
(a)
Interpretation:
The CN stretching mode that absorbs the higher-frequency IR photons is to be indicated for given pair of compounds. The reason for it is to be explained.
Concept introduction:
We simplify the picture of molecular vibrations by considering the ball-and-spring model, which treats bonds as simple springs that connect atoms together. According to Hooke’s law, the spring vibrates at a particular frequency (
Answer to Problem 15.19P
The CN stretching mode that absorbs the higher-frequency IR photons due to strong and stiffer bond is indicated below,
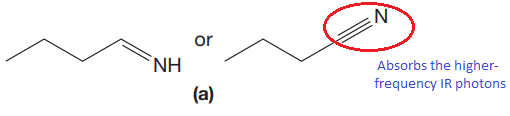
Explanation of Solution
The given pair of compounds is,
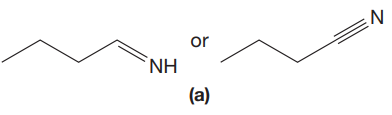
The triple bonds tend to be stronger and stiffer than double bonds. A stronger and stiffer bond tends to lead to a higher vibrational frequency. In given pair of compounds, with the faster vibration, the
The CN stretching mode that absorbs the higher-frequency IR photons is shown below,

The CN stretching mode that absorbs the higher-frequency IR photons is indicated on the basis of the relationship between strength and stiffness of the bond and vibrational frequency.
(b)
Interpretation:
The CN stretching mode that absorbs the higher-frequency IR photons is to be indicated for given pair of compounds. The reason for it is to be explained.
Concept introduction:
We simplify the picture of molecular vibrations by considering the ball-and-spring model, which treats bonds as simple springs that connect atoms together. According to Hooke’s law, the spring vibrates at a particular frequency (
Answer to Problem 15.19P
The CN stretching mode that absorbs the higher-frequency IR photons due to strong and stiffer bond is indicated below,
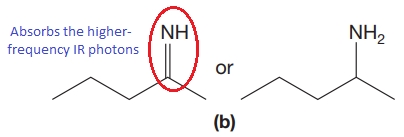
Explanation of Solution
The given pair of compounds is,
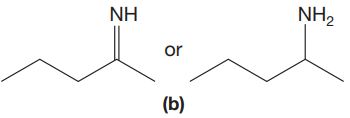
The double bonds tend to be stronger and stiffer than single bonds. A stronger and stiffer bond tends to lead to a higher vibrational frequency. In given pair of compounds, with the faster vibration, the
The CN stretching mode that absorbs the higher-frequency IR photons is shown below,

The CN stretching mode that absorbs the higher-frequency IR photons is indicated on the basis of the relationship between strength and stiffness of the bond and vibrational frequency.
(c)
Interpretation:
The CN stretching mode that absorbs the higher-frequency IR photons is to be indicated for given pair of compounds. The reason for it is to be explained.
Concept introduction:
We simplify the picture of molecular vibrations by considering the ball-and-spring model, which treats bonds as simple springs that connect atoms together. According to Hooke’s law, the spring vibrates at a particular frequency (
Answer to Problem 15.19P
The CN stretching mode that absorbs the higher-frequency IR photons due to lower mass is indicated below,
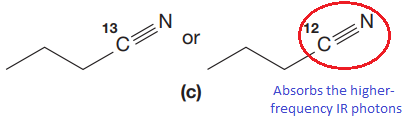
Explanation of Solution
The given pair of compounds is,
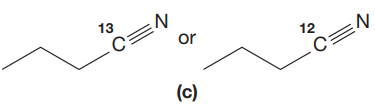
In both compounds there is
But
The CN stretching mode that absorbs the higher-frequency IR photons is shown below,

The vibrational mode that absorbs at a higher frequency in the IR region is determined on the basis of the relationship between mass and vibrational frequency.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
ORG CHEM W/ EBOOK & SW5 + STUDY GUIDE
- Which one of the following molecules is chiral? H- NH₂ H3C དང་།་ OH H HO H₂N HO- -H CHO -OH H HO- OH H- -H CH₂OH OHarrow_forwardThe structure of an unsaturated phospholipid is shown below. Which region of the molecule is most hydrophilic ? H₂N-CH₂ H₂C IV CH3 CH3 hydro-water philic-likes = Hydrophilic likes water ○ IV All regions are equally hydrophilic. IIIarrow_forwardWhich of the following compounds would you most appropriately call hydrophobic? ○ CH4 H2CO CO HCI ○ NaClarrow_forward
- Which of the following triglycerides would you most expect to be a liquid at room temperature? saturated fat trans monounsaturated fat trans polyunsaturated fat cis monounsaturated fat ○ cis polyunsaturated fatarrow_forwardWhich best describes the intermolecular forces present in NH3? dispersion forces only hydrogen bonding and dispersion forces dipole-dipole, hydrogen bonding, and dispersion forces dipole-dipole forces only ion-dipole and dispersion forcesarrow_forwardList three structural features and corresponding absorption ranges that can be used to identify cyclohexene by IR spectroarrow_forward
- The following chemical structure represents a molecule of what molecular formula? N.arrow_forwardPredict the product(s) of the following reactions. If no reaction, write "NR". a) b) HNO3 H2SO4 SO3 H2SO4 c) Bra FeBr3 Br2, FeBrз OCH3 d) تمنی e) HO f) SO3 H2SO4 CH3Cl NO2 AICI3arrow_forwardHow could you get from the starting material to product? A. OH B. OH Όarrow_forward
- Givent that the molecule below is named 2-methylbutanal (aldehyde) Choose the correct IUPAC nomenclature of the molecule: 4-methylpentanal 2-methylpentanal 4-methylbutanal 4-methylbutanalarrow_forwardО The following figures represent distributions of gas molecules between two containers connected by an open tube. In which figure is the entropy of the system maximized? O O Oarrow_forwardGiven the following data, determine the rate constant, k, of the reaction H2(g) + 21C1(g) → 12(g) + 2HCl(g) = Experiment 1 2 3 1.65 × 10 5 torr ¹s -1 6.06 104 torr -1s-1 8.17 105 torr -1s-1 1.34 torr -1s-1 3.48103 torr -¹s−1 [H2] (torr) [ICI] (torr) Rate (torr/s) 250 325 1.34 250 81 0.331 50 325 0.266arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning


