
Concept explainers
(a)
The free-body diagram of the forces acting on the ladder.
(a)
Answer to Problem 82PQ
The free-body diagram of the forces acting on the ladder is
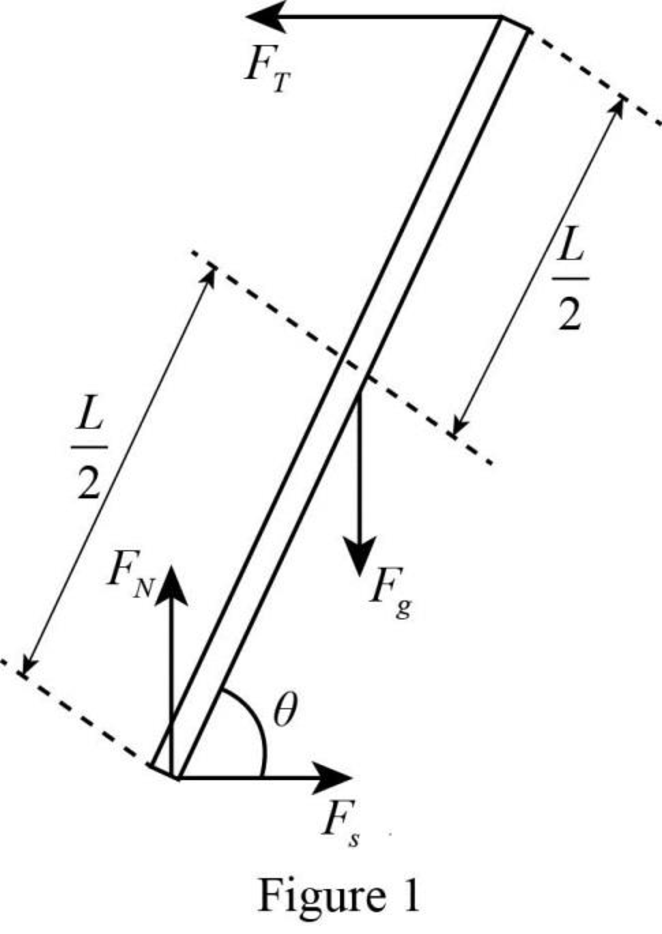
Explanation of Solution
A free-body diagram is a graphical tool used to illustrate the different forces acting on a particular object. It helps to solve complex physical problems. The free-body diagram of the ladder in the given situation is drawn in figure 1.
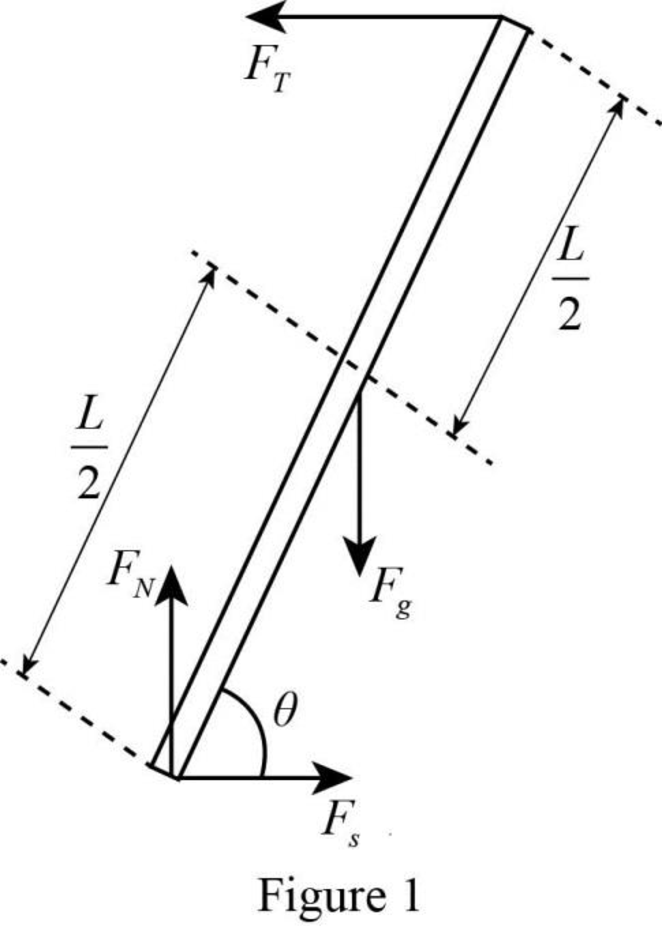
The forces acting on the ladder are the weight, the normal force, the tension and the force of static friction. In the figure weight is represented as
Conclusion:
Thus, the free-body diagram of the forces acting on the ladder is drawn in figure 1.
(b)
The tension in the rope in terms of
(b)
Answer to Problem 82PQ
The tension in the rope in terms of
Explanation of Solution
Take the lower end of the ladder as the pivot point. This will eliminate the torque due to normal force and the torque due to force of static friction.
Since the ladder is in rotational equilibrium, the net torque about the lower end of the ladder must be zero.
Write the condition for the rotational equilibrium.
Here,
Write the equation for
Here,
Put the above equation in equation (I).
Write the expression for
Write the expression for
Write the expression for
Here,
Write the expression for
Here,
Put the above four equations in equation (II) and rewrite it for
Conclusion:
Therefore, the tension in the rope in terms of
(c)
The expression for the tension in the rope in terms of
(c)
Answer to Problem 82PQ
The expression for the tension in the rope in terms of
Explanation of Solution
Since the ladder is in translational equilibrium, the net force in
Write the conditions for the translational equilibrium.
Here,
Here,
Write the equation for
Here,
Write the equation for
Here,
Put the above equation in equation (VI).
Put the above equation in equation (IV) and rewrite it for
Write the equation for
Here,
Write the equation for
Put the above equation in equation (VIII).
Put the above equation in equation (V) and rewrite it for
Put the above equation in equation (VII).
Conclusion:
Therefore, the expression for the tension in the rope in terms of
(d)
The coefficient of static friction in terms of the angle
(d)
Answer to Problem 82PQ
The coefficient of static friction in terms of the angle
Explanation of Solution
Equate equations (III) and (IX).
Conclusion:
Therefore, the coefficient of static friction in terms of the angle
(e)
The after effect of moving the ladder slightly so as to reduce the angle
(e)
Answer to Problem 82PQ
The ladder will slip if it is moved slightly to reduce the angle
Explanation of Solution
The expression for the angle
The expression for the tension force obtained in part (b),
Conclusion:
Thus, the ladder will slip if it is moved slightly to reduce the angle
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardA toy car speeds up at 1.0 m/s2 while rolling down a ramp, and slows down at a rate of 2.0 m/s2 while rolling up the same ramp. What is the slope of the ramp in degrees? Grade in %? The friction coefficient?arrow_forwardPlz solution should be complete No chatgpt pls will upvote .arrow_forward
- A box with friction coefficient of 0.2 rests on a 12 foot long plank of wood. How high (in feet) must one side of the plank be lifted in order for the box to begin to slide?arrow_forwardWhat is a good general rule to follow in order to find the best choice of coordinate system to solve a dynamics problem?arrow_forwardWhat is the meaning of a first order approximation?arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgptarrow_forwardA hydrogen atom has just a single electron orbiting the nucleus, which happens to be a single proton without any neutrons. The proton is positively charged, the electron negatively, but both with the same magnitude of charge given by e=1.602x10-19C. The mass of an electron is 9.11x10-31kg, and the proton is 1.67x10-27kg. Find the ratio of the electrostatic to the gravitational force of attraction between the electron and the proton in hydrogen. \arrow_forwardWhat is the third law pair to the normal force as you sit in a chair? What effect does the sun's pull on earth have in terms of third law pairs?arrow_forward
- Using Newton's 2nd law, show that all objects subject to the pull of gravity alone should fall at the same rate. What is that rate?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardA cart on wheels (assume frictionless) with a mass of 20 kg is pulled rightward with a 50N force. What is its acceleration?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





