
BIOLOGY 2E
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9781506699851
Author: OpenStax
Publisher: XANEDU PUBLISHING
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 15, Problem 3VCQ
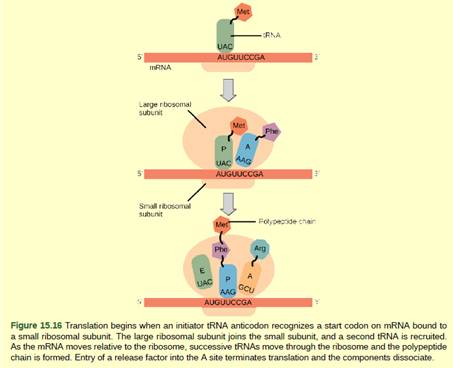
Figure 15.16 Many antibiotics inhibit bacterial protein synthesis. For example, tetracycline blocks the A site on the bacterial ribosome, and chloramphenicol blocks peptidyl transfer. What specific effect would you expect each of these antibiotics to have on protein synthesis? Tetracycline would directly affect:
- tRNA binding to the ribosome
- ribosome assembly
- growth of the protein chain Chloramphenicol would directly affect
- tRNA binding to the ribosome
- ribosome assembly
- growth of the protein chain
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Find the dental formula and enter it in the following format:
I3/3 C1/1 P4/4 M2/3 = 42 (this is not the correct number, just the correct format)
Please be aware: the upper jaw is intact (all teeth are present). The bottom jaw/mandible is not intact. The front teeth should include 6 total rectangular teeth (3 on each side) and 2 total large triangular teeth (1 on each side).
Answer i
Answer
Chapter 15 Solutions
BIOLOGY 2E
Ch. 15 - Figure 15.11 A scientist splices a eukaryotic...Ch. 15 - Figure 15.13 Errors in splicing are implicated in...Ch. 15 - Figure 15.16 Many antibiotics inhibit bacterial...Ch. 15 - The AUC and AUA codons in mRNA both specify...Ch. 15 - How many nucleotides are in 12 mRNA codons? 12 24...Ch. 15 - Which event contradicts the central dogma of...Ch. 15 - Which subunit of the E. coli polymerase confers...Ch. 15 - The -10 and -35 regions of prokaryotic promoters...Ch. 15 - Three different bacteria species have the...Ch. 15 - Which feature of promoters can be found in both...
Ch. 15 - What transcripts will be most affected by low...Ch. 15 - How do enhancers and promoters differ? Enhancers...Ch. 15 - Which pre-mRNA processing step is important for...Ch. 15 - What processing step enhances the stability of...Ch. 15 - A scientist identifies a pre-mRNA with the...Ch. 15 - The RNA components of ribosomes are synthesized in...Ch. 15 - In any given species, there are at least how many...Ch. 15 - A scientist introduces a mutation that makes the...Ch. 15 - Imagine if there were 200 commonly occurring amino...Ch. 15 - Discuss how degeneracy of the genetic code makes...Ch. 15 - A scientist sequencing itiRNA identifies the...Ch. 15 - If mRNA is complementary to the DNA template...Ch. 15 - In your own words, describe the difference between...Ch. 15 - A fragment of bacterial DNA reads: 3’...Ch. 15 - A scientist observes that a cell has an RNA...Ch. 15 - Chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients often harbor...Ch. 15 - Transcribe and translate the following DNA...Ch. 15 - Explain how single nucleotide changes can have...Ch. 15 - A normal mRNA that reads 5’ -...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
1. An object is subject to two forces that do not point in opposite directions. Is it possible to choose their ...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Fill in the blanks: a. The wrist is also known as the _________ region. b. The arm is also known as the _______...
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Why is an endospore called a resting structure? Of what advantage is an endospore to a bacterial cell?
Microbiology: An Introduction
Distinguish between microevolution, speciation, and macroevolution.
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
In the light reactions, what is the initial electron donor? Where do the electrons finally end up?
