
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The chiral center in the following compound should be located.
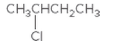
Concept Introduction:
Compounds in which an atom is attached to four different groups of atoms are known as chiral center and the compound is known as a chiral compound.
(b)
Interpretation:
The chiral center in the following compound should be located.
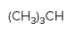
Concept Introduction:
Compounds in which an atom is attached to four different groups of atoms are known as chiral center and the compound is known as a chiral compound.
(c)
Interpretation:
The chiral center in the following compound should be located.
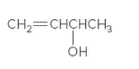
Concept Introduction:
Compounds in which an atom is attached to four different groups of atoms are known as chiral center and compound is known as a chiral compound.
(d)
Interpretation:
The chiral center in the following compound should be located.
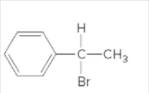
Concept Introduction:
Compounds in which an atom is attached to four different groups of atoms are known as chiral center and compound is known as a chiral compound.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
GENERAL,ORGANIC, & BIOLOGICAL CHEM-ACCES
- Show the mechanism steps to obtain the lowerenergy intermediate: *see imagearrow_forwardSoap is made by the previous reaction *see image. The main difference between one soap and another soap isthe length (number of carbons) of the carboxylic acid. However, if a soap irritates your skin, they mostlikely used too much lye.Detergents have the same chemical structure as soaps except for the functional group. Detergentshave sulfate (R-SO4H) and phosphate (R-PO4H2) functional groups. Draw the above carboxylic acidcarbon chain but as the two variants of detergents. *see imagearrow_forwardWhat are the reactions or reagents used? *see imagearrow_forward
- The two pKa values of oxalic acid are 1.25 and 3.81. Why are they not the same value? Show the protontransfer as part of your explanation. *see imagearrow_forwardасть Identify all the bonds that gauche interact with C-OMe in the most stable conformation of the above compound.arrow_forwardPredict the reactants used in the formation of the following compounds using Acid-Catalyzed dehydration reactionarrow_forward
- Can I please get help with this?arrow_forward.. Give the major organic product(s) for each of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show ll relevant stereochemistry [3 ONLY]. A H Br 1. NaCN 2 NaOH, H₂O, heat 3. H3O+ B. CH₂COOH 19000 1. LiAlH4 THF, heat 2 H₂O* C. CH Br 1. NaCN, acetone 2 H3O+, heat D. Br 1. Mg. ether 3. H₂O+ 2 CO₂ E. CN 1. (CH) CHMgBr, ether 2 H₂O+arrow_forwardAssign this COSY spectrumarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole

