
Concept explainers
Enhanced Spatial Learning Ability in Mice Engineered to Carry an Autism Mutation Autism is a neurobiological disorder with symptoms that include impaired social interactions and repetitive, stereotyped patterns of behavior. Around 10 percent of autistic people also have an extraordinary skill or talent such as greatly enhanced memory.
Mutations in the gene for neuroligin 3, an adhesion protein that connects brain cells, have been associated with autism. One of these mutations is called R451C because the altered gene encodes a protein with an amino acid substitution: a cysteine (C) instead of an arginine (R) in position 451.
In 2007, Katsuhiko Tabuchi and his colleagues introduced the R451C mutation into the neuroligin 3 gene of mice. The researchers discovered that the genetically modified mice had impaired social behavior and superior spatial learning ability.
Spatial learning in mice is tested with a water maze, which consists of a small platform submerged a bit below the surface or a pool of water so it is invisible to a swimming mouse. Mice do not particularly enjoy swimming, so they try to locate the hidden platform as quickly as they can. When tested again later, they remember the platform’s location by checking visual cues around the edge or the pool. How quickly they remember is a measure of their spatial learning ability. FIGURE 15.14 shows some or Tabuchi’s result.
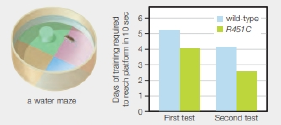
FIGURE 15.14 Spatial learning ability in mice. Mice with a mutation in neuroligin 3(R451C) were tested for learning performance: as compared with unmodified (wild-type) mice.
In the first test, how many days did it take unmodified mice to learn to find the location of a hidden platform in 10 seconds?
To determine: How many days wild mice took to learn to find the hidden platform in 10 seconds.
Introduction: Autism is a neurological disorder in which patients have impaired social interactions, repetitive, and stereotyped behaviors. The condition appears due to the mutation in the gene neuroligin-3 and an adhesion protein that connects the brain cells together. The mutation causes substitution of a cysteine (C) amino acid by arginine (R) in position 451.
Explanation of Solution
The experiment was performed to test the learning ability of autism mice. The mice were mutated for R451C in neuroligin-3 gene by Researcher K, and it was found that the mutated mice had impaired social behaviors as well as superior spatial learning abilities. The spatial learning ability of mice have experimented with a water maze in which a small platform was little bit submerged below the water surface so that it cannot be observable to the swimming mice.
Mice do not prefer to stay in the water. Therefore, as quickly as possible, they find the hidden platform by remembering the spatial visual cues. Their learning abilities were assigned as quickly as they remember the hidden platform in the water maze. Refer to Fig. 15.14 “Spatial learning ability in mice” in the question; the data shown are the number of days training required for the wild (unmodified) mice and mutated (modified mice) to reach the platform in 10 seconds. In the first test, unmodified mice took little over five days to find the location of a hidden platform in 10 seconds.
In the first test, unmodified mice took little over five days to find the location of a hidden platform in 10 seconds.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry
SEELEY'S ANATOMY+PHYSIOLOGY
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
HUMAN ANATOMY
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
- Describe the levels of structural hierarchy for the human body, starting with the organismal level and ending with the chemical level. In addition, you should make sure you link each level to the previous level, emphasizing the structural relationships.arrow_forward9 S es Read the section "Investigating Life: In (Extremely) Cold Blood." Then, drag and drop the terms on the left to complete the concept map. Red blood cells Genes Icefishes -have mutated have colorless Oxygen have few lack encode Blood Cellular respiration consists of- contain carries is a Platelets White blood cells carries low amounts of Hemoglobin is necessary for Plasma Protein Reset.arrow_forwardPlating 50 microliters of a sample diluted by a factor of 10-6 produced 91 colonies. What was the originalcell density (CFU/ml) in the sample?arrow_forward
- Every tutor here has got this wrong, don't copy off them.arrow_forwardSuppose that the population from question #1 (data is in table below) is experiencing inbreeding depression (F=.25) (and no longer experiencing natural selection). Calculate the new expected genotype frequencies (f) in this population after one round of inbreeding. Please round to 3 decimal places. Genotype Adh Adh Number of Flies 595 Adh Adh 310 Adhs Adhs 95 Total 1000 fladh Adh- flAdn Adh fAdhs Adharrow_forwardWhich of the following best describes why it is difficult to develop antiviral drugs? Explain why. A. antiviral drugs are very difficult to develop andhave no side effects B. viruses are difficult to target because they usethe host cell’s enzymes and ribosomes tometabolize and replicate C. viruses are too small to be targeted by drugs D. viral infections usually clear up on their ownwith no problemsarrow_forward
- This question has 3 parts (A, B, & C), and is under the subject of Nutrition. Thank you!arrow_forwardThey got this question wrong the 2 previous times I uploaded it here, please make sure it's correvct this time.arrow_forwardThis question has multiple parts (A, B & C), and under the subject of Nutrition. Thank you!arrow_forward
- Calculate the CFU/ml of a urine sample if 138 E. coli colonies were counted on a Nutrient Agar Plate when0.5 mls were plated on the NA plate from a 10-9 dilution tube. You must highlight and express your answerin scientific notatioarrow_forwardDon't copy off the other answer if there is anyarrow_forwardAnswerarrow_forward
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax





