
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The
Concept introduction: Cleavage of
Answer to Problem 15.30P
The
Explanation of Solution
The energy required to break the
Thus, the increasing order of bond strength is,
The
(b)
Interpretation: The radicals resulting from the cleavage of each
Concept introduction: Primary
Answer to Problem 15.30P
The radicals resulting from the cleavage of each
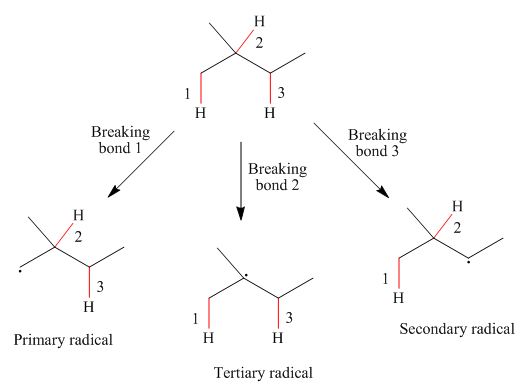
Figure 1
Explanation of Solution
Primary
The homolytic cleavage of the
The radicals resulting from the cleavage of each

Figure 1
The radicals resulting from the cleavage of each
(c)
Interpretation: The radicals resulting from the cleavage of each
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 15.30P
The radicals in increasing order of stability are
Explanation of Solution
The radicals resulting from the cleavage of each

Figure 1
The stability of radical depends upon the number of alkyl groups attached to the radical carbon. Therefore, stability of tertiary radical is more than secondary and primary radical. The radicals in increasing order of stability are
The radicals in increasing order of stability are
(d)
Interpretation: The
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 15.30P
The
Explanation of Solution
The radicals resulting from the cleavage of each

Figure 1
The stability of radical depends upon the number of alkyl groups attached to the radical carbon. Therefore, stability of tertiary radical is more than secondary and primary radical. The radicals in increasing order of stability are
Hydrogen atoms are less polarizable than alkyl groups. Therefore, alkyl group can easily donate electron density to the electron deficient carbon radical. Therefore, the increasing ease of
The
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Package: Loose Leaf for Organic Chemistry with Biological Topics with Connect Access Card
- 2. Name the following hydrocarbons. (9 marks) a) HHHHHHHH H-C-C- H-O-S b) HCEC-CH3 H H H H H d) c) H C=C- H H H e) CH3 CH3 CH2CH=CH-CH=CHCH3 HHHH H-C-C-C-C-H H HH H f) large CH2CH3 pola H3C section lovels tower, able ocart firs g) Tower H3C-CH2 then in H3C-CH-CH-CH3 enblbano bne noitsidab Copyright © 2008. Durham Continuing Education CH3arrow_forwardName the molecules & Identify any chiral center CH3CH2CH2CHCH₂CH₂CH₂CH₂ OH CH₂CHCH2CH3 Br CH3 CH3CHCH2CHCH2CH3 CH3arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electrons-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s).arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