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
4. What five specific threats to biodiversity are described in this chapter? Provide an example of each.
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- calculate the questions showing the solution including variables,unit and equations all the questiosn below using the data a) B1, b) B2, c) hybrid rate constant (1) d) hybrid rate constant (2) e) t1/2,dist f) t1/2,elim g) k10 h) k12 i) k21 j) initial concentration (C0) k) central compartment volume (V1) l) steady-state volume (Vss) m) clearance (CL) AUC (0→10 min) using trapezoidal rule n) AUC (20→30 min) using trapezoidal rule o) AUCtail (AUC360→∞) p) total AUC (using short cut method) q) volume from AUC (VAUC)arrow_forwardQUESTION 8 For the following pedigree, assume that the mode of inheritance is X-linked recessive, and that the trait has full penetrance and expressivity and occurs at a very low frequency in the hum population. Using XA for the dominant allele and Xa for the recessive allele, assign genotypes for the following individuals (if it is not possible to figure out the second allele of a genotype, that with an underscore): 2 m 1 2 1 2 4 5 6 7 8 9 IV 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 CO 9 10 12 13 V 1, 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 a. Il-1: b. 11-2: c. III-3: d. III-4: e. If individuals IV-11 and IV-12 have another child, what is the probability that they will have a boy with the disorder?arrow_forwardAnswerrarrow_forward
- please,show workings ahd solutions calculate the questions showing the solution including variables,unit and equations all the questiosn below using the data a) B1, b) B2, c) hybrid rate constant (1) d) hybrid rate constant (2) e) t1/2,dist f) t1/2,elim g) k10 h) k12 i) k21 j) initial concentration (C0) k) central compartment volume (V1) l) steady-state volume (Vss) m) clearance (CL) AUC (0→10 min) using trapezoidal rule n) AUC (20→30 min) using trapezoidal rule o) AUCtail (AUC360→∞) p) total AUC (using short cut method) q) volume from AUC (VAUC)arrow_forwardQuestion about consensus and the relationship to transcriptional activityarrow_forwardQuestion about archaea and eukaryotic general transcription homologsarrow_forward
- Question about general transcription factors and their relationship to polymerasesarrow_forwardIdentify the indicated structure?arrow_forwardrewrite: Problem 1 (Mental Health): The survivor victim is dealing with acute stress and symptoms of a post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) due to their traumatic experience during the January 2025 wildfire. Goal 1: To alleviate the client's overall level, frequency, and intensity of anxiety and PTSD symptoms so that daily functioning remains unimpaired. Objective 1: The client will learn and regularly use at least two anxieties management techniques to reduce anxiety symptoms to less than three episodes per week. Intervention 1: The therapist will provide psychoeducation about anxiety and PTSD, including their symptoms and triggers. The therapist will also teach and assist the client in adopting relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises and progressive muscle relaxation, to better manage anxiety and lessen PTSD symptoms.arrow_forward
- O Macmillan Learning You have 0.100 M solutions of acetic acid (pKa = 4.76) and sodium acetate. If you wanted to prepare 1.00 L of 0.100 M acetate buffer of pH 4.00, how many milliliters of acetic acid and sodium acetate would you add? acetic acid: mL sodium acetate: mLarrow_forwardHow does the cost of food affect the nutritional choices people make?arrow_forwardBiopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics:Two-Compartment Model Zero-Order Absorption Questions SHOW ALL WORK, including equation used, variables used and each step to your solution, report your regression lines and axes names (with units if appropriate) :Calculate a-q a) B1, b) B2, c) hybrid rate constant (1) d) hybrid rate constant (2) e) t1/2,dist f) t1/2,elim g) k10 h) k12 i) k21 j) initial concentration (C0) k) central compartment volume (V1) l) steady-state volume (Vss) m) clearance (CL) AUC (0→10 min) using trapezoidal rule n) AUC (20→30 min) using trapezoidal rule o) AUCtail (AUC360→∞) p) total AUC (using short cut method) q) volume from AUC (VAUC)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Bacterial Structure and Functions; Author: Osmosis;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b15Hy3jCPDs;License: Standard youtube license