Qp). The experimental tube will be built at a length scale of 1/20 of the actual water main. After building the experimental setup, the pressure drop per unit length in the model tube (APm/Lm) is measured. Problem (20): Given the value of APm/Lm [kPa/m], and assuming pressure coefficient similitude, calculate the drop in the pressure per unit length of the water main (APP/Lp) in [Pa/m]. Givens: AP M/L m = 590.637 kPa/m meen Answers: ( 1 ) 59.369 Pa/m ( 2 ) 73.83 Pa/m (3) 95.443 Pa/m ( 4 ) 44.444 Pa/m *******arrow_forwardFind the reaction force in y if Ain = 0.169 m^2, Aout = 0.143 m^2, p_in = 0.552 atm, Q = 0.367 m^3/s, α = 31.72 degrees. The pipe is flat on the ground so do not factor in weight of the pipe and fluid.arrow_forward
- Find the reaction force in x if Ain = 0.301 m^2, Aout = 0.177 m^2, p_in = 1.338 atm, Q = 0.669 m^3/s, and α = 37.183 degreesarrow_forwardProblem 5: Three-Force Equilibrium A structural connection at point O is in equilibrium under the action of three forces. • • . Member A applies a force of 9 kN vertically upward along the y-axis. Member B applies an unknown force F at the angle shown. Member C applies an unknown force T along its length at an angle shown. Determine the magnitudes of forces F and T required for equilibrium, assuming 0 = 90° y 9 kN Aarrow_forwardProblem 19: Determine the force in members HG, HE, and DE of the truss, and state if the members are in tension or compression. 4 ft K J I H G B C D E F -3 ft -3 ft 3 ft 3 ft 3 ft- 1500 lb 1500 lb 1500 lb 1500 lb 1500 lbarrow_forward
- Problem 14: Determine the reactions at the pin A, and the tension in cord. Neglect the thickness of the beam. F1=26kN F2 13 12 80° -2m 3marrow_forwardProblem 22: Determine the force in members GF, FC, and CD of the bridge truss and state if the members are in tension or compression. F 15 ft B D -40 ft 40 ft -40 ft 40 ft- 5 k 10 k 15 k 30 ft Earrow_forwardProblem 20: Determine the force in members BC, HC, and HG. After the truss is sectioned use a single equation of equilibrium for the calculation of each force. State if the members are in tension or compression. 5 kN 4 kN 4 kN 3 kN 2 kN B D E F 3 m -5 m- -5 m- 5 m 5 m-arrow_forward
- An experimental setup is being built to study the flow in a large water main (i.e., a large pipe). The water main is expected to convey a discharge (Qp). The experimental tube will be built at a length scale of 1/20 of the actual water main. After building the experimental setup, the pressure drop per unit length in the model tube (APm/Lm) is measured. Problem (19): Given the value of Qp [m³/s], and assuming Reynolds number similitude between the water main and experimental tube, calculate the flow rate in the model tube (Qm) in [lit/s]. = 30.015 m^3/sarrow_forwardProblem 11: The lamp has a weight of 15 lb and is supported by the six cords connected together as shown. Determine the tension in each cord and the angle 0 for equilibrium. Cord BC is horizontal. E 30° B 60° Aarrow_forwardProblem 10: If the bucket weighs 50 lb, determine the tension developed in each of the wires. B $30° 5 E D 130°arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





