
Concept explainers
Amy Lloyd is interested in leasing a new Honda and has contacted three automobile dealers for pricing information. Each dealer offered Amy a closed-end 36-month lease with no down payment due at the time of signing. Each lease includes a monthly charge and a mileage allowance. Additional miles receive a surcharge on a per-mile basis. The monthly lease cost, the mileage allowance, and the cost for additional miles follow:
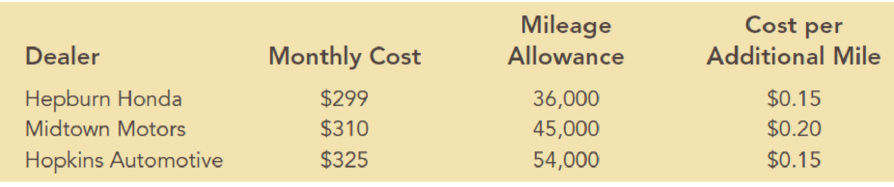
Amy decided to choose the lease option that will minimize her total 36-month cost. The difficulty is that Amy is not sure how many miles she will drive over the next three years. For purposes of this decision, she believes it is reasonable to assume that she will drive 12,000 miles per year, 15,000 miles per year, or 18,000 miles per year. With this assumption Amy estimated her total costs for the three lease options. For example, she figures that the Hepburn Honda lease will cost her 36($299) + $0.15(36,000 – 36,000) = $10,764 if she drives 12,000 miles per year, 36($299) + $0.15(45,000 – 36,000) = $12,114 if she drives 15,000 miles per year, or 36($299) + $0.15(54.000 – 36,000) = $13,464 if she drives 18,000 miles per year.
- a. What is the decision, and what is the chance
event ? - b. Construct a payoff table for Amy’s problem.
- c. If Amy has no idea which of the three mileage assumptions is most appropriate, what is the recommended decision (leasing option) using the optimistic, conservative, and minimax regret approaches?
- d. Suppose that the probabilities that Amy drives 12,000, 15,000, and 18,000 miles per year are 0.5, 0.4, and 0.1, respectively. What option should Amy choose using the
expected value approach? - e. Develop a risk profile for the decision selected in part (d). What is the most likely cost, and what is its
probability ? - f. Suppose that, after further consideration, Amy concludes that the probabilities that she will drive 12,000, 15,000, and 18,000 miles per year are 0.3, 0.4, and 0.3, respectively. What decision should Amy make using the expected value approach?
a.
Find the decision and the chance event faced by Amy.
Explanation of Solution
Here, the decision is based on selecting the best lease option. Thus the least option has three alternatives that are Hepburn Honda, Midtown Motors and Hopkins Automotive.
Here, the chance event is the number of miles Amy will drive.
b.
Find the payoff table for Amy’s problem.
Answer to Problem 3P
Thus, the payoff table for Amy’s problem is given as:
| Actual Miles Driven Annually | |||
| Decision | 12000 | 15000 | 18000 |
| Hepburn Honda | $10,764 | $12,114 | $13,464 |
| Midtown Motors | $11,160 | $11,160 | $12,960 |
| Hopkins Automotive | $11,700 | $11,700 | $11,700 |
Explanation of Solution
The payoff for any combination of alternative and the chance event is the sum of the total monthly charges and total additional mileage cost that is given as follows:
For the Hepburn Honda lease option:
For the Midtown Motors lease option:
For the Hopkins Automotive lease option:
Thus, the payoff table for Amy’s problem is given as:
| Actual Miles Driven Annually | |||
| Decision | 12000 | 15000 | 18000 |
| Hepburn Honda | $10,764 | $12,114 | $13,464 |
| Midtown Motors | $11,160 | $11,160 | $12,960 |
| Hopkins Automotive | $11,700 | $11,700 | $11,700 |
c.
Find the decision using the optimistic, conservative and minimax regret approaches.
Answer to Problem 3P
The Hepburn Honda lease option gives the optimistic approach because it has the smallest minimum profit.
The Hopkins Automotive lease option gives the conservative approach because it has the smallest maximum profit.
The minimax regret is the Hopkins Automotive lease option because it minimizes the maximum regret.
Explanation of Solution
By using the decision tree in Part (a), the maximum and minimum profit based on the decisions Hepburn Honda, Midtown Motors and Hopkins Automotive.
| Decision | Maximum Profit | Minimum Profit |
| Hepburn Honda | $10,764 | $13,464 |
| Midtown Motors | $11,160 | $12,960 |
| Hopkins Automotive | $11,700 | $11,700 |
Optimistic approach:
The optimistic approach evaluates each decision alternative in terms of best payoff that can occur.
The Hepburn Honda lease option gives the optimistic approach because it has the smallest minimum profit (from the above table).
Conservative approach:
The conservative approach evaluates each decision alternative in terms of worst payoff that can occur.
The Hopkins Automotive lease option gives the conservative approach because it has the smallest maximum profit (from the above table).
Minimax Regret approach:
The minimax regret approach is the difference between the payoff associated with a particular alternative and payoff associated with the most decision that would yield the most desirable payoff for a given state of nature.
Regret or opportunity loss table:
| Decision | 12000 | 15000 | 18000 | Maximum Regret |
| Hepburn Honda | $0 | $954 | $1,764 | $1,764 |
| Midtown Motors | $396 | $0 | $1,260 | $1,260 |
| Hopkins Automotive | $936 | $540 | $0 | $936 |
The maximum regret for the decision Hepburn Honda is $1,764, Midtown Motors is $1,260 and Hopkins Automotive is $936.
Here, the Hopkins Automotive lease option has been selected because it minimizes the maximum regret.
d.
Find the expected value approach for the probabilities of 0.5, 0.4 and 0.1.
Answer to Problem 3P
The expected value approach results in Midtown Motors lease option.
Explanation of Solution
The formula to find expected value (EV) of decision alternative di is given as follows:
Here, the expected value for the payoffs associated with each of Amy’s three alternatives:
The expected value approach results in Midtown Motors lease option because it has the minimum expected value of the three alternatives.
e.
Find the most likely cost and its probability using risk analysis.
Answer to Problem 3P
The risk analysis for midtown motors, the most likely cost is $11,160 with the probability of 0.9.
Explanation of Solution
From the data in part (d).
The risk profile for the decision to lease from Midtown Motors is:
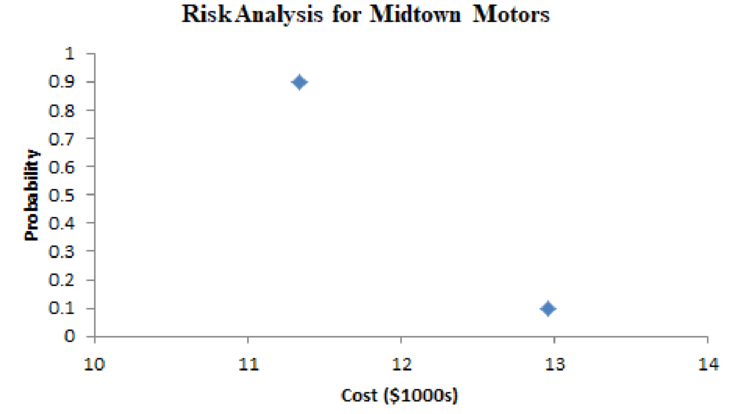
From the above risk analysis for midtown motors, the most likely cost is $11,160 with the probability of 0.9.
Here, there are only two unique costs on this graph because for the decision alternative (midtown motors) have two unique payoffs. The payoffs are associated with the three chance outcomes- the payoff (cost) associated with midtown motors lease is same for the two of the chance outcomes.
f.
Find the expected value approach for the probabilities of 0.3, 0.4 and 0.3.
Answer to Problem 3P
The expected value approach results in either Midtown Motors lease option or Hopkins Automotive lease option.
Explanation of Solution
The formula to find expected value (EV) of decision alternative di is given as follows:
Here, the expected value for the payoffs associated with each of Amy’s three alternatives:
The expected value approach results in either Midtown Motors lease option or Hopkins Automotive lease option because both have the same minimum expected value of the three alternatives.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Mindtap Business Analytics, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card For Camm/cochran/fry/ohlmann/anderson/sweeney/williams' Essentials Of Business Analytics, 2nd
- 38. Possible values of X, the number of components in a system submitted for repair that must be replaced, are 1, 2, 3, and 4 with corresponding probabilities .15, .35, .35, and .15, respectively. a. Calculate E(X) and then E(5 - X).b. Would the repair facility be better off charging a flat fee of $75 or else the amount $[150/(5 - X)]? [Note: It is not generally true that E(c/Y) = c/E(Y).]arrow_forward74. The proportions of blood phenotypes in the U.S. popula- tion are as follows:A B AB O .40 .11 .04 .45 Assuming that the phenotypes of two randomly selected individuals are independent of one another, what is the probability that both phenotypes are O? What is the probability that the phenotypes of two randomly selected individuals match?arrow_forward53. A certain shop repairs both audio and video compo- nents. Let A denote the event that the next component brought in for repair is an audio component, and let B be the event that the next component is a compact disc player (so the event B is contained in A). Suppose that P(A) = .6 and P(B) = .05. What is P(BA)?arrow_forward
- 26. A certain system can experience three different types of defects. Let A;(i = 1,2,3) denote the event that the sys- tem has a defect of type i. Suppose thatP(A1) = .12 P(A) = .07 P(A) = .05P(A, U A2) = .13P(A, U A3) = .14P(A2 U A3) = .10P(A, A2 A3) = .011Rshelfa. What is the probability that the system does not havea type 1 defect?b. What is the probability that the system has both type 1 and type 2 defects?c. What is the probability that the system has both type 1 and type 2 defects but not a type 3 defect? d. What is the probability that the system has at most two of these defects?arrow_forwardThe following are suggested designs for group sequential studies. Using PROCSEQDESIGN, provide the following for the design O’Brien Fleming and Pocock.• The critical boundary values for each analysis of the data• The expected sample sizes at each interim analysisAssume the standardized Z score method for calculating boundaries.Investigators are evaluating the success rate of a novel drug for treating a certain type ofbacterial wound infection. Since no existing treatment exists, they have planned a one-armstudy. They wish to test whether the success rate of the drug is better than 50%, whichthey have defined as the null success rate. Preliminary testing has estimated the successrate of the drug at 55%. The investigators are eager to get the drug into production andwould like to plan for 9 interim analyses (10 analyzes in total) of the data. Assume thesignificance level is 5% and power is 90%.Besides, draw a combined boundary plot (OBF, POC, and HP)arrow_forwardPlease provide the solution for the attached image in detailed.arrow_forward
- 20 km, because GISS Worksheet 10 Jesse runs a small business selling and delivering mealie meal to the spaza shops. He charges a fixed rate of R80, 00 for delivery and then R15, 50 for each packet of mealle meal he delivers. The table below helps him to calculate what to charge his customers. 10 20 30 40 50 Packets of mealie meal (m) Total costs in Rands 80 235 390 545 700 855 (c) 10.1. Define the following terms: 10.1.1. Independent Variables 10.1.2. Dependent Variables 10.2. 10.3. 10.4. 10.5. Determine the independent and dependent variables. Are the variables in this scenario discrete or continuous values? Explain What shape do you expect the graph to be? Why? Draw a graph on the graph provided to represent the information in the table above. TOTAL COST OF PACKETS OF MEALIE MEAL 900 800 700 600 COST (R) 500 400 300 200 100 0 10 20 30 40 60 NUMBER OF PACKETS OF MEALIE MEALarrow_forwardLet X be a random variable with support SX = {−3, 0.5, 3, −2.5, 3.5}. Part ofits probability mass function (PMF) is given bypX(−3) = 0.15, pX(−2.5) = 0.3, pX(3) = 0.2, pX(3.5) = 0.15.(a) Find pX(0.5).(b) Find the cumulative distribution function (CDF), FX(x), of X.1(c) Sketch the graph of FX(x).arrow_forwardA well-known company predominantly makes flat pack furniture for students. Variability with the automated machinery means the wood components are cut with a standard deviation in length of 0.45 mm. After they are cut the components are measured. If their length is more than 1.2 mm from the required length, the components are rejected. a) Calculate the percentage of components that get rejected. b) In a manufacturing run of 1000 units, how many are expected to be rejected? c) The company wishes to install more accurate equipment in order to reduce the rejection rate by one-half, using the same ±1.2mm rejection criterion. Calculate the maximum acceptable standard deviation of the new process.arrow_forward
- 5. Let X and Y be independent random variables and let the superscripts denote symmetrization (recall Sect. 3.6). Show that (X + Y) X+ys.arrow_forward8. Suppose that the moments of the random variable X are constant, that is, suppose that EX" =c for all n ≥ 1, for some constant c. Find the distribution of X.arrow_forward9. The concentration function of a random variable X is defined as Qx(h) = sup P(x ≤ X ≤x+h), h>0. Show that, if X and Y are independent random variables, then Qx+y (h) min{Qx(h). Qr (h)).arrow_forward
 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Elementary AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9780998625713Author:Lynn Marecek, MaryAnne Anthony-SmithPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
Elementary AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9780998625713Author:Lynn Marecek, MaryAnne Anthony-SmithPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Intermediate AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781285195728Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781285195728Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra for College StudentsAlgebraISBN:9781285195780Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra for College StudentsAlgebraISBN:9781285195780Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage Learning





