
Concept explainers
16-6 Answer true or false.
- te/7-Butylamine is a 3°
amine .
(a)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement: tert-Butylamine is
Concept Introduction:
Amines are the derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more than one hydrogen atoms are substituted by an alkyl or aryl group.
The amines are categorized as primary, secondary or tertiary based on the number of carbon atoms that are bonded directly to the nitrogen atom. Primary amine has only one carbon atom bonded to the nitrogen atom. Similarly, secondary amines have two carbon groups bonded to the nitrogen, and tertiary amines nave three carbon groups bonded to the nitrogen.
Answer to Problem 1P
The statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of a tert-butylamine is given below:
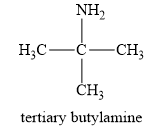
In a tert-butylamine, the carbon atom is bonded to three methyl groups, while nitrogen is attached to only one carbon group. Therefore, the tert-butyl amine is a primary amine. Therefore, this statement is false.
(b)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement about the aromatic amine is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Amines are the derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more than one hydrogen atoms are substituted by an alkyl or aryl group.
The amines are categorized as primary, secondary or tertiary based on the number of carbon atoms that are bonded directly to the nitrogen atom. Primary amine has only one carbon atom bonded to the nitrogen atom. Similarly, secondary amines have two carbon groups bonded to the nitrogen, and tertiary amines nave three carbon groups bonded to the nitrogen.
Answer to Problem 1P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
If in an amine, the nitrogen is directly bonded to one or more aryl groups or aromatic rings, and then the amine is known as an aromatic amine.
For example, aniline is an aromatic amine, as it is attached to one aromatic ring benzene. The structure of aniline is given below:
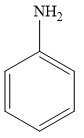
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(c)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement: In a heterocyclic amine, the main nitrogen is the part of the ringis true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Amines are the derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more than one hydrogen atoms are substituted by an alkyl or aryl group.
The amines are categorized as primary, secondary or tertiary based on the number of carbon atoms that are bonded directly to the nitrogen atom. Primary amine has only one carbon atom bonded to the nitrogen atom. Similarly, secondary amines have two carbon groups bonded to the nitrogen, and tertiary amines nave three carbon groups bonded to the nitrogen.
Answer to Problem 1P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
In a heterocyclic amine, the carbon group of the ring structure is replaced by the nitrogen atom. For example, in pyridine, the nitrogen atom replaces one —CH group of the benzene ring.
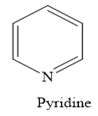
Thus, the heterocyclic amine is an amine in which nitrogen is one of the atoms of a ring. Therefore, this statement is true.
(d)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement: The NH4+ and CH4have the same number of valence electrons and both have tetrahedral geometry as per the VSEPR model is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
The VSEPR (Valence-shell electron pair repulsion) model predicts the shape of the molecules or ions by identifying the position of atoms connected to the central atom.
Answer to Problem 1P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory determines the shapes and the geometry of a molecule. In a CH4 molecule, one carbon atom is bonded to four hydrogen atoms with a single bond. In NH4+, one nitrogen atom is singly bonded to four hydrogen atoms.
According to the VSEPR model, each bond represents a pair of electrons. Since both compounds have four bonds around the central atom, they contain eight valence electrons. Also, according to the VSEPR model, these four bonding regions are arranged in a tetrahedral manner so that they are as far away from one another as possible, giving the molecule a tetrahedral geometry. Therefore, this statement is true.
(e)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement: There are four constitutional isomers with the molecular formulaC3H9N, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Constitutional isomers are those compounds which have same molecular formula, but they differ in the arrangement of atoms in the molecules.
Answer to Problem 1P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The molecular formula is given as C3H9N. Therefore, the possible constitutional isomers for this molecular formula are given below:
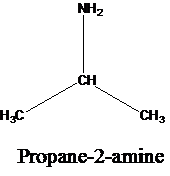
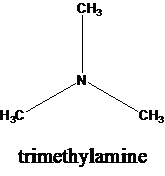
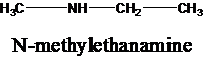
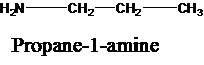
Thus, there are four constitutional isomers possible with the molecular formula C3H9N. Therefore, this statement is true.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Introduction To General, Organic, And Biochemistry
- The organic compound MTBE (methyltertiarybutylether) is used as a fuel additive that allows gasoline to burn more cleanly thus leading to a reduction in pollution. Recently, however, MTBE has been found in the drinking water of a number of communities. As a result several states are phasing out the use of MTBE as a fuel additive. A combustion experiment using 10.00 g of MTBE was found to produce 24.97g of CO2 and 12.26 g of H2O. (a) What is the empirical formula of MTBE assuming it contains C, H, and O only? (b) The molar mass of MTBE was experimentally determined to be 88.1 g/mol. Using this information what is the molecular formula of MTBEarrow_forwardPart 4: Provide a detailed retrosynthetic analysis and a plausible forward synthesis the following molecule. храдо ofarrow_forward3A: Starting with benzocyclobutene, synthesize the naphthalene derivative below.arrow_forward
- 7. The addition of HBr to 2,5-dimethyl-2,4-heptadiene gives the same product, A, at both low and high temperatures. Provide the structure of A and explain the kinetic and thermodynamic product are the same in this reaction. HBr -78°C or 60°C Aarrow_forward3B: Convert the starting material into the chiral epoxytriol below. OH OH = OH OHarrow_forward3D: Convert the aromatic triketone to the 1,3,5-triethylcyclohexane shown below. ہوئےarrow_forward
- Indicate how to find the energy difference between two levels in cm-1, knowing that its value is 2.5x10-25 joules.arrow_forwardThe gyromagnetic ratio (gamma) for 1H is 2.675x108 s-1 T-1. If the applied field is 1,409 T what will be the separation between nuclear energy levels?arrow_forwardChances Ad ~stract one 11. (10pts total) Consider the radical chlorination of 1,3-diethylcyclohexane depicted below. 4 • 6H total $4th total Statistical pro 21 total 2 H A 2H 래 • 4H totul < 3°C-H werkest bund - abstraction he leads to then mo fac a) (6pts) How many unique mono-chlorinated products can be formed and what are the structures for the thermodynamically and statistically favored products? рос 6 -વા J Number of Unique Mono-Chlorinated Products Thermodynamically Favored Product Statistically Favored Product b) (4pts) Draw the arrow pushing mechanism for the FIRST propagation step (p-1) for the formation of the thermodynamically favored product. Only draw the p-1 step. You do not need to include lone pairs of electrons. No enthalpy calculation necessary H H-Clarrow_forward
- What is the lone pair or charge that surrounds the nitrogen here to give it that negative charge?arrow_forwardLast Name, Firs Statifically more chances to abstract one of these 6H 11. (10pts total) Consider the radical chlorination of 1,3-diethylcyclohexane depicted below. 4 • 6H total $ 4th total 21 total 4H total ZH 2H Statistical H < 3°C-H werkst - product bund abstraction here leads to the mo favored a) (6pts) How many unique mono-chlorinated products can be formed and what are the structures for the thermodynamically and statistically favored products? Proclict 6 Number of Unique Mono-Chlorinated Products f Thermodynamically Favored Product Statistically Favored Product b) (4pts) Draw the arrow pushing mechanism for the FIRST propagation step (p-1) for the formation of the thermodynamically favored product. Only draw the p-1 step. You do not need to include lone pairs of electrons. No enthalpy calculation necessary 'H H-Cl Waterfoxarrow_forward2. (a) Many main group oxides form acidic solutions when added to water. For example solid tetraphosphorous decaoxide reacts with water to produce phosphoric acid. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction. (b) Calcium phosphate reacts with silicon dioxide and carbon graphite at elevated temperatures to produce white phosphorous (P4) as a gas along with calcium silicate (Silcate ion is SiO3²-) and carbon monoxide. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction.arrow_forward

 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning





