
Suppose there are no taxes. Firm ABC has no debt, and firm XYZ has debt of $5000 on which it pays interest of 10% each year. Both companies have identical projects that generate
a. Fill in the table below showing the payments debt and equity holders of each firm will receive given each of the two possible levels of free cash flows.
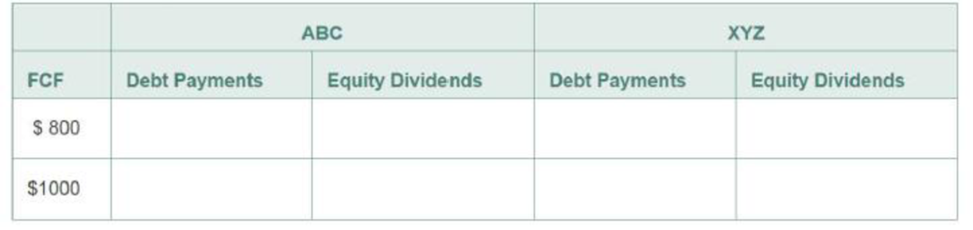
b. Suppose you hold 10% of the equity of ABC. What is another portfolio you could hold that would provide the same cash flows?
c. Suppose you hold 10% of the equity of XYZ. If you can borrow at 10%, what is an alternative strategy that would provide the same cash flows?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
Corporate Finance (4th Edition) (Pearson Series in Finance) - Standalone book
- Solve for maturity value, discount period, bank discount, and proceeds. Assume a bank discount rate of 9%. Use the ordinary interest method. (Use Days in a year table.) Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answers to the nearest cent.face value(principal) $50000rate interest =11%maturity value=?date of note =june 10date note discounted= July 18discount period=?bank discount=?proceeds=? i need an explanation I am having a lot of trouble to solve thisarrow_forwardmany experts giving wrong solAnswer should be match in options. Many experts are giving incorrect answer they are using AI /Chatgpt that is generating wrong answer. i will give unhelpful if answer will not match in option. dont use AI alsoarrow_forwardAnti-Pandemic Pharma Co. Ltd. reports the following information inits income statement:Sales = $5,250,000;Costs = $2, 173,000;Other expenses = $187,400;Depreciation expense = $79,000;Interest expense= $53,555;Taxes = $76,000;Dividends = $69,000.$136,700 worth of new shares were also issued during the year andlong-term debt worth $65,300 was redeemed.a) Compute the cash flow from assetsb) Compute the net change in working capitalarrow_forward
- Question 3 Footfall Manufacturing Ltd. reports the following financial information at the end of the current year: Net Sales $100,000 Debtor's turnover ratio (based on 2 net sales) Inventory turnover ratio 1.25 Fixed assets turnover ratio 0.8 Debt to assets ratio 0.6 Net profit margin 5% Gross profit margin 25% Return on investment 2% Use the given information to fill out the templates for income statement and balance sheet given below: Income Statement of Footfall Manufacturing Ltd. for the year ending December 31, 20XX (in $) Sales 100,000 Cost of goods sold Gross profit Other expenses Earnings before tax Tax @50% Earnings after tax Balance Sheet of Footfall Manufacturing Ltd. as at December 31, 20XX (in $) Liabilities Amount Assets Amount Equity Net fixed assets Long term 50,000 Inventory debt Short term debt Debtors Cash TOTAL TOTALarrow_forwardToodles Inc. had sales of $1,840,000. Cost of goods sold, administrative and selling expenses, and depreciation expenses were $1,180,000, $185,000 and $365,000 respectively. In addition, the company had an interest expense of $280,000 and a tax rate of 35 percent. (Ignore any tax loss carry-back or carry-forward provisions.) Arrange the financial information for Toodles Inc. in an income statement and compute its OCF? All computations must be done and shown manually. Kindly no spreadsheetcomputations. So that I am able to follow and understand clearly please.arrow_forwardJingle Ltd. and Bell Ltd. belong to the same industry. A snapshot of some of their financial information is given below: Jingle Ltd. Bell Ltd. Current ratio 3.2 1 2 1 Acid-test ratio 1.7 1 1.1 1 Debt Equity ratio 30% 40% Times interest earned 6 5 You are a loans officer and both companies have asked for an equal 2-year loan. i) ii) If you could facilitate only one loan, which company would you refuse? Explain your reasoning briefly If both companies could be facilitated, would you be willing to do so? Explain your argument briefly.arrow_forward
- Waterfront Inc. wishes to borrow on a short-term basis withoutreducing its current ratio below 1.25. At present its current assetsand current liabilities are $1,600 and $1,000 respectively. How muchcan Waterfront Inc. borrow?arrow_forwardIn the case Partridge v Mallandaine (UK, 1886) the matter of the treatment of gambling winnings for tax purposes came into focus. Analyse the case of Partridge v Mallandaine a) Do you agree with the ruling in the case? If you do defend your answer by stating and explaining at least 3 reasons for your agreement. b) If you are not in agreement with the ruling, then defend your answer by stating and explaining at least 3 valid reasons for your disagreement.arrow_forwardDuring 2019, Bitsincoins Corporation had EBIT of $100,000, a changein net fixed assets of $400,000, an increase in net current assets of$100,000, an increase in spontaneous current liabilities of $400,000,a depreciation expense of $50,000, and a tax rate of 30%. Based onthis information, what is Bitsincoin’s free cash flow?arrow_forward
- Duncan Company is a large manufacturer and distributor of cake supplies. It is based in United Kingdon (Headquarters) It sends supplies to firms throughout the United States and the Caribbean . It markets its supplies through periodic mass mailings of catalogues to those firms. Its clients can make orders over the phone and Duncan ships the supplies upon demand.The main competition for Duncan’s comes from one U.S. firm and one Canadian firm. Another British firm has a small share of the U.S. market but is at a disadvantage because of its distance. The British firm’s marketing and transportation costs in the U.S. marketare relatively high.b) Given that one-third of the company sales are exports to the United Kingdom and invoices for exports are in US dollars, the demand for its exports is highly sensitive to the value of the British pound. In order to maintain its inventory at a proper level, it must forecast the total demand for its products which is somewhat dependent on the…arrow_forwardAn employee contributes $15,000 to a 401(k) plan each year, and the company matches 10 percent of this annually, or $1,500. The employee can allocate the contributions among equities (earning 12 percent annually), bonds (earning 5 percent annually), and money market securities (earning 3 percent annually). The employee expects to work at the company 20 years. The employee can contribute annually along one of the three following patterns: Equities Bonds Option 1 60% Option 2 Option 3 50% 40% 40 45 50 Money market securities 0 100% 5 100% 10 100% Calculate the terminal value of the 401(k) plan for each of the 3 options, assuming all returns and contributions remain constant over the 20 years. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest whole number. (e.g., 32) × Answer is complete but not entirely correct. Option 1 Option 2 $ 915,588 X $ 100,785 x Option 3 $ 88,548 xarrow_forwardDuncan Company is a large manufacturer and distributor of cake supplies. It is based in United Kingdon (Headquarters) It sends supplies to firms throughout the United States and the Caribbean . It markets its supplies through periodic mass mailings of catalogues to those firms. Its clients can make orders over the phone and Duncan ships the supplies upon demand.The main competition for Duncan’s comes from one U.S. firm and one Canadian firm. Another British firm has a small share of the U.S. market but is at a disadvantage because of its distance. The British firm’s marketing and transportation costs in the U.S. marketare relatively high.a) Duncan Company plans to penetrate either the Canadian market or two other Caribbean Countries (Jamaica and Haiti). What factors deserve to be considered in deciding which market is more feasible? I NEED PROPER REFERENCES IN THE ANSWER AND A VERY DETAILED AND RESEARCH ANSWER.arrow_forward
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





