
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT (LL) W/CONNECT
14th Edition
ISBN: 9781265502942
Author: Stevenson
Publisher: MCG CUSTOM
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 14, Problem 6P
Determine the number of cycles per day and a production quantity per cycle for this set of products that achieves fairly level production:
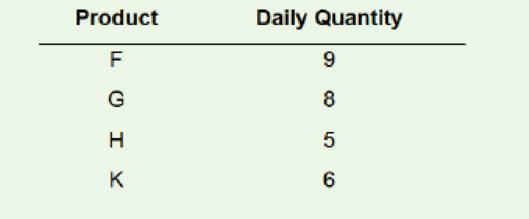
Assume the production sequence will be F-G-H-K.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A copy machine is available 24 hours a day. On a typical day, the machine produces 100 jobs. Each job takes about 3 minutes on the machine, 2 minutes of which is processing time and 1 minute is setup time (logging in, defining the job). About 20 percent of the jobs need to be reworked, in which case the setup time and the processing time have to be repeated. The remainder of the time, the equipment is idle. What is the OEE of the equipment?
How do you think we can keep updating Toyota's ideas as new technologies come out and what customers want keeps changing?
Given how TPS has helped change things in so many fields, do you think there are parts of it that might be hard to use in areas that aren’t about making things, like in healthcare or services? If so, why do you think that might be?
Chapter 14 Solutions
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT (LL) W/CONNECT
Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 1.1RQCh. 14.4 - Prob. 1.2RQCh. 14.4 - Prob. 1.3RQCh. 14.S - Prob. 1DRQCh. 14.S - Prob. 2DRQCh. 14.S - Prob. 3DRQCh. 14.S - Prob. 4DRQCh. 14.S - Prob. 5DRQCh. 14.S - Prob. 6DRQCh. 14.S - Prob. 7DRQ
Ch. 14.S - Prob. 8DRQCh. 14.S - Prob. 9DRQCh. 14.S - Prob. 10DRQCh. 14.S - The probability that equipment used in a hospital...Ch. 14.S - The frequency of breakdown of a machine that...Ch. 14.S - Prob. 3PCh. 14 - Prob. 1DRQCh. 14 - Prob. 2DRQCh. 14 - Prob. 3DRQCh. 14 - Prob. 4DRQCh. 14 - Prob. 5DRQCh. 14 - Prob. 6DRQCh. 14 - Prob. 7DRQCh. 14 - Contrast push and pull methods ofmovi.ttg goods...Ch. 14 - Prob. 9DRQCh. 14 - Prob. 10DRQCh. 14 - Prob. 1TSCh. 14 - Prob. 2TSCh. 14 - Prob. 3TSCh. 14 - Prob. 1CTECh. 14 - Prob. 2CTECh. 14 - Prob. 1PCh. 14 - Prob. 2PCh. 14 - Prob. 3PCh. 14 - Determine the number of cycles per day and the...Ch. 14 - Given this set of daily service operations, and...Ch. 14 - Determine the number of cycles per day and a...Ch. 14 - Compute the takt time for a system where the total...Ch. 14 - Prob. 8PCh. 14 - Prob. 9PCh. 14 - What might Stephanie determine as the best...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, operations-management and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Do you feel there is anything positive about rework?arrow_forwardDo you think technology can achieve faster setup times? How would it be implemented in the hospital workforce?arrow_forwardIn your experience or opinion, do you think process changes like organizing workspaces make a bigger difference, or is investing in technology usually the better solution for faster setups?arrow_forward
- Have you seen rework done in your business, and what was done to prevent that from occurring again?arrow_forwardResearch a company different than case studies examined and search the internet and find an example of a business that had to rework a process. How was the organization affected to rework a process in order to restore a good flow unit? Did rework hurt a process or improve the organization's operational efficiency? • Note: Include a reference with supportive citations in the discussion reply in your post.arrow_forwardSetup time is very important in affecting a process and the capacity of a process. How do you reduce setup time? Give examples of reducing setup time. Please Provide a referenecearrow_forward
- Do you think TPS was successful? If so, how? Are there other companies that have used TPS? If so, give examples. Please provide a referencearrow_forwardGiven the significant impact on finances, production timelines, and even equipment functionality, as you pointed out, what do you believe is the most effective single strategy a company can implement to significantly reduce the occurrence of rework within their operations?arrow_forwardDurban woman, Nombulelo Mkumla, took to social media last week to share how she discovered the rodent.In a lengthy Facebook post, she said she purchased the loaf of bread from a local shop after work on August 27.For the next days, Mkumla proceeded to use slices of bread from the load to make toast."Then, on the morning of August 31, I took the bread out of the fridge to make toast and noticed something disgusting andscary. I took a picture and sent it to my friends, and one of them said, 'Yi mpuku leyo tshomi' [That's a rat friend]“."I was in denial and suggested it might be something else, but the rat scenario made sense - it's possible the rat got into thebread at the factory, and no one noticed," Mkumla said.She went back to the shop she'd bought the bread from and was told to lay a complaint directly with the supplier.She sent an email with a video and photographs of the bread.Mkumla said she was later contacted by a man from Sasko who apologised for the incident.According to…arrow_forward
- PepsiCo South Africa says the incident where a woman discovered part of a rodent in her loaf of bread, is anisolated occurrence.Durban woman, Nombulelo Mkumla, took to social media last week to share how she discovered the rodent.In a lengthy Facebook post, she said she purchased the loaf of bread from a local shop after work on August 27.For the next days, Mkumla proceeded to use slices of bread from the load to make toast."Then, on the morning of August 31, I took the bread out of the fridge to make toast and noticed something disgusting andscary. I took a picture and sent it to my friends, and one of them said, 'Yi mpuku leyo tshomi' [That's a rat friend]“."I was in denial and suggested it might be something else, but the rat scenario made sense - it's possible the rat got into thebread at the factory, and no one noticed," Mkumla said.She went back to the shop she'd bought the bread from and was told to lay a complaint directly with the supplier.She sent an email with a video and…arrow_forwardDurban woman, Nombulelo Mkumla, took to social media last week to share how she discovered the rodent.In a lengthy Facebook post, she said she purchased the loaf of bread from a local shop after work on August 27.For the next days, Mkumla proceeded to use slices of bread from the load to make toast."Then, on the morning of August 31, I took the bread out of the fridge to make toast and noticed something disgusting andscary. I took a picture and sent it to my friends, and one of them said, 'Yi mpuku leyo tshomi' [That's a rat friend]“."I was in denial and suggested it might be something else, but the rat scenario made sense - it's possible the rat got into thebread at the factory, and no one noticed," Mkumla said.She went back to the shop she'd bought the bread from and was told to lay a complaint directly with the supplier.She sent an email with a video and photographs of the bread.Mkumla said she was later contacted by a man from Sasko who apologised for the incident.According to…arrow_forwardRead the project statement and answer ALL of the questions that follow PROJECT STATEMENT The African Integrated High-Speed Railway Network (AIHSRN). African nations are preparing to invest billions in a significant overhaul of their rail infrastructure as part of an ambitious plan for the continent. One of the key projects underway is the African Integrated High-Speed Railway Network (AIHSRN), which aims to connect Africa's capital cities and major commercial centres with a high-speed railway network to enhance continental trade and competition. This network will span 2,000 km (1,243 miles) and connect 60 cities, including Nairobi, Lagos, Cairo, and Dakar. It will improve access to essential markets, enhance economic cooperation, and encourage regional collaboration. The plan is poised to revolutionise intra-African trade by reducing travel times and lowering transportation costs, making trade between African nations more competitive. The trains will be capable of reaching speeds of up…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Contemporary MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033777Author:Louis E. Boone, David L. KurtzPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033777Author:Louis E. Boone, David L. KurtzPublisher:Cengage Learning

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:9781337406659
Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:Cengage,

Contemporary Marketing
Marketing
ISBN:9780357033777
Author:Louis E. Boone, David L. Kurtz
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Inventory Management | Concepts, Examples and Solved Problems; Author: Dr. Bharatendra Rai;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2n9NLZTIlz8;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY