
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product obtained on reaction of
Concept introduction:
Conjugated dienes are defined as two double bonds separated by one single bond. They are more stable than non-conjugated double bonds due to resonance and hybridization energy. Along with that the heat of hydrogenation effects the stability of conjugated dienes. It states that higher the heat of hydrogenation energy lowers the stability of dienes.
Answer to Problem 15.43AP
The complete reaction is written as shown below.
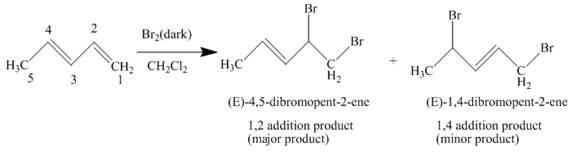
Explanation of Solution
When
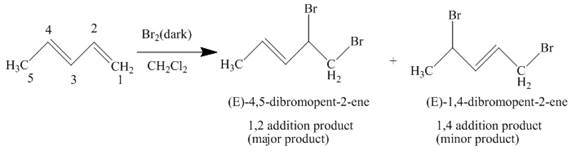
Figure 1
The product obtained on reaction of
(b)
Interpretation:
The product obtained on reaction of
Concept introduction:
Conjugated dienes areb defined as two double bonds separated by one single bond. They are more stable than non-conjugated double bonds due to resonance and hybridization energy. Along with that the heat of hydrogenation effects the stability of conjugated dienes. It states that higher the heat of hydrogenation energy lowers the stability of dienes.
Answer to Problem 15.43AP
The complete reaction is written as shown below.
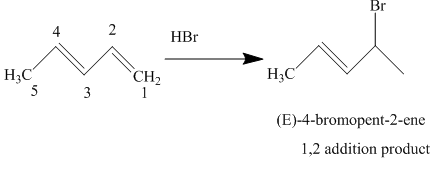
Explanation of Solution
When

Figure 2
The product obtained on reaction of
(c)
Interpretation:
The product obtained on reaction of
Concept introduction:
Conjugated dienes are defined as two double bonds separated by one single bond. They are more stable than non-conjugated double bonds due to resonance and hybridization energy. Along with that the heat of hydrogenation effects the stability of conjugated dienes. It states that higher the heat of hydrogenation energy lowers the stability of dienes.
Answer to Problem 15.43AP
The complete reaction is written as shown below.
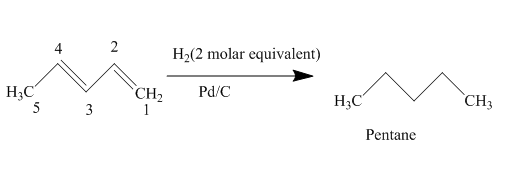
Explanation of Solution
When

Figure 3
The product obtained on reaction of
(d)
Interpretation:
The product obtained on reaction of
Concept introduction:
Conjugated dienes are defined as two double bonds separated by one single bond. They are more stable than non-conjugated double bonds due to resonance and hybridization energy. Along with that the heat of hydrogenation effects the stability of conjugated dienes. It states that higher the heat of hydrogenation energy lowers the stability of dienes.
Answer to Problem 15.43AP
The complete reaction is written as shown below.
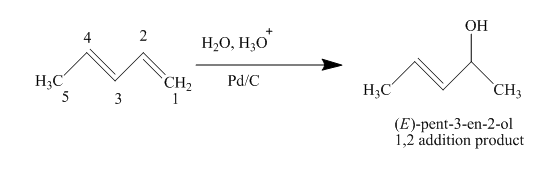
Explanation of Solution
When

Figure 4
The product obtained on reaction of
(e)
Interpretation:
The product obtained on reaction of
Concept introduction:
Conjugated dienes are defined as two double bonds separated by one single bond. They are more stable than non-conjugated double bonds due to resonance and hybridization energy. Along with that the heat of hydrogenation effects the stability of conjugated dienes. It states that higher the heat of hydrogenation energy lowers the stability of dienes.
Answer to Problem 15.43AP
The reaction does not undergo any chemical change because
Explanation of Solution
When
Alkenes do not undergo any nucleophilic addition reaction it means no product is formed in this reaction.
(f)
Interpretation:
The product obtained on reaction of
Concept introduction:
A chemical reaction that involves cycloaddition is known as Diels-Alder reaction. The reactant molecules that give rise to the product are diene and dienophile. The
Answer to Problem 15.43AP
The complete reaction is written below.
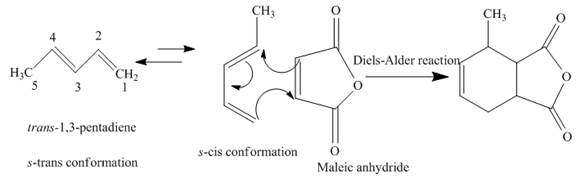
Explanation of Solution
When

Figure 5
The product obtained on reaction of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Ebook And Single-course Homework Access
- What would happen if the carboxylic acid and alcohol groups were on the same molecule? In essence, the molecule reacts with itself. Draw the structure of the products formed in this manner using the reactants below. If two functional groups interact with one another on the same molecule, this is called an “intramolecular" (within one) rather than "intermolecular" (between two or more) attack. OH OH catalyst OH HO catalyst catalyst HO OHarrow_forwardQ3: Write in the starting alkyl bromide used to form the following products. Include any reactants, reagents, and solvents over the reaction arrow. If more than one step is required, denote separate steps by using 1), 2), 3), etc. H OH racemic OH OH 5 racemicarrow_forwardDraw the Lewis structure of the SO3-O(CH3)2 complex shown in the bottom right of slide 2in lecture 3-3 (“Me” means a CH3 group) – include all valence electron pairs and formal charges.From this structure, should the complex be a stable molecule? Explain.arrow_forward
- please add appropriate arrows, and tell me clearly where to add arrows, or draw itarrow_forwardWhat I Have Learned Directions: Given the following reaction and the stress applied in each reaction, answer the question below. A. H2(g) + Cl2(g) 2 HCl(g) Stress applied: Decreasing the pressure 1. What is the Keq expression? 2. What will be the effect in the number of moles of HCl(g)? 3. What will be the Equilibrium Shift or the reaction? B. Fe3O4(s) + 4 H2(g) + heat 53 Fe(s) + 4 H₂O(g) Stress applied: Increasing the temperature 1. What is the Keq expression?. 2. What will be the effect in the volume of water vapor collected? 3. What will be the Equilibrium Shift or the reaction? C. 4 NH3(g) + 5 O2(g) 4 NO(g) + 6 H2O(g) + heat Stress applied: Increasing the volume of the container 1. What is the Keq expression?. 2. What will be the effect in the amount of H₂O? 3. What will be the Equilibrium Shift or the reaction?arrow_forwardConsider the solubility products (Ksp values) for the following compounds:SrSO4 (Ksp = 7.6 x 10−7), BaSO4 (Ksp = 1.5 x 10−9), SrCO3 (Ksp = 7.0 x 10−10), BaCO3 (Ksp = 1.6 x 10−9)Which anion is the harder base, CO32− or SO42−? Justify your answer.arrow_forward
- Q1: a) Arrange the compounds in order of decreasing pKa, highest first. ОН ΟΗ ῸΗ дон ОН ОН CI Brarrow_forward(4 pts - 2 pts each part) A route that can be taken to prepare a hydrophobic (water-repellent) aerogel is to start with trichloromethylsilane, CH3SiCl3 as the silicon source. a. What is the chemical reaction that this undergoes to form a product with Si-OH groups? Write as complete of a chemical equation as you can. CI CI-SI-CH3 CI b. The formation of a byproduct is what drives this reaction - what is the byproduct (if you didn't already answer it in part (a)) and how/why does it form?arrow_forwardb) Circle the substrate that would not efficiently generate a Grignard reagent upon reaction with Mg in ether. CI Br ד c) Circle the Grignard reagents that contain incompatible functional groups. MgBr HO MgBr MgBr MgBr MgBr HO MgBrarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

