
EBK THERMODYNAMICS: AN ENGINEERING APPR
9th Edition
ISBN: 8220106796979
Author: CENGEL
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 14.7, Problem 109P
A wet cooling tower is to cool 60 kg/s of water from 40 to 33°C. Atmospheric air enters the tower at 1 atm with dry- and wet-bulb temperatures of 22 and 16°C, respectively, and leaves at 30°C with a relative humidity of 95 percent. Using the psychrometric chart, determine (a) the volume flow rate of air into the cooling tower and (b) the mass flow rate of the required makeup water.
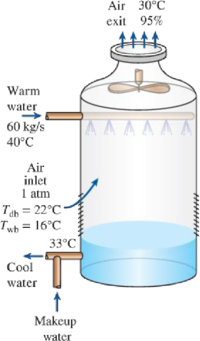
FIGURE P14–109
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
6) If (k = 0,7 cm) find Imax for figure below.
225mm
100mm
ثلاثاء.
100mm
150mm
75mm
Ans: Tmax=45:27 N/cm
F-400 N
The man has a weight W and stands halfway along the beam. The beam is not smooth, but the planes at A and B are smooth (and plane A is horizontal). Determine the magnitude of the tension in the cord in terms of W and θ.
Determine the reactions at the two supports for this plate. Express the reactions in Cartesian vector form.
Chapter 14 Solutions
EBK THERMODYNAMICS: AN ENGINEERING APPR
Ch. 14.7 - What is the difference between dry air and...Ch. 14.7 - What is vapor pressure?Ch. 14.7 - What is the difference between the specific...Ch. 14.7 - Can the water vapor in air be treated as an ideal...Ch. 14.7 - Explain how vapor pressure of the ambient air is...Ch. 14.7 - Is the relative humidity of saturated air...Ch. 14.7 - Moist air is passed through a cooling section...Ch. 14.7 - How will (a) the specific humidity and (b) the...Ch. 14.7 - Prob. 9PCh. 14.7 - Consider a tank that contains moist air at 3 atm...
Ch. 14.7 - Is it possible to obtain saturated air from...Ch. 14.7 - Why are the chilled water lines always wrapped...Ch. 14.7 - How would you compare the enthalpy of water vapor...Ch. 14.7 - A tank contains 15 kg of dry air and 0.17 kg of...Ch. 14.7 - Prob. 15PCh. 14.7 - An 8-m3 tank contains saturated air at 30C, 105...Ch. 14.7 - Determine the masses of dry air and the water...Ch. 14.7 - A room contains air at 85F and 13.5 psia at a...Ch. 14.7 - Prob. 19PCh. 14.7 - Prob. 20PCh. 14.7 - Prob. 21PCh. 14.7 - In summer, the outer surface of a glass filled...Ch. 14.7 - In some climates, cleaning the ice off the...Ch. 14.7 - Andy and Wendy both wear glasses. On a cold winter...Ch. 14.7 - Prob. 25PCh. 14.7 - Prob. 26PCh. 14.7 - Prob. 27PCh. 14.7 - A thirsty woman opens the refrigerator and picks...Ch. 14.7 - The air in a room has a dry-bulb temperature of...Ch. 14.7 - Prob. 31PCh. 14.7 - Prob. 32PCh. 14.7 - Prob. 33PCh. 14.7 - How do constant-enthalpy and...Ch. 14.7 - At what states on the psychrometric chart are the...Ch. 14.7 - How is the dew-point temperature at a specified...Ch. 14.7 - Can the enthalpy values determined from a...Ch. 14.7 - Atmospheric air at a pressure of 1 atm and...Ch. 14.7 - Prob. 39PCh. 14.7 - Prob. 40PCh. 14.7 - Prob. 41PCh. 14.7 - Atmospheric air at a pressure of 1 atm and...Ch. 14.7 - Reconsider Prob. 1443. Determine the adiabatic...Ch. 14.7 - What does a modern air-conditioning system do...Ch. 14.7 - How does the human body respond to (a) hot...Ch. 14.7 - How does the air motion in the vicinity of the...Ch. 14.7 - Consider a tennis match in cold weather where both...Ch. 14.7 - Prob. 49PCh. 14.7 - Prob. 50PCh. 14.7 - Prob. 51PCh. 14.7 - Prob. 52PCh. 14.7 - What is metabolism? What is the range of metabolic...Ch. 14.7 - Why is the metabolic rate of women, in general,...Ch. 14.7 - What is sensible heat? How is the sensible heat...Ch. 14.7 - Prob. 56PCh. 14.7 - Prob. 57PCh. 14.7 - Prob. 58PCh. 14.7 - Prob. 59PCh. 14.7 - Repeat Prob. 1459 for an infiltration rate of 1.8...Ch. 14.7 - An average (1.82 kg or 4.0 lbm) chicken has a...Ch. 14.7 - An average person produces 0.25 kg of moisture...Ch. 14.7 - How do relative and specific humidities change...Ch. 14.7 - Prob. 64PCh. 14.7 - Humid air at 150 kPa, 40C, and 70 percent relative...Ch. 14.7 - Humid air at 40 psia, 50F, and 90 percent relative...Ch. 14.7 - Prob. 67PCh. 14.7 - Air enters a 30-cm-diameter cooling section at 1...Ch. 14.7 - Prob. 69PCh. 14.7 - Prob. 70PCh. 14.7 - Why is heated air sometimes humidified?Ch. 14.7 - Air at 1 atm, 15C, and 60 percent relative...Ch. 14.7 - Air at 14.7 psia, 35F, and 50 percent relative...Ch. 14.7 - An air-conditioning system operates at a total...Ch. 14.7 - Prob. 75PCh. 14.7 - Why is cooled air sometimes reheated in summer...Ch. 14.7 - Atmospheric air at 1 atm, 30C, and 80 percent...Ch. 14.7 - Ten thousand cubic feet per hour of atmospheric...Ch. 14.7 - Air enters a 40-cm-diameter cooling section at 1...Ch. 14.7 - Repeat Prob. 1479 for a total pressure of 88 kPa...Ch. 14.7 - On a summer day in New Orleans, Louisiana, the...Ch. 14.7 - Prob. 83PCh. 14.7 - Prob. 84PCh. 14.7 - Prob. 85PCh. 14.7 - Saturated humid air at 70 psia and 200F is cooled...Ch. 14.7 - Humid air is to be conditioned in a...Ch. 14.7 - Atmospheric air at 1 atm, 32C, and 95 percent...Ch. 14.7 - Prob. 89PCh. 14.7 - Prob. 90PCh. 14.7 - Does an evaporation process have to involve heat...Ch. 14.7 - Prob. 92PCh. 14.7 - Prob. 93PCh. 14.7 - Air enters an evaporative (or swamp) cooler at...Ch. 14.7 - Prob. 95PCh. 14.7 - Air at 1 atm, 20C, and 70 percent relative...Ch. 14.7 - Two unsaturated airstreams are mixed...Ch. 14.7 - Consider the adiabatic mixing of two airstreams....Ch. 14.7 - Two airstreams are mixed steadily and...Ch. 14.7 - A stream of warm air with a dry-bulb temperature...Ch. 14.7 - Prob. 104PCh. 14.7 - Prob. 105PCh. 14.7 - How does a natural-draft wet cooling tower work?Ch. 14.7 - What is a spray pond? How does its performance...Ch. 14.7 - The cooling water from the condenser of a power...Ch. 14.7 - A wet cooling tower is to cool 60 kg/s of water...Ch. 14.7 - Prob. 110PCh. 14.7 - Prob. 111PCh. 14.7 - Water at 30C is to be cooled to 22C in a cooling...Ch. 14.7 - Prob. 113PCh. 14.7 - Prob. 114RPCh. 14.7 - Determine the mole fraction of dry air at the...Ch. 14.7 - Prob. 116RPCh. 14.7 - Prob. 117RPCh. 14.7 - Prob. 118RPCh. 14.7 - Prob. 119RPCh. 14.7 - Prob. 120RPCh. 14.7 - Prob. 121RPCh. 14.7 - Prob. 122RPCh. 14.7 - Prob. 124RPCh. 14.7 - Prob. 125RPCh. 14.7 - Prob. 126RPCh. 14.7 - Prob. 128RPCh. 14.7 - Prob. 129RPCh. 14.7 - Air enters a cooling section at 97 kPa, 35C, and...Ch. 14.7 - Prob. 131RPCh. 14.7 - Atmospheric air enters an air-conditioning system...Ch. 14.7 - Humid air at 101.3 kPa, 36C dry bulb and 65...Ch. 14.7 - An automobile air conditioner uses...Ch. 14.7 - Prob. 135RPCh. 14.7 - Prob. 137RPCh. 14.7 - Conditioned air at 13C and 90 percent relative...Ch. 14.7 - Prob. 141FEPCh. 14.7 - A 40-m3 room contains air at 30C and a total...Ch. 14.7 - A room is filled with saturated moist air at 25C...Ch. 14.7 - Prob. 144FEPCh. 14.7 - The air in a house is at 25C and 65 percent...Ch. 14.7 - Prob. 146FEPCh. 14.7 - Air at a total pressure of 90 kPa, 15C, and 75...Ch. 14.7 - On the psychrometric chart, a cooling and...Ch. 14.7 - On the psychrometric chart, a heating and...Ch. 14.7 - An airstream at a specified temperature and...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Determine the magnitudes of the reactions at the supports for this large plate.arrow_forwardOnly expert should solvearrow_forwardA 15 cm-OD pipe is buried with its centerline 1.25 m below the surface of the ground [k of soil is 0.35 W/(m K)]. An oil having a density of 800 kg/m³ and a specific heat of 2.1 kJ/(kg K) flows in the pipe at 5.6 L/s. Assuming a ground surface temperature of 5°C and a pipe wall temperature of 95°C, estimate the length of pipe in which the oil temperature decreases by 5.5°C. + Tε = 5ºC Z= 1.25 m D= 15 cm 7p=95°Carrow_forward
- Find the solution of the following Differential Equations 1) 4y+y=0, y(0)=2, y'(0) = 0. 2) y+y=0, y(0) = A, y'(0) = B. 3) "+2y'-8y=0, y(0)=1, y'(0)=8. 4) y"-2y-3y=0, y(0)=1, y'(0)=7. 5) y"-ky' =0, y(0)=2, y'(0) =k. 6) y+ky'-2k2y=0, y(0)=2, y'(0) = 2k. 7) y'+4y=0, y(0)=2.8 y+y-17sin(21) y(0)=-1. 9) y-y'-6y=0, y(0)=6. y'(0)=13. 10) y-y=0, 11) y"-4y+4y=0, y(0)=4, y'(0) = 0. y(0) = 2.1, y'(0)=3.9 12) y+2y+2y=0, y(0)=1, y'(0)=-3. 13) "+7y+12y=21e", y(0)=3.5, y'(0)=-10. 14) "+9y=10e", y(0)=0. y'(0) = 0. 15) y+3y+2.25y=91³ +64. y(0)=1, y'(0) = 31.5 16) "-6y+5y= 29 cos(21), y(0)=3.2, y'(0) = 6.2 17) y+2y+2y=0, y(0)=0, y'(0)=1. 18) y+2y+17y=0, y(0)=0, y'(0)=12. 19) y-4y+5y=0, y(0)-1, y'(0) 2. 20) 9y-6y+y=0. y(0)=3, y'(0)=1. 21) -2y+10y=0, y(0)=3, y'(0)=3. 22) 4y-4y+37y=0, (0) 3. y(0) 1.5 23) 4y-8y+5y=0, (0)-0, y(0) 1. 24) y+y+1.25y=0, y(0) 1. y'(0) -0.5 25) y+y=2 cos(1). y(0) 2. y'(0) = 0. 26) -4y+3y=0, (0)-3, y'(0) = 7. 27) y+2y+y=e", y(0)-0. y'(0) = 0. 29) 28) y+2y-3y-10sinh(2),…arrow_forwardNote: Please provide a clear, step-by-step simplified handwritten working out (no explanations!), ensuring it is done without any AI involvement. I require an expert-level answer, and I will assess and rate based on the quality and accuracy of your work and refer to the provided image for more clarity. Make sure to double-check everything for correctness before submitting appreciate your time and effort!. Question:arrow_forward4. Block A and B are two different pieces of wood. Determine the minimum dimension for "a", if the shear stress of the wood is 50Mpa. The thickness of the wood is 30cm. 600N Aarrow_forward
- 1. Determine the reaction force at A. 60 kN 5 B 1 m 1 m- -1 m 4 3 m 30 kN marrow_forwardFind the Laplace Transform of the following functions 1) f() cos(ar) Ans. F(s)=7 2ws 2) f() sin(at) Ans. F(s)= s² + a² 3) f(r)-rcosh(at) Ans. F(s)= 2as 4)(t)=sin(at) Ans. F(s)= 2 5) f(1) = 2te' Ans. F(s)= (S-1) 5+2 6) (1) e cos() Ans. F(s) = (+2)+1 7) (1) (Acostẞr)+ Bsin(Br)) Ans. F(s)- A(s+a)+BB (s+a)+B 8) f()-(-)() Ans. F(s)= 9)(1)(1) Ans. F(s): 10) f(r),()sin() Ans. F(s): 11) 2 k 12) 0 13) 0 70 ㄷ.. a 2a 3a 4a 2 3 4 14) f(1)=1, 0<1<2 15) (1) Ksin(t) 0arrow_forward2. Determine the average normal stress developed in rod AB. The mass is 50kg and the diameter of the rod AB is 8mm. B 8 mmarrow_forward2.64 A 2.75-kN tensile load is applied to a test coupon made from 1.6-mm flat steel plate (E = 200 GPa, v = 0.30). Determine the resulting change in (a) the 50-mm gage length, (b) the width of portion AB of the test coupon, (c) the thickness of portion AB, (d) the cross-sectional area of portion AB. 2.75 kN A 12 mm 50 mm B 2.75 kNarrow_forwardProcedure:1- Cartesian system, 2(D)/(3)D,type of support2- Free body diagram3 - Find the support reactions4- If you find a negativenumber then flip the force5- Find the internal force3D\sum Fx=0\sum Fy=0\sum Fz=0\sum Mx=0\sum My=0\Sigma Mz=02D\Sigma Fx=0\Sigma Fy=0\Sigma Mz=05- Use method of sectionand cut the elementwhere you want to findthe internal force andkeep either side of thesectionarrow_forward3. The design of a pump and pipe system has been completed, except for the valves. The system is used to transpor10t water at 120°F through 2 nom sch 40 commercial steel pipe at a required flow rate of 85 gpm. Without the valves, the pump selected has the capability to overcome an additional 18 psi of pressure drop due to the valves and still provide the required flow rate. The pipe/valve joints are threaded. Determine how many 2-inch globe valves can be installed in this pump and pipe system.arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
The Refrigeration Cycle Explained - The Four Major Components; Author: HVAC Know It All;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zfciSvOZDUY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY