
Determine the minimum dimension a to the nearest mm of the beam’s cross section to safely support the load. The wood has an allowable normal stress of σallow = 10 MPa and an allowable shear stress of τallow = 1 MPa.
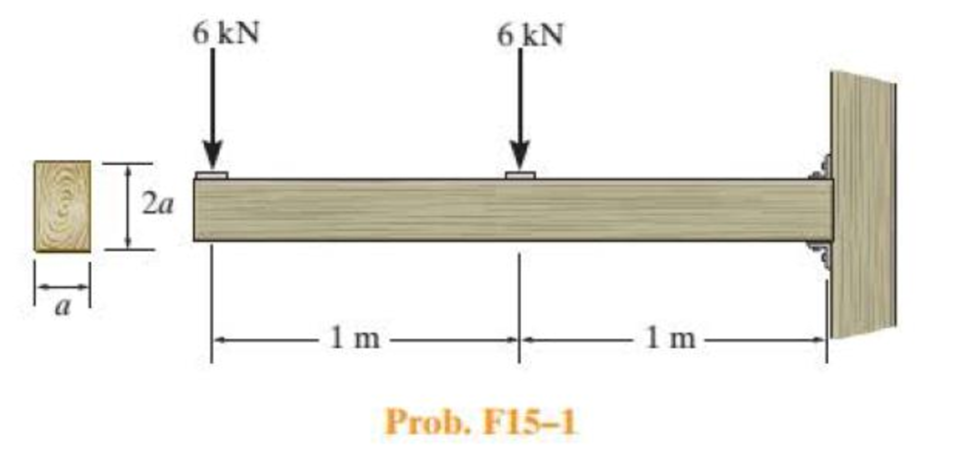
Find the minimum dimension a to the nearest beam cross section.
Answer to Problem 1FP
The minimum dimension a to the nearest beam cross section is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The allowable bending stress is 10 MPa.
The allowable shear stress is 1 MPa.
The width of the cross section is a.
The depth of the cross section is 2a.
Calculation:
Sketch the free body diagram of beam as shown in Figure 1.
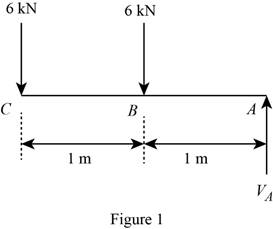
Consider a section,
Apply the equilibrium condition along y –direction.
Determine the bending moment at point A.
Calculate the moment of inertia (I) using the relation.
Here, b is the width of the section and d is the depth of the section.
Substitute a for b and 2a for d.
Calculate the dimension (a) value using the relation:
Here,
Substitute
Use,
Hence, the minimum dimension a to the nearest beam cross section is
Find the value of I using the relation:
Substitute 140 mm for a.
Find the value of
Here, A is the area of the cross section and y is the centroid of area.
Substitute
Check:
Calculate the
Here
Substitute
Hence it is OK.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Statics and Mechanics of Materials (5th Edition)
- (b) A steel 'hot rolled structural hollow section' column of length 5.75 m, has the cross-section shown in Figure Q.5(b) and supports a load of 750 kN. During service, it is subjected to axial compression loading where one end of the column is effectively restrained in position and direction (fixed) and the other is effectively held in position but not in direction (pinned). i) Given that the steel has a design strength of 275 MN/m², determine the load factor for the structural member based upon the BS5950 design approach using Datasheet Q.5(b). [11] ii) Determine the axial load that can be supported by the column using the Rankine-Gordon formula, given that the yield strength of the material is 280 MN/m² and the constant *a* is 1/30000. [6] 300 600 2-300 mm wide x 5 mm thick plates. Figure Q.5(b) L=5.75m Pinned Fixedarrow_forwardHelp ارجو مساعدتي في حل هذا السؤالarrow_forwardHelp ارجو مساعدتي في حل هذا السؤالarrow_forward
- Q2: For the following figure, find the reactions of the system. The specific weight of the plate is 500 lb/ft³arrow_forwardQ1: For the following force system, find the moments with respect to axes x, y, and zarrow_forwardQ10) Body A weighs 600 lb contact with smooth surfaces at D and E. Determine the tension in the cord and the forces acting on C on member BD, also calculate the reaction at B and F. Cable 6' 3' wwwarrow_forward
- Help ارجو مساعدتي في حل هذا السؤالarrow_forwardQ3: Find the resultant of the force system.arrow_forwardQuestion 1 A three-blade propeller of a diameter of 2 m has an activity factor AF of 200 and its ratio of static thrust coefficient to static torque coefficient is 10. The propeller's integrated lift coefficient is 0.3.arrow_forward
- (L=6847 mm, q = 5331 N/mm, M = 1408549 N.mm, and El = 8.6 x 1014 N. mm²) X A ΕΙ B L Y Marrow_forwardCalculate the maximum shear stress Tmax at the selected element within the wall (Fig. Q3) if T = 26.7 KN.m, P = 23.6 MPa, t = 2.2 mm, R = 2 m. The following choices are provided in units of MPa and rounded to three decimal places. Select one: ○ 1.2681.818 O 2. 25745.455 O 3. 17163.636 O 4. 10727.273 ○ 5.5363.636arrow_forwardIf L-719.01 mm, = 7839.63 N/m³, the normal stress σ caused by self-weight at the location of the maximum normal stress in the bar can be calculated as (Please select the correct value of σ given in Pa and rounded to three decimal places.) Select one: ○ 1. 1409.193 2. 845.516 O 3. 11273.545 ○ 4.8455.159 ○ 5.4509.418 6. 2818.386 7.5636.772arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





