
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
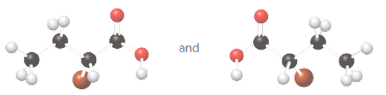
Whether the given pair of molecules are identical, or enantiomers should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
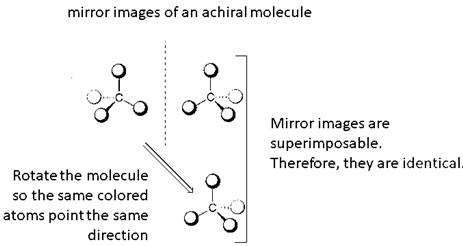
Identical molecules are the ones with no isomers, neither constitutional isomers nor stereoisomers. Identical molecules have the same structural arrangement of atoms and the same three-dimensional arrangement.
Isomers are the molecules with the same formula but either with different structural arrangement (constitutional isomers) or different three-dimensional arrangement (stereoisomers).
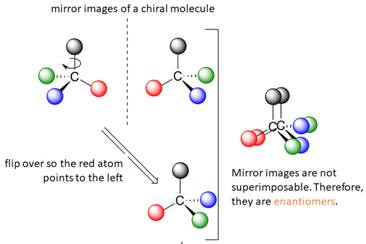
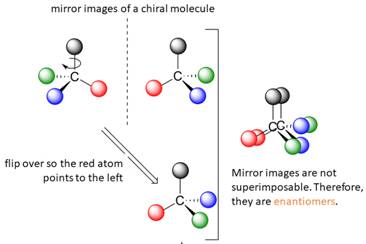
A tetrahedral carbon atom bonded to four different groups is called a chiral center. A Molecule having at least one chiral center is a chiral molecule. Molecules that do not have any chiral centers are called achiral. Identical molecules do not have any chiral centers; therefore, they are achiral.
When the mirror images of a chiral molecule are not superimposable, those mirror images become stereoisomers called enantiomers.
(b)
Interpretation:
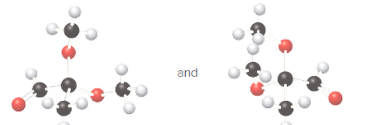
Whether the given pair of molecules are identical, or enantiomers should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Identical molecules are the ones with the same chemical formula but no isomers, neither constitutional isomers nor stereoisomers. Identical molecules have the same structural arrangement of atoms and the same three-dimensional arrangement.
Isomers are the molecules with the same formula but either with different structural arrangement (constitutional isomers) or different three-dimensional arrangement (stereoisomers).
A tetrahedral carbon atom bonded to four different groups is called a chiral center. A Molecule having at least one chiral center is a chiral molecule. Molecules that do not have any chiral centers are called achiral. Identical molecules do not have any chiral centers; therefore, they are achiral.
When the mirror images of a chiral molecule are not superimposable, those mirror images become stereoisomers called enantiomers.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
ALEKS 360 ACCESS CARD F/GEN. ORG.CHEM
- If we react tetraethoxypropane with hydrazine, what is the product obtained (explain its formula). State the reason why the corresponding dialdehyde is not used.arrow_forwarddrawing, no aiarrow_forwardIf CH3COCH2CH(OCH3)2 (4,4-dimethoxy-2-butanone) and hydrazine react, two isomeric products are formed. State their structure and which will be the majority.arrow_forward
- + Reset Provide the correct IUPAC name for the compound shown here. 4-methylhept-2-ene (Z)- (E)- 1-6-5-2-3-4- cyclo iso tert- sec- di tri hept hex oct meth eth pent ane yne ene ylarrow_forward+ Provide the correct IUPAC name for the compound shown here. Reset H3C H H C CH3 CH-CH3 1-3-methylpent ene trans- cis- 5-6-3-1-2-4- tert- tri sec- di cyclo iso but pent hex meth prop eth yl ane ene yne ☑arrow_forwarddrawing, no aiarrow_forward
- drawing, no aiarrow_forwardDraw the major organic product when each of the bellow reagents is added to 3,3-dimethylbutere. ✓ 3rd attempt Part 1 (0.3 point) H.C CH CH + 1. BHG THF 210 NaOH NJ 10000 Part 2 (0.3 point) HC- CH HC 2741 OH a Search 1. He|DA HO 2. NIBH さ 士 Ju See Periodic Table See Hint j = uz C H F F boxarrow_forwardSynthesis of 2-metilbenzimidazol from 1,2-diaminobenceno y propanona.arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


