
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
A concept map is to be drawn and the liters of
Concept introduction:
A mole is a basic unit used in the International system of units (SI). It is abbreviated as
Answer to Problem 18E
The concept map is shown below.
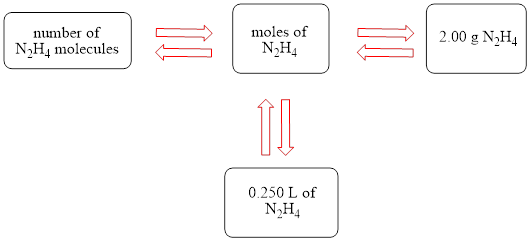
The liters of
Explanation of Solution
When

Figure 1
The formula to calculate the number of moles of
The mass of
The molar mass of
Substitute the mass and molar mass of
The volume occupied by
The formula to calculate the volume occupied by
Substitute the volume of
Therefore, the liters of
The liters of
(b)
Interpretation:
A concept map is to be drawn and the molecules of
Concept introduction:
A mole is a basic unit used in the International system of units (SI). It is abbreviated as
Answer to Problem 18E
The concept map is shown below.

The molecules of
Explanation of Solution
When

Figure 1
The formula to calculate the number of moles of
The mass of
The molar mass of
Substitute the mass and molar mass of
The molecules present in
The formula to calculate the molecules occupied by
Substitute the molecules in
Therefore, the molecules of
The molecules of
(c)
Interpretation:
A concept map is to be drawn and molar concentration of the hydrazine solution in the solution in when
Concept introduction:
A mole is a basic unit used in the International system of units (SI). It is abbreviated as
Answer to Problem 18E
The concept map is shown below.

The molar concentration of the hydrazine solution is
Explanation of Solution
When

Figure 1
The formula to calculate the number of moles of
The mass of
The molar mass of
Substitute the mass and molar mass of
The number of moles in
The formula to determine molarity is shown below.
Where
•
•
•
Substitute the value of number of moles and volume in equation (1).
The relation between
The unit factors are given below.
The unit factor to determine
Therefore,
Therefore, the molar concentration of
The molar concentration of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY
- Q2: Explain why epoxides that react in an SN1 manner will not show any stereochemical inversion in the product. Q3: Rationalize why Alcohol B will react under the indicated reaction conditions, but Alcohol A will not. A ☑ OH B OH PBr3 R-Brarrow_forwardQ1: Predict the major organic product(s) of the following reactions. Include stereochemistry when necessary. Write NR if no reaction, try to explain. 1.) LDA, THF 2.) СОН CI OH H2SO4, heat OH m...... OH 1.) PCC, CH2Cl2 2.) CH3CH2MgBr, THF 3.) H3O+ 4.) TsCl, pyr 5.) tBuOK, tBuOH 1.) SOCI 2, CHCI 3 2.) CH3CH2ONA, DMF OH 1.) HBr 2.) Mg, THF 3.) H₂CO, THE 4.) H3O+ OH NaH, THFarrow_forwardWhat is the stepwise mechanism for this reaction?arrow_forward
- Draw the major product of this reactionarrow_forwardPlease provide the IUPAC name for the compound shown herearrow_forwardProblem 6-29 Identify the functional groups in the following molecules, and show the polarity of each: (a) CH3CH2C=N CH, CH, COCH (c) CH3CCH2COCH3 NH2 (e) OCH3 (b) (d) O Problem 6-30 Identify the following reactions as additions, eliminations, substitutions, or rearrangements: (a) CH3CH2Br + NaCN CH3CH2CN ( + NaBr) Acid -OH (+ H2O) catalyst (b) + (c) Heat NO2 Light + 02N-NO2 (+ HNO2) (d)arrow_forward
- Predict the organic product of Y that is formed in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic product. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardPlease choose the best reagents to complete the following reactionarrow_forwardProblem 6-17 Look at the following energy diagram: Energy Reaction progress (a) Is AG for the reaction positive or negative? Label it on the diagram. (b) How many steps are involved in the reaction? (c) How many transition states are there? Label them on the diagram. Problem 6-19 What is the difference between a transition state and an intermediate? Problem 6-21 Draw an energy diagram for a two-step reaction with Keq > 1. Label the overall AG°, transition states, and intermediate. Is AG° positive or negative? Problem 6-23 Draw an energy diagram for a reaction with Keq = 1. What is the value of AG° in this reaction?arrow_forward
- Problem 6-37 Draw the different monochlorinated constitutional isomers you would obtain by the radical chlorination of the following compounds. (b) (c) Problem 6-39 Show the structure of the carbocation that would result when each of the following alkenes reacts with an acid, H+. (a) (b) (c)arrow_forwardPlease draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts and the carboxylic side productarrow_forwardPlease draw the major product of this reaction.arrow_forward
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning




