
Organic Chemistry - Standalone book
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780073511214
Author: Francis A Carey Dr., Robert M. Giuliano
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 14.5, Problem 6P
Assign the chemical shifts
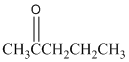
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
NMR spectrum of ethyl acetate has signals whose chemical shifts are indicated below. Which hydrogen or set of hydrogens corresponds to the signal at
4.1 ppm? Select the single best answer.
The
H
O
HỌC—C—0—CH, CH,
2
A
ethyl acetate
H NMR: 1.3 ppm, 2.0 ppm, 4.1 ppm
Check
OA
B
OC
ch
B
C
Save For Later
Submit Ass
© 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center |
How many signals do you expect in the H NMR spectrum for this molecule?
Br Br
Write the answer below.
Also, in each of the drawing areas below is a copy of the molecule, with Hs shown. In each copy, one of the H atoms is colored red. Highlight in red all other H
atoms that would contribute to the same signal as the H already highlighted red
Note for advanced students: In this question, any multiplet is counted as one signal.
1
Number of signals in the 'H NMR spectrum.
For the molecule in the top drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to
the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red.
If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right.
Check
For the molecule in the bottom drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute
to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red.
If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right.
O
✓
No additional Hs to color in top
molecule
ง
No additional Hs to color in bottom…
in the kinetics experiment, what were the values calculated? Select all that apply.a) equilibrium constantb) pHc) order of reactiond) rate contstant
Chapter 14 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - Standalone book
Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 1PCh. 14.3 - Prob. 2PCh. 14.4 - The 1H NMR signal for bromoform (CHBr3) appears at...Ch. 14.5 - identify the most shielded and least shielded...Ch. 14.5 - (a) Assign the chemical shifts 1.6, 2.2, and 4.8...Ch. 14.5 - Assign the chemical shifts 1.1, 1.7, 2.0, and 2.3...Ch. 14.5 - Assign the chemical shifts 1.6, 4.0, 7.5, 8.2, and...Ch. 14.6 - The 300-MHz 1H NMR spectrum of 1,4-dimethylbenzene...Ch. 14.6 - Prob. 9PCh. 14.6 - How many signals would you expect to find in the...
Ch. 14.7 - Describe the appearance of the 1H NMR spectrum of...Ch. 14.8 - Describe the appearance of the 1H NMR spectrum of...Ch. 14.11 - Prob. 13PCh. 14.11 - Prob. 14PCh. 14.12 - Hydrogen bonding between the oxygen of dimethyl...Ch. 14.14 - Prob. 16PCh. 14.15 - The 13C NMR spectrum of 1-bromo-3-chloropropane...Ch. 14.15 - Consider carbons x, y, and z in p-methylanisole....Ch. 14.15 - Prob. 19PCh. 14.16 - To which of the compounds of Problem 14.16 does...Ch. 14.18 - DEPT spectra for a compound with the formula...Ch. 14.20 - Vibrational frequencies are sensitive to isotopic...Ch. 14.21 - Prob. 23PCh. 14.22 - Prob. 24PCh. 14.23 - Prob. 25PCh. 14.23 - Which one of the C5H8 isomers shown has its max at...Ch. 14.24 - Knowing what to look for with respect to isotopic...Ch. 14.24 - The base peak appears at m/z105 for one of the...Ch. 14.24 - Mass spectra of 1-bromo-4-propylbenzene and...Ch. 14.25 - Prob. 30PCh. 14 - Each of the following compounds is characterized...Ch. 14 - Deduce the structure of each of the following...Ch. 14 - From among the isomeric compounds of molecular...Ch. 14 - The H1NMR spectrum of fluorene has signals at 3.8...Ch. 14 - Prob. 35PCh. 14 - H1NMR spectra of four isomeric alcohols with...Ch. 14 - Prob. 37PCh. 14 - We noted in Section 14.13 that an NMR spectrum is...Ch. 14 - Identify each of the C4H10O isomers on the basis...Ch. 14 - A compound (C3H7ClO2) exhibited three peaks in its...Ch. 14 - Label nonequivalent carbons in the following...Ch. 14 - Compounds A and B are isomers of molecular formula...Ch. 14 - C13 NMR spectra for four isomeric alkyl bromides...Ch. 14 - Prob. 44PCh. 14 - Prob. 45PCh. 14 - Identify the C3H5Br isomers on the basis of the...Ch. 14 - Prob. 47PCh. 14 - A compound (C8H10O) has the IR and H1NMR spectra...Ch. 14 - Deduce the structure of a compound having the...Ch. 14 - Figure 14.53 presents IR, H1NMR, C13NMR and mass...Ch. 14 - H1NMR, C13NMR, IR, and mass spectra are shown for...Ch. 14 - 1H NMR and IR spectra for a compound with the...Ch. 14 - FriedelCraftsalkylation of benzene with...Ch. 14 - Prob. 54DSPCh. 14 - Prob. 55DSPCh. 14 - Prob. 56DSPCh. 14 - Prob. 57DSPCh. 14 - Prob. 58DSP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- true or false, given that a 20.00 mL sample of NaOH took 24.15 mL of 0.141 M HCI to reach the endpoint in a titration, the concentration of the NaOH is 1.17 M.arrow_forwardin the bromothymol blue experiment, pKa was measured. A closely related compound has a Ka of 2.10 x 10-5. What is the pKa?a) 7.1b) 4.7c) 2.0arrow_forwardcalculate the equilibrium concentration of H2 given that K= 0.017 at a constant temperature for this reaction. The inital concentration of HBr is 0.050 M.2HBr(g) ↔ H2(g) + Br2(g)a) 4.48 x 10-2 M b) 5.17 x 10-3 Mc) 1.03 x 10-2 Md) 1.70 x 10-2 Marrow_forward
- true or falsegiven these two equilibria with their equilibrium constants:H2(g) + CI2(l) ↔ 2HCI(g) K= 0.006 CI2(l) ↔ CI2(g) K= 0.30The equilibrium contstant for the following reaction is 1.8H2(g) + CI2 ↔ 2HCI(g)arrow_forwardI2(g) + CI2(g) ↔ 2ICIK for this reaction is 81.9. Find the equilibrium concentration of I2 if the inital concentration of I2 and CI2 are 0.010 Marrow_forwardtrue or false,the equilibrium constant for this reaction is 0.50.PCI5(g) ↔ PCI3(g) + CI2(g)Based on the above, the equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 0.25.2PCI5(g) ↔. 2PCI3(g) + 2CI2(g)arrow_forward
- true or false, using the following equilibrium, if carbon dioxide is added the equilibrium will shift toward the productsC(s) + CO2(g) ↔ 2CO(g)arrow_forward2S2O2/3- (aq) + I2 (aq) ---> S4O2/6- (aq) +2I- (aq) Experiment I2 (M) S2O3- (M) Initital Rate (M/s) 1 0.01 0.01 0.0004 2 0.01 0.02 0.0004 3 0.02 0.01 0.0008 Calculate the overall order for this reaction using the table data a) 3b) 0c) 2d) 1arrow_forwardthe decomposition of N2O5 is the first order with a half-life of 1.98 minutes. If the inital concentration of N2O5 is 0.200 M, what is the concentration after 6 minutes?a) 0.612 Mb) 0.035 Mc) 0.024 Md) 0.100 Marrow_forward
- 20.00 mL of 0.150 M HCI is titrated with 0.075 M NaOH. What volume of NaOH is needed?a) 50 mLb) 20 mLc) 40 mLd) 26.66 mLarrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is titrated with 37.75 mL of HCI. What is the molarity of the HCI?a) 0.150 Mb) 0.079 Mc) 0.025 Md) 0.050 Marrow_forwardin the following reaction, the OH- acts as which of these?NO2- (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ OH- (aq) + HNO2 (aq)a) not a weak acidb) basec) acidarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning
NMR Spectroscopy; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SBir5wUS3Bo;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY